Abstract
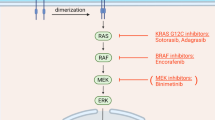
Anti-epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) therapy has established efficacy in metastatic colorectal cancer, but a significant number of patients do not respond to such treatment. Recently, various biomarkers were reported to be useful in predicting resistance to anti-EGFR. All the potential biomarkers predicting resistance to anti-EGFR are reviewed herein from five aspects. First, upstream molecules, including epiregulin (EREG) and amphiregulin (AREG), might play different roles according to their abnormal levels in tumor tissue and serum. Second, the EGFR amplification and distinct polymorphisms may have roles in identifying patients for initial anti-EGFR mAbs therapy, while rare EGFR mutations have limited predictive values. Third, among the downstream molecularly related factors, rat sarcoma viral oncogene (Ras) has been identified as a successful predictor, while B-Raf proto-oncogene (BRAF) is considered as a prognostic factor rather than a predictor. Fourth, among the molecular bypass pathway components, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) and phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) may be potential biomarkers in the future, while activation of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)/c-Met signaling confers resistance to anti-EGFR therapy. Fifth, many microRNAs and additional molecular biomarkers are promising in predicting the efficacy of anti-EGFR therapy. Applications of multiple biomarkers are more effective than the use of a single biomarker in selecting patients who might benefit from cetuximab- or panitumumab-based treatments. Comprehensive molecular analyses of the EGFR signaling pathways should be considered in the future. Subsequent prospective trials will be required to further confirm the clinical utility of these biomarkers.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heinemann V, Weikersthal LF, Decker T, Kiani A, Vehling-Kaiser U, Al-Batran SE, et al. FOLFIRI plus cetuximab versus FOLFIRI plus bevacizumab as first-line treatment for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (FIRE-3): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15(10):1065–75. doi:10.1016/s1470-2045(14)70330-4.
Khambata-Ford S, Garrett CR, Meropol NJ, Basik M, Harbison CT, Wu S, et al. Expression of epiregulin and amphiregulin and K-ras mutation status predict disease control in metastatic colorectal cancer patients treated with cetuximab. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2007;25(22):3230–7. doi:10.1200/jco.2006.10.5437.
Jacobs B, De Roock W, Piessevaux H, Van Oirbeek R, Biesmans B, De Schutter J, et al. Amphiregulin and epiregulin mRNA expression in primary tumors predicts outcome in metastatic colorectal cancer treated with cetuximab. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2009;27(30):5068–74. doi:10.1200/jco.2008.21.3744.
Jonker DJ, Karapetis CS, Harbison C, O’Callaghan CJ, Tu D, Simes RJ, et al. Epiregulin gene expression as a biomarker of benefit from cetuximab in the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 2014;110(3):648–55. doi:10.1038/bjc.2013.753.
Seligmann JF, Elliott Faye, Richman S, Jacobs B, Hemmings G, Barrett J, et al. Combined epiregulin (EREG) and amphiregulin (AREG) expression levels as a biomarker of prognosis and panitumumab benefit in RAS-wt advanced colorectal cancer (aCRC). J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2014;32(5s):abstr 3520.
Cushman SM, Jiang C, Hatch AJ, Shterev I, Sibley AB, Niedzwiecki D, et al. Gene expression markers of efficacy and resistance to cetuximab treatment in metastatic colorectal cancer: results from CALGB 80203 (Alliance). Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21(5):1078–86. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-14-2313.
Takahashi N, Yamada Y, Furuta K, Honma Y, Iwasa S, Takashima A, et al. Serum levels of hepatocyte growth factor and epiregulin are associated with the prognosis on anti-EGFR antibody treatment in KRAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 2014;110(11):2716–27. doi:10.1038/bjc.2014.230.
Seligmann JF, Elliott F, Richman SD, Jacobs B, Hemmings G, Brown S. Combined epiregulin and amphiregulin expression levels as a predictive biomarker for panitumumab therapy benefit or lack of benefit in patients with RAS wild-type advanced colorectal cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2016. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2015.6065.
Sebio A, Paez D, Salazar J, Berenguer-Llergo A, Pare-Brunet L, Lasa A, et al. Intergenic polymorphisms in the amphiregulin gene region as biomarkers in metastatic colorectal cancer patients treated with anti-EGFR plus irinotecan. Pharmacogenomics J. 2014;14(3):256–62. doi:10.1038/tpj.2013.29.
Loupakis F, Cremolini C, Fioravanti A, Orlandi P, Salvatore L, Masi G, et al. EGFR ligands as pharmacodynamic biomarkers in metastatic colorectal cancer patients treated with cetuximab and irinotecan. Target Oncol. 2014;9(3):205–14. doi:10.1007/s11523-013-0284-7.
Yonesaka K, Takegawa N, Satoh T, Ueda H, Yoshida T, Takeda M, et al. Combined analysis of plasma amphiregulin and heregulin predicts response to cetuximab in metastatic colorectal cancer. PLoS One. 2015;10(11), e0143132. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0143132.
Hobor S, Van Emburgh BO, Crowley E, Misale S, Di Nicolantonio F, Bardelli A. TGFalpha and amphiregulin paracrine network promotes resistance to EGFR blockade in colorectal cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20(24):6429–38. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-14-0774.
Italiano A, Follana P, Caroli FX, Badetti JL, Benchimol D, Garnier G, et al. Cetuximab shows activity in colorectal cancer patients with tumors for which FISH analysis does not detect an increase in EGFR gene copy number. Ann Surg Oncol. 2008;15(2):649–54. doi:10.1245/s10434-007-9667-2.
Laurent-Puig P, Cayre A, Manceau G, Buc E, Bachet JB, Lecomte T, et al. Analysis of PTEN, BRAF, and EGFR status in determining benefit from cetuximab therapy in wild-type KRAS metastatic colon cancer. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2009;27(35):5924–30. doi:10.1200/jco.2008.21.6796.
Algars A, Lintunen M, Carpen O, Ristamaki R, Sundstrom J. EGFR gene copy number assessment from areas with highest EGFR expression predicts response to anti-EGFR therapy in colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 2011;105(2):255–62. doi:10.1038/bjc.2011.223.
Algars A, Avoranta T, Osterlund P, Lintunen M, Sundstrom J, Jokilehto T, et al. Heterogeneous EGFR gene copy number increase is common in colorectal cancer and defines response to anti-EGFR therapy. PLoS One. 2014;9(6), e99590. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0099590.
Razis E, Pentheroudakis G, Rigakos G, Bobos M, Kouvatseas G, Tzaida O, et al. EGFR gene gain and PTEN protein expression are favorable prognostic factors in patients with KRAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer treated with cetuximab. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2014;140(5):737–48. doi:10.1007/s00432-014-1626-2.
Yang ZY, Shen WX, Hu XF, Zheng DY, Wu XY, Huang YF, et al. EGFR gene copy number as a predictive biomarker for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer with anti-EGFR monoclonal antibodies: a meta-analysis. J Hematol Oncol. 2012;5:52. doi:10.1186/1756-8722-5-52.
Shen WD, Chen HL, Liu PF. EGFR gene copy number as a predictive biomarker for resistance to anti-EGFR monoclonal antibodies in metastatic colorectal cancer treatment: a meta-analysis. Chin J Cancer Res. 2014;26(1):59–71. doi:10.3978/j.issn.1000-9604.2014.01.10.
Phua LC, Ng HW, Yeo AH, Chen E, Lo MS, Cheah PY, et al. Prevalence of KRAS, BRAF, PI3K and EGFR mutations among Asian patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Oncol Lett. 2015;10(4):2519–26. doi:10.3892/ol.2015.3560.
Montagut C, Dalmases A, Bellosillo B, Crespo M, Pairet S, Iglesias M, et al. Identification of a mutation in the extracellular domain of the epidermal growth factor receptor conferring cetuximab resistance in colorectal cancer. Nat Med. 2012;18(2):221–3. doi:10.1038/nm.2609.
Esposito C, Rachiglio AM, La Porta ML, Sacco A, Roma C, Iannaccone A, et al. The S492R EGFR ectodomain mutation is never detected in KRAS wild-type colorectal carcinoma before exposure to EGFR monoclonal antibodies. Cancer Biol Ther. 2013;14(12):1143–6. doi:10.4161/cbt.26340.
Morelli MP, Overman MJ, Dasari A, Kazmi SM, Mazard T, Vilar E, et al. Characterizing the patterns of clonal selection in circulating tumor DNA from patients with colorectal cancer refractory to anti-EGFR treatment. Ann Oncol. 2015;26(4):731–6. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdv005.
Arena S, Bellosillo B, Siravegna G, Martinez A, Canadas I, Lazzari L, et al. Emergence of multiple EGFR extracellular mutations during cetuximab treatment in colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21(9):2157–66. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-14-2821.
Jaka A, Gutierrez-Rivera A, Ormaechea N, Blanco J, La Casta A, Sarasqueta C, et al. Association between EGFR gene polymorphisms, skin rash and response to anti-EGFR therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Exp Dermatol. 2014;23(10):751–3. doi:10.1111/exd.12510.
Inoue Y, Hazama S, Iwamoto S, Miyake Y, Matsuda C, Tsunedomi R, et al. FcgammaR and EGFR polymorphisms as predictive markers of cetuximab efficacy in metastatic colorectal cancer. Mol Diagn Ther. 2014;18(5):541–8. doi:10.1007/s40291-014-0103-6.
Bertotti A, Migliardi G, Galimi F, Sassi F, Torti D, Isella C, et al. A molecularly annotated platform of patient-derived xenografts (“xenopatients”) identifies HER2 as an effective therapeutic target in cetuximab-resistant colorectal cancer. Cancer Discov. 2011;1(6):508–23. doi:10.1158/2159-8290.cd-11-0109.
Yonesaka K, Zejnullahu K, Okamoto I, Satoh T, Cappuzzo F, Souglakos J, et al. Activation of ERBB2 signaling causes resistance to the EGFR-directed therapeutic antibody cetuximab. Sci Transl Med. 2011;3(99):99ra86. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3002442.
Martin V, Landi L, Molinari F, Fountzilas G, Geva R, Riva A, et al. HER2 gene copy number status may influence clinical efficacy to anti-EGFR monoclonal antibodies in metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Br J Cancer. 2013;108(3):668–75. doi:10.1038/bjc.2013.4.
Kavuri SM, Jain N, Galimi F, Cottino F, Leto SM, Migliardi G, et al. HER2 activating mutations are targets for colorectal cancer treatment. Cancer Discov. 2015;5(8):832–41. doi:10.1158/2159-8290.cd-14-1211.
Kawakami H, Okamoto I, Yonesaka K, Okamoto K, Shibata K, Shinkai Y, et al. The anti-HER3 antibody patritumab abrogates cetuximab resistance mediated by heregulin in colorectal cancer cells. Oncotarget. 2014;5(23):11847–56.
Karapetis CS, Khambata-Ford S, Jonker DJ, O’Callaghan CJ, Tu D, Tebbutt NC, et al. K-ras mutations and benefit from cetuximab in advanced colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(17):1757–65. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0804385.
Amado RG, Wolf M, Peeters M, Van Cutsem E, Siena S, Freeman DJ, et al. Wild-type KRAS is required for panitumumab efficacy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2008;26(10):1626–34. doi:10.1200/jco.2007.14.7116.
Van Cutsem E, Kohne CH, Hitre E, Zaluski J, Chang Chien CR, Makhson A, et al. Cetuximab and chemotherapy as initial treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2009;360(14):1408–17. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0805019.
Van Cutsem E, Kohne CH, Lang I, Folprecht G, Nowacki MP, Cascinu S, et al. Cetuximab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin as first-line treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer: updated analysis of overall survival according to tumor KRAS and BRAF mutation status. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2011;29(15):2011–9. doi:10.1200/jco.2010.33.5091.
Bokemeyer C, Bondarenko I, Hartmann JT, de Braud F, Schuch G, Zubel A, et al. Efficacy according to biomarker status of cetuximab plus FOLFOX-4 as first-line treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer: the OPUS study. Ann Oncol. 2011;22(7):1535–46. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdq632.
Ciardiello F, Lenz H-J, Kohne CH et al. Treatment outcome according to tumor RAS mutation status in CRYSTAL study patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) randomized to FOLFIRI with/without cetuximab. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32: abstr 3506.
Kaczirek K, Ciuleanu TE, Vrbanec D, Marton E, Messinger D, Liegl-Atzwanger B, et al. FOLFOX4 plus cetuximab for patients with previously untreated metastatic colorectal cancer according to tumor RAS and BRAF mutation status: updated analysis of the CECOG/CORE 1.2.002 study. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2015;14(2):91–8. doi:10.1016/j.clcc.2014.12.003.
Peeters M, Oliner KS, Price TJ, et al. Analysis of KRAS/NRAS mutations in phase 3 study 20050181 of panitumumab (pmab) plus FOLFIRI versus FOLFIRI for second-line treatment (tx) of metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC). J Clin Oncol. 2014;32:abstr LBA387.
Douillard JY, Siena S, Cassidy J, Tabernero J, Burkes R, Barugel M, et al. Final results from PRIME: randomized phase III study of panitumumab with FOLFOX4 for first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann Oncol. 2014;25(7):1346–55. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdu141.
Sorich MJ, Wiese MD, Rowland A, Kichenadasse G, McKinnon RA, Karapetis CS. Extended RAS mutations and anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody survival benefit in metastatic colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials. Ann Oncol. 2015;26(1):13–21. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdu378.
Stintzing S, Jung A, Rossius L, et al. Mutations within the EGFR signaling pathway: influence on efficacy in FIRE-3-A randomized phase III study of FOLFIRI plus cetuximab or bevacizumab as first-line treatment for wild-type (WT) KRAS (exon 2) metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) patients. J Clin Oncol. 2014; 32:abstr 445.
Di Nicolantonio F, Martini M, Molinari F, Sartore-Bianchi A, Arena S, Saletti P, et al. Wild-type BRAF is required for response to panitumumab or cetuximab in metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2008;26(35):5705–12. doi:10.1200/jco.2008.18.0786.
Therkildsen C, Bergmann TK, Henrichsen-Schnack T, Ladelund S, Nilbert M. The predictive value of KRAS, NRAS, BRAF, PIK3CA and PTEN for anti-EGFR treatment in metastatic colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Oncol (Stockh). 2015;53(7):852–64. doi:10.3109/0284186x.2014.895036.
Cui D, Cao D, Yang Y, Qiu M, Huang Y, Yi C. Effect of BRAF V600E mutation on tumor response of anti-EGFR monoclonal antibodies for first-line metastatic colorectal cancer treatment: a meta-analysis of randomized studies. Mol Biol Rep. 2014;41(3):1291–8. doi:10.1007/s11033-013-2974-8.
Yuan ZX, Wang XY, Qin QY, Chen DF, Zhong QH, Wang L, et al. The prognostic role of BRAF mutation in metastatic colorectal cancer receiving anti-EGFR monoclonal antibodies: a meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2013;8(6), e65995. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0065995.
Bokemeyer C, Van Cutsem E, Rougier P, Ciardiello F, Heeger S, Schlichting M, et al. Addition of cetuximab to chemotherapy as first-line treatment for KRAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer: pooled analysis of the CRYSTAL and OPUS randomised clinical trials. Eur J Cancer. 2012;48(10):1466–75. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2012.02.057.
Tol J, Nagtegaal ID, Punt CJ. BRAF mutation in metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(1):98–9. doi:10.1056/NEJMc0904160.
Karapetis CS, Jonker D, Daneshmand M, Hanson JE, O’Callaghan CJ, Marginean C, et al. PIK3CA, BRAF, and PTEN status and benefit from cetuximab in the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer—results from NCIC CTG/AGITG CO.17. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20(3):744–53. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-13-0606.
Douillard JY, Oliner KS, Siena S, Tabernero J, Burkes R, Barugel M, et al. Panitumumab-FOLFOX4 treatment and RAS mutations in colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(11):1023–34. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1305275.
Rowland A, Dias MM, Wiese MD, Kichenadasse G, McKinnon RA, Karapetis CS, et al. Meta-analysis of BRAF mutation as a predictive biomarker of benefit from anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody therapy for RAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 2015;112(12):1888–94. doi:10.1038/bjc.2015.173.
Sartore-Bianchi A, Martini M, Molinari F, Veronese S, Nichelatti M, Artale S, et al. PIK3CA mutations in colorectal cancer are associated with clinical resistance to EGFR-targeted monoclonal antibodies. Cancer Res. 2009;69(5):1851–7. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-08-2466.
Saridaki Z, Tzardi M, Papadaki C, Sfakianaki M, Pega F, Kalikaki A, et al. Impact of KRAS, BRAF, PIK3CA mutations, PTEN, AREG, EREG expression and skin rash in >/= 2 line cetuximab-based therapy of colorectal cancer patients. PLoS One. 2011;6(1), e15980. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0015980.
Prenen H, De Schutter J, Jacobs B, De Roock W, Biesmans B, Claes B, et al. PIK3CA mutations are not a major determinant of resistance to the epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor cetuximab in metastatic colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15(9):3184–8. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-08-2961.
De Roock W, Claes B, Bernasconi D, De Schutter J, Biesmans B, Fountzilas G, et al. Effects of KRAS, BRAF, NRAS, and PIK3CA mutations on the efficacy of cetuximab plus chemotherapy in chemotherapy-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer: a retrospective consortium analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11(8):753–62. doi:10.1016/s1470-2045(10)70130-3.
Yang ZY, Wu XY, Huang YF, Di MY, Zheng DY, Chen JZ, et al. Promising biomarkers for predicting the outcomes of patients with KRAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer treated with anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibodies: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Int J Cancer. 2013;133(8):1914–25. doi:10.1002/ijc.28153.
Huang L, Liu Z, Deng D, Tan A, Liao M, Mo Z, et al. Anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody-based therapy for metastatic colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis of the effect of PIK3CA mutations in KRAS wild-type patients. Arch Med Sci. 2014;10(1):1–9. doi:10.5114/aoms.2014.40728.
Llovet P, Sastre J, Ortega JS, Bando I, Ferrer M, Garcia-Alfonso P, et al. Prognostic value of BRAF, PI3K, PTEN, EGFR copy number, amphiregulin and epiregulin status in patients with KRAS codon 12 wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer receiving first-line chemotherapy with anti-EGFR therapy. Mol Diagn Ther. 2015. doi:10.1007/s40291-015-0165-0.
Sartore-Bianchi A, Di Nicolantonio F, Nichelatti M, Molinari F, De Dosso S, Saletti P, et al. Multi-determinants analysis of molecular alterations for predicting clinical benefit to EGFR-targeted monoclonal antibodies in colorectal cancer. PLoS One. 2009;4(10), e7287. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0007287.
Kishiki T, Ohnishi H, Masaki T, Ohtsuka K, Ohkura Y, Furuse J, et al. Impact of genetic profiles on the efficacy of anti-EGFR antibodies in metastatic colorectal cancer with KRAS mutation. Oncol Rep. 2014;32(1):57–64. doi:10.3892/or.2014.3179.
Zanella ER, Galimi F, Sassi F, Migliardi G, Cottino F, Leto SM, et al. IGF2 is an actionable target that identifies a distinct subpopulation of colorectal cancer patients with marginal response to anti-EGFR therapies. Sci Transl Med. 2015;7(272):272ra12. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3010445.
Yonesaka K, Satoh T, Ueda S, Yoshida T, Takeda M, Shimizu T, et al. Circulating hepatocyte growth factor is correlated with resistance to cetuximab in metastatic colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res. 2015;35(3):1683–9.
Cappuzzo F, Varella-Garcia M, Finocchiaro G, Skokan M, Gajapathy S, Carnaghi C, et al. Primary resistance to cetuximab therapy in EGFR FISH-positive colorectal cancer patients. Br J Cancer. 2008;99(1):83–9. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6604439.
Inno A, Di Salvatore M, Cenci T, Martini M, Orlandi A, Strippoli A, et al. Is there a role for IGF1R and c-MET pathways in resistance to cetuximab in metastatic colorectal cancer? Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2011;10(4):325–32. doi:10.1016/j.clcc.2011.03.028.
Kishiki T, Ohnishi H, Masaki T, Ohtsuka K, Ohkura Y, Furuse J, et al. Overexpression of MET is a new predictive marker for anti-EGFR therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer with wild-type KRAS. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2014;73(4):749–57. doi:10.1007/s00280-014-2401-4.
Bardelli A, Corso S, Bertotti A, Hobor S, Valtorta E, Siravegna G, et al. Amplification of the MET receptor drives resistance to anti-EGFR therapies in colorectal cancer. Cancer Discov. 2013;3(6):658–73. doi:10.1158/2159-8290.cd-12-0558.
Liska D, Chen CT, Bachleitner-Hofmann T, Christensen JG, Weiser MR. HGF rescues colorectal cancer cells from EGFR inhibition via MET activation. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17(3):472–82. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-10-0568.
Mlcochova J, Faltejskova-Vychytilova P, Ferracin M, Zagatti B, Radova L, Svoboda M, et al. MicroRNA expression profiling identifies miR-31-5p/3p as associated with time to progression in wild-type RAS metastatic colorectal cancer treated with cetuximab. Oncotarget. 2015;6(36):38695–704. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.5735.
Igarashi H, Kurihara H, Mitsuhashi K, Ito M, Okuda H, Kanno S, et al. Association of microRNA-31-5p with clinical efficacy of anti-EGFR therapy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015;22(8):2640–8. doi:10.1245/s10434-014-4264-7.
Manceau G, Imbeaud S, Thiebaut R, Liebaert F, Fontaine K, Rousseau F, et al. Hsa-miR-31-3p expression is linked to progression-free survival in patients with KRAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer treated with anti-EGFR therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20(12):3338–47. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-13-2750.
Cappuzzo F, Sacconi A, Landi L, Ludovini V, Biagioni F, D’Incecco A, et al. MicroRNA signature in metastatic colorectal cancer patients treated with anti-EGFR monoclonal antibodies. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2014;13(1):37–45. doi:10.1016/j.clcc.2013.11.006.
Pichler M, Winter E, Ress AL, Bauernhofer T, Gerger A, Kiesslich T, et al. miR-181a is associated with poor clinical outcome in patients with colorectal cancer treated with EGFR inhibitor. J Clin Pathol. 2014;67(3):198–203. doi:10.1136/jclinpath-2013-201904.
Schou JV, Rossi S, Jensen BV, Nielsen DL, Pfeiffer P, Hogdall E, et al. miR-345 in metastatic colorectal cancer: a non-invasive biomarker for clinical outcome in non-KRAS mutant patients treated with 3rd line cetuximab and irinotecan. PLoS One. 2014;9(6):e99886. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0099886.
Zhou J, Lv L, Lin C, Hu G, Guo Y, Wu M, et al. Combinational treatment with microRNA133b and cetuximab has increased inhibitory effects on the growth and invasion of colorectal cancer cells by regulating EGFR. Mol Med Rep. 2015;12(4):5407–14. doi:10.3892/mmr.2015.4046.
Suto T, Yokobori T, Yajima R, Morita H, Fujii T, Yamaguchi S. MicroRNA-7 expression in colorectal cancer is associated with poor prognosis and regulates cetuximab sensitivity via EGFR regulation. Carcinogenesis. 2015;36(3):338–45. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgu242.
Lee KW, Lee SS, Kim SB, Sohn BH, Lee HS, Jang HJ, et al. Significant association of oncogene YAP1 with poor prognosis and cetuximab resistance in colorectal cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21(2):357–64. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-14-1374.
Pietrantonio F, Maggi C, Di Bartolomeo M, Facciorusso MG, Perrone F, Testi A, et al. Gain of ALK gene copy number may predict lack of benefit from anti-EGFR treatment in patients with advanced colorectal cancer and RAS-RAF-PI3KCA wild-type status. PLoS One. 2014;9(4), e92147. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0092147.
Ying HQ, Wang F, Chen XL, He BS, Pan YQ, Jie C et al. FCGR2A, FCGR3A polymorphisms and therapeutic efficacy of anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody in metastatic colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. 2015.
Liu N, Fang XD, Vadis Q. CD73 as a novel prognostic biomarker for human colorectal cancer. J Surg Oncol. 2012;106(7):918–9. doi:10.1002/jso.23159. author reply 20.
Wu XR, He XS, Chen YF, Yuan RX, Zeng Y, Lian L, et al. High expression of CD73 as a poor prognostic biomarker in human colorectal cancer. J Surg Oncol. 2012;106(2):130–7. doi:10.1002/jso.23056.
Augustine TA, Baig M, Sood A, Budagov T, Atzmon G, Mariadason JM, et al. Telomere length is a novel predictive biomarker of sensitivity to anti-EGFR therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 2015;112(2):313–8. doi:10.1038/bjc.2014.561.
Ouchi K, Takahashi S, Yamada Y, Tsuji S, Tatsuno K, Takahashi H, et al. DNA methylation status as a biomarker of anti-EGFR treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer. Cancer Sci. 2015. doi:10.1111/cas.12827.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, J., Li, S., Wang, B. et al. Potential biomarkers for anti-EGFR therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer. Tumor Biol. 37, 11645–11655 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5140-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5140-9