Abstract
Background
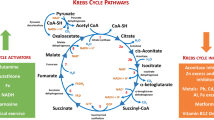
Many of the hallmarks of cancer are not inherently unique to cancer, but rather represent a re-enactment of normal host responses and activities. A vivid example is aerobic glycolysis (‘Warburg effect’), which is used not only by cancer cells but also by normal cells that undergo rapid proliferation. A common feature of this metabolic adaptation is a shift in the expression of pyruvate kinase (PK) isoform M1 to isoform M2. Here, we highlight the key role of PKM2 in shifting cancer metabolism between ATP production and biosynthetic processes. Since anabolic processes are highly energy dependent, the fate of glucose in energy production versus the contribution of carbon in biosynthetic processes needs to be finely synchronised. PKM2 acts to integrate cellular signalling and allosteric regulation of metabolites in order to align metabolic activities with the changing needs of the cell.
Conclusions
The central role of PKM2 in directing the flow of carbon between catabolic (ATP-producing) and anabolic processes provides unique opportunities for extending the therapeutic window of currently available and/or novel anti-neoplastic agents.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Hanahan, R.A. Weinberg, Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 144, 646–674 (2011)
J.M.S. Lemons, X.-J. Feng, B.D. Bennett, A. Legesse-Miller, E.L. Johnson, I. Raitman, E.A. Pollina, H.A. Rabitz, J.D. Rabinowitz, H.A. Coller, Quiescent fibroblasts exhibit high metabolic activity. PLoS Biol. 8, e1000514 (2010)
G. Eelen, P. de Zeeuw, M. Simons, P. Carmeliet, Endothelial cell metabolism in normal and diseased vasculature. Circ. Res. 116, 1231–1244 (2015)
L.A.J. O’Neill, R.J. Kishton, J. Rathmell, A guide to immunometabolism for immunologists. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 16, 553–565 (2016)
S.Y. Lunt, M.G. Vander Heiden, Aerobic glycolysis: Meeting the metabolic requirements of cell proliferation. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 27, 441–464 (2011)
C.T. Jones, Fertil, fetal metabolism and fetal growth. J. Reprod. 47, 189–201 (1976)
J. Wahlberg, B. Ekman, L. Nyström, U. Hanson, B. Persson, H.J. Arnqvist, Gestational diabetes: Glycaemic predictors for fetal macrosomia and maternal risk of future diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 114, 99–105 (2016)
A. Mohammadbeigi, F. Farhadifar, N. Soufizadeh, N. Mohammadsalehi, M. Rezaiee, M. Aghaei, Fetal macrosomia: Risk factors, maternal, and perinatal outcome. Ann. Med. Health Sci. Res. 3, 546 (2013)
M. Persson, D. Pasupathy, U. Hanson, M. Norman, Birth size distribution in 3,705 infants born to mothers with type 1 diabetes: A population-based study. Diabetes Care 34, 1145–1149 (2011)
L.A. Flores-López, M.G. Martínez-Hernández, R. Viedma-Rodríguez, M. Díaz-Flores, L.A. Baiza-Gutman, High glucose and insulin enhance uPA expression, ROS formation and invasiveness in breast cancer-derived cells. Cell. Oncol. 39, 365–378 (2016)
H. Makinoshima, M. Takita, K. Saruwatari, S. Umemura, Y. Obata, G. Ishii, S. Matsumoto, E. Sugiyama, A. Ochiai, R. Abe, K. Goto, H. Esumi, K. Tsuchihara, Signaling through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) Axis is responsible for aerobic glycolysis mediated by glucose transporter in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-mutated lung adenocarcinoma. J. Biol. Chem. 290, 17495–17504 (2015)
M. Muller, M. Mentel, J.J. van Hellemond, K. Henze, C. Woehle, S.B. Gould, R.-Y. Yu, M. van der Giezen, A.G.M. Tielens, W.F. Martin, Biochemistry and evolution of anaerobic energy metabolism in eukaryotes. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 76, 444–495 (2012)
T. Pfeiffer, S. Schuster, S. Bonhoeffer, Cooperation and competition in the evolution of ATP-producing pathways. Science 292, 504–507 (2001)
T.L. Dayton, T. Jacks, M.G. Vander Heiden, PKM2, cancer metabolism, and the road ahead. EMBO Rep. 17, 1721–1730 (2016)
M. Saqcena, S. Mukhopadhyay, C. Hosny, A. Alhamed, A. Chatterjee, D.A. Foster, Blocking anaplerotic entry of glutamine into the TCA cycle sensitizes K-Ras mutant cancer cells to cytotoxic drugs. Oncogene 34, 2672–2680 (2015)
J. Son, C.A. Lyssiotis, H. Ying, X. Wang, S. Hua, M. Ligorio, R.M. Perera, C.R. Ferrone, E. Mullarky, N. Shyh-Chang, Glutamine supports pancreatic cancer growth through a KRAS-regulated metabolic pathway. Nature 496, 101–105 (2013)
S. Cardaci, M.R. Ciriolo, TCA cycle defects and cancer: When metabolism tunes redox state. Int. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 1–9 (2012)
A. King, M.A. Selak, E. Gottlieb, Succinate dehydrogenase and fumarate hydratase: Linking mitochondrial dysfunction and cancer. Oncogene 25, 4675–4682 (2006)
M. Sciacovelli, E. Gonçalves, T.I. Johnson, V.R. Zecchini, E. Gaude, A.V. Drubbel, S.J. Theobald, S.R. Abbo, M.G. Tran, V. Rajeeve, Fumarate is an epigenetic modifier that elicits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Nature 537(544), 544–547 (2016)
Z. Xie, J. Dai, L. Dai, M. Tan, Z. Cheng, Y. Wu, J.D. Boeke, Y. Zhao, Lysine succinylation and lysine malonylation in histones. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 11, 100–107 (2012)
X. Mu, T. Zhao, C. Xu, W. Shi, B. Geng, J. Shen, C. Zhang, J. Pan, J. Yang, S. Hu, Oncometabolite succinate promotes angiogenesis by upregulating VEGF expression through GPR91-mediated STAT3 and ERK activation. Oncotarget 8, 13174 (2017)
A. Stincone, A. Prigione, T. Cramer, M. Wamelink, K. Campbell, E. Cheung, V. Olin-Sandoval, N. Grüning, A. Krüger, M. Tauqeer Alam, The return of metabolism: Biochemistry and physiology of the pentose phosphate pathway. Biol. Rev. 90, 927–963 (2015)
A.C. Newman, O.D.K. Maddocks, One-carbon metabolism in cancer. Br. J. Cancer 116, 1499–1504 (2017)
E.H. Ma, G. Bantug, T. Griss, S. Condotta, R.M. Johnson, B. Samborska, N. Mainolfi, V. Suri, H. Guak, M.L. Balmer, Serine is an essential metabolite for effector T cell expansion. Cell Metab. 25, 345–357 (2017)
K.C. Patra, N. Hay, The pentose phosphate pathway and cancer. Trends Biochem. Sci. 39, 347–354 (2014)
J. Fan, J. Ye, J.J. Kamphorst, T. Shlomi, C.B. Thompson, J.D. Rabinowitz, Quantitative flux analysis reveals folate-dependent NADPH production. Nature 510, 298–302 (2014)
M. Ost, S. Keipert, E.M. van Schothorst, V. Donner, I. van der Stelt, A.P. Kipp, K.-J. Petzke, M. Jove, R. Pamplona, M. Portero-Otin, Muscle mitohormesis promotes cellular survival via serine/glycine pathway flux. FASEB J. 29, 1314–1328 (2015)
K. Yamada, T. Noguchi, Nutrient and hormonal regulation of pyruvate kinase gene expression. Biochem. J. 337(Pt 1), 1–11 (1999)
E.L. Pearce, M.C. Poffenberger, C.H. Chang, R.G. Jones, Fueling immunity: Insights into metabolism and lymphocyte function. Science 342, 1242454 (2013)
C.J. David, M. Chen, M. Assanah, P. Canoll, J.L. Manley, HnRNP proteins controlled by c-Myc deregulate pyruvate kinase mRNA splicing in cancer. Nature 463, 364–368 (2010)
R. Sears, F. Nuckolls, E. Haura, Y. Taya, K. Tamai, J.R. Nevins, Multiple Ras-dependent phosphorylation pathways regulate Myc protein stability. Genes Dev. 14, 2501–2514 (2000)
C.D. Little, M.M. Nau, D.N. Carney, A.F. Gazdar, J.D. Minna, Amplification and expression of the c-myc oncogene in human lung cancer cell lines. Nature 306, 194–196 (1983)
W. Yang, Y. Zheng, Y. Xia, H. Ji, X. Chen, F. Guo, C.A. Lyssiotis, K. Aldape, L.C. Cantley, Z. Lu, ERK1/2-dependent phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of PKM2 promotes the Warburg effect. Nat. Cell Biol. 14, 1295–1304 (2012)
T. Hitosugi, S. Kang, M.G. Vander Heiden, T.W. Chung, S. Elf, K. Lythgoe, S. Dong, S. Lonial, X. Wang, G.Z. Chen, J. Xie, T.L. Gu, R.D. Polakiewicz, J.L. Roesel, T.J. Boggon, F.R. Khuri, D.G. Gilliland, L.C. Cantley, J. Kaufman, J. Chen, Tyrosine phosphorylation inhibits PKM2 to promote the Warburg effect and tumor growth. Sci. Signal. 2, ra73 (2009)
H.R. Christofk, M.G. Vander Heiden, N. Wu, J.M. Asara, L.C. Cantley, Pyruvate kinase M2 is a phosphotyrosine-binding protein. Nature 452, 181–186 (2008)
I. Nemazanyy, C. Espeillac, M. Pende, G. Panasyuk, Role of PI3K, mTOR and Akt2 signalling in hepatic tumorigenesis via the control of PKM2 expression. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 41, 917–922 (2013)
P. Wang, C. Sun, T. Zhu, Y. Xu, Structural insight into mechanisms for dynamic regulation of PKM2. Protein Cell 6, 275–287 (2015)
J.D. Dombrauckas, B.D. Santarsiero, A.D. Mesecar, Structural basis for tumor pyruvate kinase M2 allosteric regulation and catalysis. Biochemistry 44, 9417–9429 (2005)
B. Chaneton, P. Hillmann, L. Zheng, A.C.L. Martin, O.D.K. Maddocks, A. Chokkathukalam, J.E. Coyle, A. Jankevics, F.P. Holding, K.H. Vousden, C. Frezza, M. O’Reilly, E. Gottlieb, Serine is a natural ligand and allosteric activator of pyruvate kinase M2. Nature 491, 458–462 (2012)
M. Yang, K.H. Vousden, Serine and one-carbon metabolism in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 16, 650–662 (2016)
C. Kung, J. Hixon, S. Choe, K. Marks, S. Gross, E. Murphy, B. DeLaBarre, G. Cianchetta, S. Sethumadhavan, X. Wang, Small molecule activation of PKM2 in cancer cells induces serine auxotrophy. Chem. Biol. 19, 1187–1198 (2012)
H.P. Morgan, F.J. O’Reilly, M.A. Wear, J.R. O’Neill, L.A. Fothergill-Gilmore, T. Hupp, M.D. Walkinshaw, M2 pyruvate kinase provides a mechanism for nutrient sensing and regulation of cell proliferation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 110, 5881–5886 (2013)
A.M. Castellaro, A. Tonda, H.H. Cejas, H. Ferreyra, B.L. Caputto, O.A. Pucci, G.A. Gil, Oxalate induces breast cancer. BMC Cancer 15, 761 (2015)
T. Sakata, G. Ferdous, T. Tsuruta, T. Satoh, S. Baba, T. Muto, A. Ueno, Y. Kanai, H. Endou, I. Okayasu, L-type amino-acid transporter 1 as a novel biomarker for high-grade malignancy in prostate cancer. Pathol. Int. 59, 7–18 (2009)
H. Nawashiro, N. Otani, N. Shinomiya, S. Fukui, H. Ooigawa, K. Shima, H. Matsuo, Y. Kanai, H. Endou, L-type amino acid transporter 1 as a potential molecular target in human astrocytic tumors. Int. J. Cancer 119, 484–492 (2006)
M.-A. Bjornsti, P.J. Houghton, The TOR pathway: A target for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. 4, 335–348 (2004)
D. Anastasiou, G. Poulogiannis, J.M. Asara, M.B. Boxer, J.K. Jiang, M. Shen, G. Bellinger, A.T. Sasaki, J.W. Locasale, D.S. Auld, C.J. Thomas, M.G. Vander Heiden, L.C. Cantley, Inhibition of pyruvate kinase M2 by reactive oxygen species contributes to cellular antioxidant responses. Science 334, 1278–1283 (2011)
W.J. Israelsen, T.L. Dayton, S.M. Davidson, B.P. Fiske, A.M. Hosios, G. Bellinger, J. Li, Y. Yu, M. Sasaki, J.W. Horner, PKM2 isoform-specific deletion reveals a differential requirement for pyruvate kinase in tumor cells. Cell 155, 397–409 (2013)
T.L. Dayton, V. Gocheva, K.M. Miller, W.J. Israelsen, A. Bhutkar, C.B. Clish, S.M. Davidson, A. Luengo, R.T. Bronson, T. Jacks, M.G. Vander Heiden, Germline loss of PKM2 promotes metabolic distress and hepatocellular carcinoma. Genes Dev. 30, 1020–1033 (2016)
A.N. Lau, W.J. Israelsen, J. Roper, M.J. Sinnamon, L. Georgeon, T.L. Dayton, A.L. Hillis, O.H. Yilmaz, D. Di Vizio, K.E. Hung, M.G. Vander Heiden, PKM2 is not required for colon cancer initiated by APC loss. Cancer Metab. 5, 10 (2017)
X. Gao, H. Wang, J.J. Yang, X. Liu, Z.R. Liu, Pyruvate kinase M2 regulates gene transcription by acting as a protein kinase. Mol. Cell 45, 598–609 (2012)
W. Yang, Y. Xia, D. Hawke, X. Li, J. Liang, D. Xing, K. Aldape, T. Hunter, W.K. Alfred Yung, Z. Lu, PKM2 phosphorylates histone H3 and promotes gene transcription and tumorigenesis. Cell 150, 685–696 (2012)
S. Wolff, J.S. Weissman, A. Dillin, Differential scales of protein quality control. Cell 157, 52–64 (2014)
F. Buttgereit, M.D. Brand, A hierarchy of ATP-consuming processes in mammalian cells. Biochem. J. 312, 163–167 (1995)
A. Mullard, Cancer metabolism pipeline breaks new ground. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 15, 735–737 (2016)
K.M. Nieman, H.A. Kenny, C.V. Penicka, A. Ladanyi, R. Buell-Gutbrod, M.R. Zillhardt, I.L. Romero, M.S. Carey, G.B. Mills, G.S. Hotamisligil, S.D. Yamada, M.E. Peter, K. Gwin, E. Lengyel, Adipocytes promote ovarian cancer metastasis and provide energy for rapid tumor growth. Nat. Med. 17, 1498–1503 (2011)
H. Ye, B. Adane, N. Khan, T. Sullivan, M. Minhajuddin, M. Gasparetto, B. Stevens, S. Pei, M. Balys, J.M. Ashton, Leukemic stem cells evade chemotherapy by metabolic adaptation to an adipose tissue niche. Cell Stem Cell 19, 23–37 (2016)
S. Pavlides, D. Whitaker-Menezes, R. Castello-Cros, N. Flomenberg, A.K. Witkiewicz, P.G. Frank, M.C. Casimiro, C. Wang, P. Fortina, S. Addya, R.G. Pestell, U.E. Martinez-Outschoorn, F. Sotgia, M.P. Lisanti, The reverse Warburg effect: Aerobic glycolysis in cancer associated fibroblasts and the tumor stroma. Cell Cycle 8, 3984–4001 (2009)
L. Yang, S. Venneti, D. Nagrath, Glutaminolysis: A hallmark of cancer metabolism. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 19, 163–194 (2017)
S.L. Warner, K.J. Carpenter, D.J. Bearss, Activators of PKM2 in cancer metabolism. Future Med. Chem. 6, 1167–1178 (2014)
S.Y. Lunt, V. Muralidhar, A.M. Hosios, W.J. Israelsen, D.Y. Gui, L. Newhouse, M. Ogrodzinski, V. Hecht, K. Xu, P.N.M. Acevedo, D.P. Hollern, G. Bellinger, T.L. Dayton, S. Christen, I. Elia, A.T. Dinh, G. Stephanopoulos, S.R. Manalis, M.B. Yaffe, E.R. Andrechek, S.M. Fendt, M.G. Vander Heiden, Pyruvate kinase isoform expression alters nucleotide synthesis to impact cell proliferation. Mol. Cell 57, 95–107 (2015)
S.P. Gravel, L. Hulea, N. Toban, E. Birman, M.J. Blouin, M. Zakikhani, Y. Zhao, I. Topisirovic, J. St-Pierre, M. Pollak, Serine deprivation enhances antineoplastic activity of biguanides. Cancer Res. 74, 7521–7533 (2014)
A. Janzer, N.J. German, K.N. Gonzalez-Herrera, J.M. Asara, M.C. Haigis, K. Struhl, Metformin and phenformin deplete tricarboxylic acid cycle and glycolytic intermediates during cell transformation and NTPs in cancer stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 111, 10574–10579 (2014)
E.M. Palsson-Mcdermott, A.M. Curtis, G. Goel, M.A.R. Lauterbach, F.J. Sheedy, L.E. Gleeson, M.W.M. Van Den Bosch, S.R. Quinn, R. Domingo-Fernandez, D.G.W. Johnson, J.K. Jiang, W.J. Israelsen, J. Keane, C. Thomas, C. Clish, M. Vanden Heiden, R.J. Xavier, L.A.J. O’Neill, Pyruvate kinase M2 regulates Hif-1α activity and IL-1β induction and is a critical determinant of the Warburg effect in LPS-activated macrophages. Cell Metab. 21, 65–80 (2015)
A. Yuan, Y.J. Hsiao, H.Y. Chen, H.W. Chen, C.C. Ho, Y.Y. Chen, Y.C. Liu, T.H. Hong, S.L. Yu, J.J. W. Chen, P.C. Yang, Opposite effects of M1 and M2 macrophage subtypes on lung cancer progression. Sci. Rep. 5, 14273 (2015)
M. Zhang, Y. He, X. Sun, Q. Li, W. Wang, A. Zhao, W. Di, A high M1/M2 ratio of tumor-associated macrophages is associated with extended survival in ovarian cancer patients. J. Ovarian Res. 7, 1 (2014)
G. Comito, E. Giannoni, C.P. Segura, P. Barcellos-De-Souza, M.R. Raspollini, G. Baroni, M. Lanciotti, S. Serni, P. Chiarugi, Cancer-associated fibroblasts and M2-polarized macrophages synergize during prostate carcinoma progression. Oncogene 33, 2423–2431 (2014)
L.M. Nusblat, M.J. Carroll, C.M. Roth, Crosstalk between M2 macrophages and glioma stem cells. Cell. Oncol. 40, 471–482 (2017)
J.I. Fletcher, R.T. Williams, M.J. Henderson, M.D. Norris, M. Haber, ABC transporters as mediators of drug resistance and contributors to cancer cell biology. Drug Resist. Updat. 26, 1–9 (2016)
R.J. Kathawala, P. Gupta, C.R. Ashby, Z.-S. Chen, The modulation of ABC transporter-mediated multidrug resistance in cancer: A review of the past decade. Drug Resist. Updat. 18, 1–17 (2015)
Y. Kam, T. Das, H. Tian, P. Foroutan, E. Ruiz, G. Martinez, S. Minton, R.J. Gillies, R.A. Gatenby, Sweat but no gain: Inhibiting proliferation of multidrug resistant cancer cells with “ersatzdroges”. Int. J. Cancer 136, E188–E196 (2015)
C. Pan, X. Wang, K. Shi, Y. Zheng, J. Li, Y. Chen, L. Jin, Z. Pan, MiR-122 Reverses the doxorubicinresistance in hepatocellular carcinoma cells through regulating the tumor metabolism. PLoS One 11, e0152090 (2016)
Y. Lin, F. Lv, F. Liu, X. Guo, Y. Fan, F. Gu, J. Gu, L. Fu, High expression of pyruvate kinase M2 is associated with Chemosensitivity to Epirubicin and 5-fluorouracil in breast Cancer. J. Cancer 6, 1130–1139 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no potential conflict of interest to declare.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van Niekerk, G., Engelbrecht, AM. Role of PKM2 in directing the metabolic fate of glucose in cancer: a potential therapeutic target. Cell Oncol. 41, 343–351 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-018-0383-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-018-0383-7