Abstract
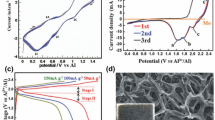
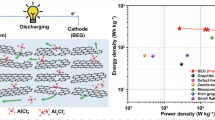
Aluminum-ion batteries (AIBs) are considered promising post lithium-ion batteries owing to their outstanding safety, gravimetric and volumetric capacities, and cost efficiency advantages. However, one practical obstacle to their development is the lack of reliable cathode materials that can be coupled with the distinguished Al anode. To address this issue, we synthesized a S@GO composite material for use as a cathode material in AIBs. The synthesized S@GO material exhibits a rod structure with a diameter of around 100 nm. Inside these nanorods, sulfur nanoparticles with a size of around 5 nm were uniformly anchored on the graphene sheets. By taking the advantage of an introduction of graphene sheets, the capacities were significantly preserved, displaying a capacity that was more than double that of a bare S active material. In addition, a 3000-cycle long-term repeated charge/discharge measurement exhibited extremely stable capacity values with a high Coulombic efficiency of 98% at the 3000th cycle. The charge/discharge processes were clearly shown during the repeated cycling measurement at a high current density of 1000 mA g−1. This work is expected to stimulate further study of elemental S used as a cathode material for high-performance AIBs.
Graphic Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang, K., Lee, T.H., Noh, H., Islamoglu, T., Farha, O.K., Jang, H.W., Choi, J.-W., Shokouhimehr, M.: Realization of lithium-ion capacitors with enhanced energy density via the use of gadolinium hexacyanocobaltate as a cathode material. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b07711
Zhang, K., Lee, T.H., Bubach, B., Ostadhassan, M., Jang, H.W., Choi, J.-W., Shokouhimehr, M.: Coordinating gallium hexacyanocobaltate: prussian blue-based nanomaterial for Li-ion storage. RSC Adv. 9(46), 26668–26675 (2019)
Zhang, K., Lee, T.H., Bubach, B., Ostadhassan, M., Jang, H.W., Choi, J.-W., Shokouhimehr, M.: Layered metal–organic framework based on tetracyanonickelate as a cathode material for in situ Li-ion storage. RSC Adv. 9(37), 21363–21370 (2019)
Yu, S.H., Shokouhimehr, M., Hyeon, T., Sung, Y.-E.: Iron hexacyanoferrate nanoparticles as cathode materials for lithium and sodium rechargeable batteries. ECS Electrochem. Lett. 2(4), A39–A41 (2013)
Zhang, K., Varma, R.S., Jang, H.W., Choi, J.-W., Shokouhimehr, M.: Iron hexacyanocobaltate metal–organic framework: highly reversible and stationary electrode material with rich borders for lithium-ion batteries. J. Alloys Compd. 791, 911–917 (2019)
Zhang, K., Lee, T.H., Jang, H.W., Shokouhimehr, M., Choi, J.-W.: A hybrid energy storage mechanism of zinc hexacyanocobaltate-based metal–organic framework endowing stationary and high-performance lithium-ion storage. Electron. Mater. Lett. 15(4), 444–453 (2019)
Ko, J., Kang, S.H., Cheong, H.W., Yoon, Y.S.: Recent progress in cathode materials for thermal batteries. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 56(3), 233–255 (2019)
Park, H., Lee, S., Jo, M., Park, S., Kwon, K., Shobana, M.K., Choe, H.: Nanowire-like copper oxide grown on porous copper, a promising anode material for lithium-ion battery. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 54(5), 438–442 (2017)
Choi, M., Lee, S.H., Jung, Y.I., Choi, W.-K., Moon, J.-K., Choi, J., Seo, B.-K., Kim, S.-B.: The preparation of Fe3O4 thin film and its electrochemical characterization for Li-ion battery. Trans. Electr. Electron. Mater. 19(6), 417–422 (2018)
Kalashani, M.B., Nazarpour, D.: New symmetric and hybrid multilevel inverter topology employed in solar energy systems. Trans. Electr. Electron. Mater. 19(4), 304–310 (2018)
Zhang, Y., Liu, S., Ji, Y., Ma, J., Yu, H.: Emerging nonaqueous aluminum-ion batteries: challenges, status, and perspectives. Adv. Mater. 30(38), 1706310 (2018)
Cai, T., Zhao, L., Hu, H., Li, T., Li, X., Guo, S., Li, Y., Xue, Q., Xing, W., Yan, Z., Wang, L.: Stable CoSe2/carbon nanodice@reduced graphene oxide composites for high-performance rechargeable aluminum-ion batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 11(9), 2341–2347 (2018)
Pang, Q., Kwok, C.Y., Kundu, D., Liang, X., Nazar, L.F.: Lightweight metallic MgB2 mediates polysulfide redox and promises high-energy-density lithium–sulfur batteries. Joule 3(1), 136–148 (2019)
Liu, Y.T., Han, D.D., Wang, L., Li, G.-R., Liu, S., Gao, X.-P.: Lithium–sulfur batteries: NiCo2O4 nanofibers as carbon-free sulfur immobilizer to fabricate sulfur-based composite with high volumetric capacity for lithium–sulfur battery. Adv. Energy Mater. 9(11), 1970030 (2019)
Cohn, G., Ma, L., Archer, L.A.: A novel non-aqueous aluminum sulfur battery. J. Power Sources 283, 416–422 (2015)
Chu, W., Zhang, X., Wang, J., Zhao, S., Liu, S., Yu, H.: A low-cost deep eutectic solvent electrolyte for rechargeable aluminum–sulfur battery. Energy Storage Mater. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ensm.2019.01.025
Guo, Y., Jin, H., Qi, Z., Hu, Z., Ji, H., Wan, L.-J.: Carbonized-MOF as a sulfur host for aluminum–sulfur batteries with enhanced capacity and cycling life. Adv. Funct. Mater. 29(7), 1807676 (2019)
Yu, X., Manthiram, A.: Electrochemical energy storage with a reversible nonaqueous room-temperature aluminum–sulfur chemistry. Adv. Energy Mater. 7(18), 1700561 (2017)
Hummers Jr., W.S., Offeman, R.E.: Preparation of graphitic oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 80(6), 1339 (1958)
Wu, J.B., Lin, M.L., Cong, X., Liu, H.-N., Tan, P.-H.: Raman spectroscopy of graphene-based materials and its applications in related devices. Chem. Soc. Rev. 47(5), 1822–1873 (2018)
McAllister, M.J., Li, J.L., Adamson, D.H., Schniepp, H.C., Abdala, A.A., Liu, J., Herrera-Alonso, M., Milius, D.L., Car, R., Prud’homme, R.K., Aksay, I.A.: Single sheet functionalized graphene by oxidation and thermal expansion of graphite. Chem. Mater. 19(18), 4396–4404 (2007)
Hu, Y., Ye, D., Luo, B., Hu, H., Zhu, X., Wang, S., Li, L., Peng, S., Wang, L.: A binder-free and free-standing cobalt sulfide@carbon nanotube cathode material for aluminum-ion batteries. Adv. Mater. 30(2), 1703824 (2018)
Wu, Y., Gong, M., Lin, M.C., Yuan, C., Angell, M., Huang, L., Wang, D.-Y., Zhang, X., Yang, J., Hwang, B.-J., Dai, H.: 3D graphitic foams derived from chloroaluminate anion intercalation for ultrafast aluminum-ion battery. Adv. Mater. 28(41), 9218–9222 (2016)
Wang, S., Yu, Z., Tu, J., Wang, J., Tian, D., Liu, Y., Jiao, S.: A novel aluminum-ion battery: Al/AlCl3-[EMIm]Cl/Ni3S2@graphene. Adv. Energy Mater. 6(13), 1600137 (2016)
Chen, H., Guo, F., Liu, Y., Huang, T., Zheng, B., Ananth, N., Xu, Z., Gao, W., Gao, C.: A defect-free principle for advanced graphene cathode of aluminum-ion battery. Adv. Mater. 29(12), 1605958 (2017)
Wang, S., Jiao, S., Wang, J., Chen, H.-S., Tian, D., Lei, H., Fang, D.-N.: High-performance aluminum-ion battery with CuS@C microsphere composite cathode. ACS Nano 11(1), 469–477 (2016)
Gao, T., Li, X., Wang, X., Hu, J., Han, F., Fan, X., Suo, L., Pearse, A.J., Lee, S.B., Rubloff, G.W., Gaskell, K.J., Noked, M., Wang, C.: A rechargeable Al/S battery with an ionic-liquid electrolyte. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 55(34), 9898–9901 (2016)
Yang, H., Yin, L., Liang, J., Sun, Z., Wang, Y., Li, H., He, K., Ma, L., Peng, Z., Qiu, S., Sun, C., Cheng, H.-M., Li, F.: An aluminum–sulfur battery with a fast kinetic response. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 57(7), 1898–1902 (2018)
Razzaq, A.A., Yao, Y., Shah, R., Qi, P., Miao, L., Chen, M., Zhao, X., Peng, Y., Deng, Z.: High-performance lithium sulfur batteries enabled by a synergy between sulfur and carbon nanotubes. Energy Storage Mater. 16, 194–202 (2019)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Korea Institute of Science and Technology Future Resource Program (2E29400). Furthermore, the financial supports of the Future Material Discovery Program (2016M3D1A1027666), the Basic Science Research Program (2017R1A2B3009135) through the National Research Foundation of Korea, and China Scholarship Council are appreciated (201808260042).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, K., Lee, T.H., Cha, J.H. et al. S@GO as a High-Performance Cathode Material for Rechargeable Aluminum-Ion Batteries. Electron. Mater. Lett. 15, 720–726 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-019-00170-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-019-00170-7