Abstract
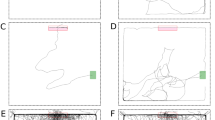
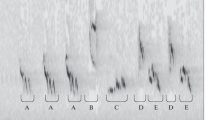
The locomotory activities of individual males ofPeriplaneta americana in a circular arena 2.5 m in diameter were investigated during the portion of the photocycle in which the cockroaches are most active. Control animals ran at an average speed of 10.86 cm/sec but remained immobile 68 % of the time. Pauses in locomotion occurred frequently and at fairly regular intervals (x=0.88 sec). Males showed a strong tendency to remain near the sides of the arena. Sex pheromone presented in the center of the arena produced a reduction in immobility time and a slight increase in running speed. The frequency of pauses decreased, and the time between pauses became less regular. The proportion of time spent near the sides of the arena was greatly reduced also.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Block, E.F., andBell, W.J. 1974. Ethometric analysis of pheromone receptor function in cockroaches.J. Insect Physiol. 20:993–1003.
Darchen, R. 1952. Sur l'activité exploratrice deBlatella (Blattella)germanica.Z. Tierpsychol. 9:362–372.
Darchen, R. 1955. Stimuli nouveaux et tendance exploratrice chezBlatella (Blattella)germanica.Z. Tierpsychol. 12:1–11.
Darchen, R. 1957. Sur le compartement d'exploration deBlatella (Blattella)germanica. Exploration d'un plan.J. Psychol. 54:190–205.
Darchen, R., andRichard, P-B. 1960. Quelques recherches sur le comportement explorateur “chronique” deBlatella (Blattella)germanica.J. Psychol. 57:77–94.
Delcomyn, F. 1969. Reflexes and locomotion in the American cockroach. Ph.D. thesis, University of Oregon.
Delcomyn, F. 1971a. The locomotion of the cockroachPeriplaneta americana.J. Exp. Biol. 54:443–452.
Delcomyn, F. 1971b. The effect of limb amputation on locomotion in the cockroachPeriplaneta americana.J. Exp. Biol. 54:453–469.
Erber, J. 1975. Turning behavior related to optical stimuli inTenebrio molitor.J. Insect Physiol. 21:1575–1580.
Hawkins, W.A. 1978. Sex pheromone-induced chemolocation in the male American cockroach,Periplaneta americana. J. Comp. Physiol. Submitted.
Hawkins, W.A., andRust, M.K. 1977. Factors influencing male sexual response in the American cockroach,Periplaneta americana.J. Chem. Ecol. 3:85–99.
Hughes, G.M. 1952. The co-ordination of insect movements I. The walking movement of insects.J. Exp. Biol. 29:267–284.
Jackson, W.B., andMaier, P.P. 1955. Dispersion of marked American cockroaches from sewer manholes in Phoenix, Arizona.Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 4:141–146.
McConnell, E., andRichards, A.G. 1955. How fast can a cockroach run?Bull. Brooklyn Entomol. Soc. 50:36–43.
Rust, M.K. 1976. Quantitative analysis of male responses released by female sex pheromone inPeriplaneta americana.Anim. Behav. 24:681–685.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hawkins, W.A. Effects of sex pheromone on locomotion in the male American cockroach,Periplaneta americana . J Chem Ecol 4, 149–160 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00988051
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00988051