Abstract
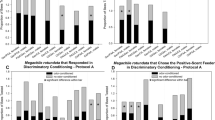
Many insects find resources by means of the olfactory cues of general odors after learning. To evaluate behavioral responses to the odor of a particular chemical after learning with reward or punishment quantitatively, we developed a standardized odor-training method in the German cockroach, Blattella germanica (Linnaeus), an important urban pest species. A classical olfactory conditioning procedure for a preference test was modified to become applicable to a single odor, by which a (−)-menthol or vanillin odor was independently associated with sucrose (reward) or sodium chloride solution (punishment). The strength of the association with the odor was evaluated with the increase or decrease in visit frequencies to the odor source after olfactory conditioning. The frequency increased after (−)-menthol was presented with a reward, while it did not change with the rewarded vanillin odor. With both odors, the frequency decreased significantly after training with a punishment. These results indicate that cockroaches learn a single compound odor presented as a conditioned stimulus, although the association of the odor with a reward or punishment depends on the chemical. This olfactory conditioning method can not only facilitate the analysis of cockroach behavior elicited by a learned single chemical odor, but also quantify the potential attractiveness or repellency of the chemical after learning.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balderrama N (1980) One trial learning in the American cockroach, Periplaneta americana. J Insect Physiol 26:499–504
Bell WJ, Kramer E (1980) Sex pheromone-stimulated orientation of the American cockroach on a servosphere apparatus. J Chem Ecol 6:287–295
Bell WJ, Tobin TR (1981) Orientation to sex pheromone in the American cockroach: analysis of chemo-orientation mechanisms. J Insect Physiol 27:501–508
Bell WJ, Tobin TR (1982) Chemo-orientation. Biol Rev 57:219–260
Cardé RT, Willis MA (2008) Navigational strategies used by insects to find distant, wind-borne source of odor. J Chem Ecol 34:854–866
Dethier VG (1957) Communication by insects: physiology of dancing. Science 125:331–336
Durier V, Rivault C (2001) Effects of spatial knowledge and feeding experience on foraging choices in German cockroaches. Anim Behav 62:681–688
Hawkins WA (1978) Effects of sex pheromone on locomotion in the male American cockroach, Periplaneta americana. J Chem Ecol 4:149–160
Ishii S, Kuwahara Y (1968) Aggregation of German cockroach (Blattella germanica) nymphs. Experientia 24:88–89
Kennedy JS (1978) The concepts of olfactory ‘arrestment’ and ‘attraction’. Physiol Entomol 3:91–98
Mackintosh NJ (1983) Conditioning and associative learning. Oxford University Press, London
Matsumoto Y, Mizunami M (2000) Olfactory learning in the cricket Gryllus bimaculatus. J Exp Biol 203:2581–2588
Matsumoto Y, Mizunami M (2002) Temporal determinants of long-term retention of olfactory memory in the cricket Gryllus bimaculatus. J Exp Biol 205:1429–1437
Nalyanya G, Liang D, Kopanic RJ, Schal C (2001) Attractiveness of insecticide baits for cockroach control (Dictyoptera: Blattellidae) laboratory and field studies. J Econ Entomol 94:686–693
Nojima S, Schal C, Webster FX, Santangelo RG, Roelofs WL (2005) Identification of the sex pheromone of the German cockroach, Blattella germanica. Science 307:1104–1106
Papini MR, Bitterman ME (1993) The two test strategy in the study of inhibitory conditioning. J Exp Psychol 19:342–352
Rescorla RA (1988) Behavioral studies of Pavlovian conditioning. Ann Rev Neurosci 11:329–352
Rust MK, Burk T, Bell WJ (1976) Pheromone-stimulated locomotory and orientation responses in the American cockroach. Anim Behav 24:52–67
Sakuma M (2002) Virtual reality experiments on a digital servo sphere: guiding male silkworm moths to a virtual odour source. Comput Electron Agric 35:243–254
Sakuma M, Fukami H (1985) The linear track olfactometer: an assay device for taxes of the German cockroach, Blattella germanica (L.) (Dictyoptera: Blattellidae) toward their aggregation pheromone. Appl Entomol Zool 20:387–402
Sakuma M, Fukami H (1990) The aggregation pheromone of the German cockroach, Blattella germanica (L.) (Dictyoptera: Blattellidae): isolation and identification of the attractant components of the pheromone. Appl Entomol Zool 25:355–368
Sakura M, Mizunami M (2001) Olfactory learning and memory in the cockroach, Periplaneta americana. Zool Sci 18:21–28
Seelinger G, Gagel S (1985) On the function of sex pheromone components in Periplaneta americana: improved odour source localization with periplanone-A. Physiol Entomol 10:221–234
Seelinger G, Schuderer B (1985) Release of male courtship display in Periplaneta americana: evidence for female contact sex pheromone. Anim Behav 33:599–607
Takahashi S, Kitamura C (1972) Bioassay procedure of the sex stimulant of the American cockroach, Periplaneta americana (L.) (Orthoptera: Blattidae). Appl Ent Zool 7:133–141
Thompson RF, Spencer WA (1966) Habituation: a model phenomenon for the study of neuronal substrates of behavior. Psychol Rev 73:16–43
Tobin TR (1981) Pheromone orientation: role of internal control mechanisms. Science 214:1147–1149
Tsuji H (1966) Attractive and feeding stimulative effect of some fatty acids and related compounds on three species of cockroaches. Jpn J Sanit Zool 17:89–97
Unoki S, Matsumoto Y, Mizunami M (2005) Participation of octopaminergic reward system and dopaminergic punishment system in insect olfactory learning revealed by pharmacological study. Eur J Neurosci 22:1409–1416
Watanabe H, Kobayashi Y, Sakura M, Matsumoto Y, Mizunami M (2003) Classical olfactory conditioning in the cockroach, Periplaneta americana. Zool Sci 20:1447–1454
Wileyto PE, Boush MG (1983) Attraction of the German cockroach, Blattella germanica (Orthoptera: Blattellidae), to some volatile food components. J Econ Entomol 76:752–756
Willis MA, Avondet JL (2005) Odor-modulated orientation in walking male cockroaches Periplaneta americana, and the effects of odor plumes of different structure. J Exp Biol 208:721–735
Acknowledgments
We express our sincere gratitude to Prof. Mizunami of the Graduate School of Life Science, Hokkaido University, Japan, for the invaluable comments and critical reading of this manuscript. We also thank two anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, JL., Sakuma, M. Olfactory conditioning with single chemicals in the German Cockroach, Blattella germanica (Dictyoptera: Blattellidae). Appl Entomol Zool 48, 387–396 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13355-013-0199-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13355-013-0199-x