Abstract
Purpose
Breast cancer cells frequently metastasize to distant organs, including bone. Interactions between breast cancer cells and the bone microenvironment are known to enhance tumor growth and osteolytic damage. Here we investigated whether BMP9 (a secretary protein) may change the bone microenvironment and, by doing so, regulate the cross-talk between breast cancer cells and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells.
Methods
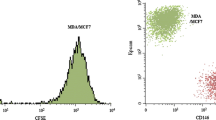
After establishing a co-culture system composed of MDA-MB-231breast cancer cells and HS-5 bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells, and exposure of this system to BMP9 conditioned media, we assessed putative changes in migration and invasion capacities of MDA-MB-231 cells and concomitant changes in osteogenic marker expressionin HS-5 cells and metastases-related genes in MDA-MB-231 cells.
Results
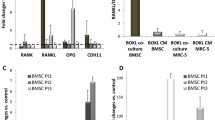
We found that BMP9 can inhibit the migration and invasion of MDA-MB-231 cells, and promote osteogenesis and proliferation of HS-5 cells, in the co-culture system. We also found that the BMP9-induced inhibition of migration and invasion of MDA-MB-231 cells may be caused by a decreased RANK ligand (RANKL) secretion by HS-5 cells, leading to a block in the AKT signaling pathway.
Conclusions
From our data we conclude that BMP9 inhibits the migration and invasion of breast cancer cells, and promotes the osteoblastic differentiation and proliferation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells by regulating cross-talk between these two types of cells through the RANK/RANKL signaling axis.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BMP9:
-
Bone morphogenetic protein 9
- BCC:
-
Breast cancer cells
- BMSC:
-
Bone marrow –derived mesenchymal stem cells
- MSCs:
-
Mesenchymal stem cells
- OPG:
-
Osteoprotegerin
- RANK:
-
Receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B
- RANKL:
-
The RANK ligand
- Ad-BMP9:
-
Adenovirus expressing BMP9 protein
- Ad-GFP:
-
Adenovirus expressing green fluorescent protein
- ERK1/2:
-
Extracellular signal regulated kinases
- p-ERK1/2:
-
Phospho-ERK1/2
- OPN:
-
Osteopontin
- OCN:
-
Osteocalcin
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin-6
- IL11:
-
Interleukin-11
- PTH-rp:
-
Parathyroid hormone-related protein
- MMP9:
-
Matrix metallopeptidase 9
- MMP2:
-
Matrix metallopeptidase 2
- DKK1:
-
Dickkopf WNT signaling pathway inhibitor 1
- ALP:
-
Alkaline phosphatase
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- GSK-3β:
-
Glycogen synthase kinase-3β
- pGSK-3β:
-
Phospho-GSK-3β
- CTGF:
-
Connective Tissue Growth Factor
- LRP-6:
-
Low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6
- BMP9-CM:
-
BMP9 condition medium
- GFR-CM:
-
GFP Vector control condition medium
References
A. Halon, P. Donizy, P. Surowiak, R. Matkowski, ERM/Rho protein expression in ductal breast cancer: a 15 year follow-up. Cell Oncol (Dordr) 36, 181–190 (2013)
A. Lipton, R. Uzzo, R.J. Amato, G.K. Ellis, B. Hakimian, G.D. Roodman, M.R. Smith, The science and practice of bone health in oncology: managing bone loss and metastasis in patients with solid tumors. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw 7(Suppl 7), S1–S29 (2009). quiz S30
I. Zinonos, K.W. Luo, A. Labrinidis, V. Liapis, S. Hay, V. Panagopoulos, M. Denichilo, C.H. Ko, G.G. Yue, C.B. Lau, W. Ingman, V. Ponomarev, G.J. Atkins, D.M. Findlay, A.C. Zannettino, A. Evdokiou, Pharmacologic inhibition of bone resorption prevents cancer-induced osteolysis but enhances soft tissue metastasis in a mouse model of osteolytic breast cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 45, 532–540 (2014)
R.L. Theriault, R.L. Theriault, Biology of bone metastases. Cancer Control 19, 92–101 (2012)
R. Krawetz, Y.E. Wu, D.E. Rancourt, J. Matyas, Osteoblasts suppress high bone turnover caused by osteolytic breast cancer in-vitro. Exp. Cell Res. 315, 2333–2342 (2009)
P.O. Favaron, A. Mess, S.E. Will, P.C. Maiorka, M.F. de Oliveira, M.A. Miglino, Yolk sac mesenchymal progenitor cells from New World mice (Necromys lasiurus) with multipotent differential potential. PLoS One 9, e95575 (2014)
J. Luo, M. Tang, J. Huang, B.C. He, J.L. Gao, L. Chen, G.W. Zuo, W. Zhang, Q. Luo, Q. Shi, B.Q. Zhang, Y. Bi, X. Luo, W. Jiang, Y. Su, J. Shen, S.H. Kim, E. Huang, Y. Gao, J.Z. Zhou, K. Yang, H.H. Luu, X. Pan, R.C. Haydon, Z.L. Deng, T.C. He, TGFbeta/BMP type I receptors ALK1 and ALK2 are essential for BMP9-induced osteogenic signaling in mesenchymal stem cells. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 29588–29598 (2010)
D. Mendoza-Villanueva, L. Zeef, P. Shore, Metastatic breast cancer cells inhibit osteoblast differentiation through the Runx2/CBFβ-dependent expression of the Wnt antagonist, sclerostin. Breast Cancer Res. 13, R106 (2011)
A.P. Molloy, F.T. Martin, R.M. Dwyer, T.P. Griffin, M. Murphy, F.P. Barry, T. O’Brien, M.J. Kerin, Mesenchymal stem cell secretion of chemokines during differentiation into osteoblasts, and their potential role in mediating interactions with breast cancer cells. Int. J. Cancer 124, 326–332 (2009)
K. Wang, H. Feng, W. Ren, X. Sun, J. Luo, M. Tang, L. Zhou, Y. Weng, T.C. He, Y. Zhang, BMP9 inhibits the proliferation and invasiveness of breast cancer cells MDA-MB-231. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 137, 1687–1696 (2011)
X. Sun, K. Wang, H. Feng, Effects and possible mechanism of BMP9 on the bone metastasis of human breast cancer cells MDA-MB- 231. Chin Biotechnol 32, 7–13 (2012)
N. Tang, W.X. Song, J. Luo, X. Luo, J. Chen, K.A. Sharff, Y. Bi, B.C. He, J.Y. Huang, G.H. Zhu, Y.X. Su, W. Jiang, M. Tang, Y. He, Y. Wang, L. Chen, G.W. Zuo, J. Shen, X. Pan, R.R. Reid, H.H. Luu, R.C. Haydon, T.C. He, BMP-9-induced osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal progenitors requires functional canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signalling. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 13, 2448–2464 (2009)
N. Serna-Marquez, S. Villegas-Comonfort, O. Galindo-Hernandez, N. Navarro-Tito, A. Millan, E.P. Salazar, Role of LOXs and COX-2 on FAK activation and cell migration induced by linoleic acid in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Cell Oncol 36, 65–77 (2013)
J.S. Park, S.Y. Choi, J.H. Lee, J.H. Lee, M. Lee, E.S. Nam, A.L. Jeong, S. Lee, S. Han, M.S. Lee, J.S. Lim, Y. Yoon do, Y. Kwon, Y. Yang, Interleukin-32β stimulates migration of MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7cells via the VEGF-STAT3 signaling pathway. Cell Oncol 36, 493–503 (2013)
H.H. Luu, W.X. Song, X. Luo, D. Manning, J. Luo, Z.L. Deng, K.A. Sharff, A.G. Montag, R.C. Haydon, T.C. He, Distinct roles of bone morphogenetic proteins in osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. J. Orthop. Res. 25, 665–677 (2007)
J.A. Sterling, S.A. Guelcher, Bone structural components regulating sites of tumor metastasis. Curr Osteoporos Rep 9, 89–95 (2011)
J.L. Gilmore, J.A. Scott, Z. Bouizar, A. Robling, S.E. Pitfield, D.J. Riese 2nd, J. Foley, Amphiregulin-EGFR signaling regulates PTHrP gene expression in breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 110, 493–505 (2008)
S. Ley, A. Weigert, B. Weichand, N. Henke, B. Mille-Baker, R.A. Janssen, B. Brune, The role of TRKA signaling in IL-10 production by apoptotic tumor cell-activated macrophages. Oncogene 32, 631–640 (2013)
J.Y. Jang, Y.K. Jeon, C.W. Kim, Degradation of HER2/neu by ANT2 shRNA suppresses migration and invasiveness of breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer 10, 391 (2010)
K. Tawara, J.T. Oxford, C.L. Jorcyk, Clinical significance of interleukin (IL)-6 in cancer metastasis to bone: potential of anti-IL-6 therapies. Cancer Manag. Res. 3, 177–189 (2011)
Y. Guo, P.F. Li, X.C. Shu, H. Deng, H.L. Ma, L. Sun, Involvement of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in the osteogenesis of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells induced by drynaria total flavonoids. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 92, 2288–2291 (2012)
L. Zhang, Y. Teng, Y. Zhang, J. Liu, L. Xu, J. Qu, K. Hou, X. Yang, Y. Liu, X. Qu, C-Src-mediated RANKL-induced breast cancer cell migration by activation of the ERK and Akt pathway. Oncol Lett 3, 395–400 (2012)
Y. Zhang, L. Wang, M. Zhang, M. Jin, C. Bai, X. Wang, Potential mechanism of interleukin-8 production from lung cancer cells: an involvement of EGF-EGFR-PI3K-Akt-Erk pathway. J. Cell. Physiol. 227, 35–43 (2012)
S. Ibaragi, T. Shimo, M. Iwamoto, N.M. Hassan, S. Kodama, S. Isowa, A. Sasaki, Parathyroid hormone-related peptide regulates matrix metalloproteinase-13 gene expression in bone metastatic breast cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 30, 5029–5036 (2010)
L. Zhang, Y. Teng, Y. Zhang, J. Liu, L. Xu, J. Qu, K. Hou, Y. Liu, X. Qu, Proteasome inhibitor bortezomib (PS-341) enhances RANKL-induced MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell migration. Mol Med Rep 5, 580–584 (2012)
L. Ye, H. Kynaston, W.G. Jiang, Bone morphogenetic protein-9 induces apoptosis in prostate cancer cells, the role of prostate apoptosis response-4. Mol. Cancer Res. 6, 1594–1606 (2008)
L. Ye, H. Kynaston, W.G. Jiang, Bone morphogenetic protein-10 suppresses the growth and aggressiveness of prostate cancer cells through a Smad independent pathway. J. Urol. 181, 2749–2759 (2009)
W. Irvin Jr., H.B. Muss, D.K. Mayer, Symptom management in metastatic breast cancer. Oncologist 16, 1203–1214 (2011)
Y.C. Chen, D.M. Sosnoski, A.M. Mastro, Breast cancer metastasis to the bone: mechanisms of bone loss. Breast Cancer Res. 12, 215 (2010)
W. Ren, X. Sun, K. Wang, H. Feng, Y. Liu, C. Fei, S. Wan, W. Wang, J. Luo, Q. Shi, M. Tang, G. Zuo, Y. Weng, T. He, Y. Zhang, BMP9 inhibits the bone metastasis of breast cancer cells by downregulating CCN2 (connective tissue growth factor, CTGF) expression. Mol. Biol. Rep. 41, 1373–1383 (2014)
Y.H. Wang, Y.Y. Dong, W.M. Wang, X.Y. Xie, Z.M. Wang, R.X. Chen, J. Chen, D.M. Gao, J.F. Cui, Z.G. Ren, Vascular endothelial cells facilitated HCC invasion and metastasis through the Akt and NF-κB pathways induced by paracrine cytokines. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 32, 51 (2013)
A. De Luca, L. Lamura, M. Gallo, V. Maffia, N. Normanno, Mesenchymal stem cell-derived interleukin-6 and vascular endothelial growth factor promote breast cancer cell migration. J. Cell. Biochem. 113, 3363–3370 (2012)
L.E. Wright, J.B. Frye, A.L. Lukefahr, B.N. Timmermann, K.S. Mohammad, T.A. Guise, J.L. Funk, Curcuminoids block TGF-β signaling in human breast cancer cells and limit osteolysis in a murine model of breast cancer bone metastasis. J. Nat. Prod. 76, 316–321 (2013)
S. Das, R.S. Samant, L.A. Shevde, Hedgehog signaling induced by breast cancer cells promotes osteoclastogenesis and osteolysis. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 9612–9622 (2011)
S. Das, J.A. Tucker, S. Khullar, R.S. Samant, L.A. Shevde, Hedgehog signaling in tumor cells facilitates osteoblast-enhanced osteolytic metastases. PLoS One 7, e34374 (2012)
T.A. Owen, M. Aronow, V. Shalhoub, L.M. Barone, L. Wilming, M.S. Tassinari, M.B. Kennedy, S. Pockwinse, J.B. Lian, G.S. Stein, Progressive development of the rat osteoblast phenotype in vitro: reciprocal relationships in expression of genes associated with osteoblast proliferation and differentiation during formation of the bone extracellular matrix. J. Cell. Physiol. 143, 420–430 (1990)
G. Bu, W. Lu, C.C. Liu, K. Selander, T. Yoneda, C. Hall, E.T. Keller, Y. Li, Breast cancer-derived Dickkopf1 inhibits osteoblast differentiation and osteoprotegerin expression: implication for breast cancer osteolytic bone metastases. Int. J. Cancer 123, 1034–1042 (2008)
Z. Zhai, X. Qu, W. Yan, H. Li, G. Liu, X. Liu, T. Tang, A. Qin, K. Dai, Andrographolide prevents human breast cancer-induced osteoclastic bone loss via attenuated RANKL signaling. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 144, 33–45 (2014)
N. Kurio, T. Shimo, T. Fukazawa, M. Takaoka, T. Okui, N.M. Hassan, T. Honami, S. Hatakeyama, M. Ikeda, Y. Naomoto, A. Sasaki, Anti-tumor effect in human breast cancer by TAE226, a dual inhibitor for FAK and IGF-IR in vitro and in vivo. Exp. Cell Res. 317, 1134–1146 (2011)
C. Bolin, K. Tawara, C. Sutherland, J. Redshaw, P. Aranda, J. Moselhy, R. Anderson, C.L. Jorcyk, Oncostatin m promotes mammary tumor metastasis to bone and osteolytic bone degradation. Genes Cancer 3, 117–130 (2012)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Nature Science Foundation of China (81172017) and the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, 2011CB707906).
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Shaoheng Wan and Yuehong Liu these authors contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wan, S., Liu, Y., Weng, Y. et al. BMP9 regulates cross-talk between breast cancer cells and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Oncol. 37, 363–375 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-014-0197-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-014-0197-1