Abstract
Introduction
Cetuximab is a monoclonal epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-targeting antibody, used in the treatment of colon cancer. KRAS mutation status is strongly predictive of cetuximab efficacy, but more predictive factors are needed for better patient selection. PTEN is a downstream inhibitor of the EGFR pathway and has been evaluated as a predictive factor of cetuximab efficacy in colorectal cancer.
Patients and methods
Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tumor tissue samples were collected from 226 patients with advanced or metastatic colorectal cancer that had been treated with cetuximab. Clinical information was collected retrospectively from the patients’ medical records. After central evaluation, 147 cases with adequate material were eligible for further evaluation. EGFR and PTEN status was evaluated with immunohistochemistry (IHC) and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). Data were associated with cetuximab treatment outcome. Additional analysis was performed with previously published data on PIK3CA, BRAF and KRAS mutation status and EGFR ligand amphiregulin (AREG) and epiregulin intratumoral mRNA expression levels. PIK3CA mutation status and PTEN protein expression were also analyzed as a single complex parameter, to evaluate the predictive value of PI3K/PTEN axis dysfunction as one entity.
Results
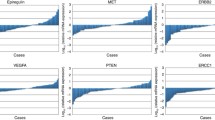
Analysis showed a borderline association of overall response rate (ORR) and time to progression (TTP) with EGFR protein overexpression by IHC (p = 0.059 and p = 0.057, respectively) and a positive association of EGFR gain by FISH (found in only five cases) with longer TTP (p = 0.026). No association was found between ORR or TTP and PTEN IHC or FISH status. Comparative analysis with previously published data showed that PTEN protein expression is associated with longer TTP in patients with wild-type (WT) KRAS (p = 0.036) and especially in the ones with elevated AREG levels (p = 0.046), as well as in patients with both KRAS and BRAF WT (p = 0.019). Patients with both PIK3CA WT and PTEN protein expression had significantly longer TTP (p = 0.010) versus all others, in the absence of BRAF and KRAS mutations, a finding which persisted in the KRAS WT/AREG high subgroup (p = 0.046).
Conclusions
In this cetuximab-treated colorectal cancer population, EGFR gain was associated with better outcome and PTEN protein expression with longer TTP in KRAS WT, KRAS WT/AREG high and KRAS/BRAF WT subpopulations. Cetuximab efficacy is greater with intact and activated EGFR signaling, without activating mutations of KRAS/BRAF and in the presence of preserved PTEN inhibitory activity upon the PI3K/AKT pathway. These results reflect a solid biological rationale and warrant further evaluation of the predictive role of PTEN in prospective studies.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bokemeyer C, Bondarenko I, Makhson A, Hartmann JT, Aparicio J, de Braud F, Donea S, Ludwig H, Schuch G, Stroh C, Loos AH, Zubel A, Koralewski P (2009) Fluorouracil, leucovorin, and oxaliplatin with and without cetuximab in the first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 27(5):663–671 Epub 2008 Dec 29
Carpenter G, Cohen S (1990) Epidermal growth factor. J Biol Clin 265:7709–7712
Chung KY, Shia J, Kemeny NE, Shah M, Schwartz GK, Tse A, Hamilton A, Pan D, Schrag D, Schwartz L, Klimstra DS, Fridman D, Kelsen DP, Saltz LB (2005) Cetuximab shows activity in colorectal cancer patients with tumors that do not express the epidermal growth factor receptor by immunohistochemistry. J Clin Oncol 23:1803–1810
Cunningham D, Humblet Y, Siena S, Khayat D, Bleiberg H, Santoro A, Bets D, Mueser M, Harstrick A, Verslype C, Chau I, Van Cutsem E (2004) Cetuximab monotherapy and cetuximab plus irinotecan in irinotecan-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 351(4):337–345
De Roock W, Claes B, Bernasconi D, De Schutter J, Biesmans B, Fountzilas G, Kalogeras KT, Kotoula V, Papamichael D, Laurent-Puig P, Penault-Llorca F, Rougier P, Vincenzi B, Santini D, Tonini G, Cappuzzo F, Frattini M, Molinari F, Saletti P, De Dosso S, Martini M, Bardelli A, Siena S, Sartore-Bianchi A, Tabernero J, Macarulla T, Di Fiore F, Gangloff AO, Ciardiello F, Pfeiffer P, Qvortrup C, Hansen TP, Van Cutsem E, Piessevaux H, Lambrechts D, Delorenzi M, Tejpar S (2010) Effects of KRAS, BRAF, NRAS, and PIK3CA mutations on the efficacy of cetuximab plus chemotherapy in chemotherapy-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer: a retrospective consortium analysis. Lancet Oncol 11(8):753–762. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(10)70130-3
Di Nicolantonio F, Martini M, Molinari F, Sartore-Bianchi A, Arena S, Saletti P, De Dosso S, Mazzucchelli L, Frattini M, Siena S, Bardelli A (2008) Wild-type BRAF is required for response to panitumumab or cetuximab in metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 26(35):5705–5712
Frattini M, Saletti P, Romagnani E, Martin V, Molinari F, Ghisletta M, Camponovo A, Etienne LL, Cavalli F, Mazzucchelli L (2007) PTEN loss of expression predicts cetuximab efficacy in metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Br J Cancer 97:1139–1145
Italiano A, Saint-Paul MC, Caroli-Bosc FX, Francois E, Bourgeon A, Benchimol D, Gugenheim J, Michiels JF (2005) Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) status in primary colorectal tumors correlates with EGFR expression in related metastatic sites: biological and clinical implications. Ann Oncol 16:1503–1507
Karapetis CS, Jonker D, Daneshmand M, Hanson JE, O’Callaghan CJ, Marginean C, Zalcberg JR, Simes J, Moore MJ, Tebbutt NC, Price TJ, Shapiro JD, Pavlakis N, Gibbs P, Van Hazel GA, Lee U, Haq R, Virk S, Tu D, Lorimer IAJ, for the NCIC Clinical Trials Group and the Australasian Gastro-Intestinal Trials Group (2013) PIK3CA, BRAF, and PTEN status and benefit from cetuximab in the Treatment of Advanced Colorectal Cancer—Results from NCIC CTG/AGITG CO.17. Published doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-0606
Khambata-Ford S, Garrett CR, Meropol NJ, Basik M, Harbison CT, Wu S, Wong TW, Huang X, Takimoto CH, Godwin AK, Tan BR, Krishnamurthi SS, Burris HA 3rd, Poplin EA, Hidalgo M, Baselga J, Clark EA, Mauro DJ (2007) Expression of epiregulin and amphiregulin and KRAS mutation status predict disease control in metastatic colorectal cancer patients treated with cetuximab. J Clin Oncol 25:3230–3237
Kononen J, Bubendorf L, Kallioniemi A, Barlund M, Schraml P, Leighton S, Torhorst J, Mihatsch MJ, Sauter G, Kallioniemi OP (1998) Tissue microarrays for high-throughput molecular profiling of tumor specimens. Nat Med 4(7):844–847
Lenz HJ, Van-Cutsem E, Khambata-Ford S, Mayer RJ, Gold P, Stella P, Mirtsching B, Cohn AL, Pipas AW, Azarnia N, Tsuchihashi Z, Mauro DJ, Rowinsky EK (2006) Multicenter phase II and translational study of cetuximab in metastatic colorectal carcinoma refractory to irinotecan, oxaliplatin and fluoropyrimidines. J Clin Oncol 24:4914–4921
Lievre A, Bachet JB, Le Corre D, Boige V, Landi B, Emile JF, Côté JF, Tomasic G, Penna C, Ducreux M, Rougier P, Penault-Llorca F, Laurent-Puig P (2005) KRAS mutation status is predictive of response to cetuximab therapy in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res 66:3992–3995
Mayer A, Takimoto M, Fritz E, Schellander G, Kofler K, Ludwig H (1993) The prognostic significance of proliferating cell nuclear antigen, epidermal growth factor receptor and mdr gene expression in colorectal cancer. Cancer 71:2454–2460
McShane LM, Altman DG, Sauerbrei W, Taube SE, Gion M, Clark GM (2006) Reporting recommendations for tumor MARKer prognostic studies (REMARK). Breast Cancer Res Treat 100(2):229–235
Mekenkamp LJ, Tol J, Dijkstra JR, de Krijger I, Vink-Borger E, Teerenstra S, Kamping E, Verwiel E, Koopman M, Meijer GA, van Krieken HJ, Kuiper R, Punt CJ, Nagtegaal ID, van Vliet S (2012) Beyond KRAS mutation status: influence of KRAS copy number status and microRNAs on clinical outcome to cetuximab in metastatic colorectal cancer patients. BMC Cancer 12(1):292
Moroni M, Veronese S, Benvenuti S, Marrapese G, Sartore-Bianchi A, Di Nicolantonio F, Gambacorta M, Siena S, Bardelli A (2005) Gene copy number of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and clinical response to anti EGFR treatment in colorectal cancer: a cohort study. Lancet Oncol 6:279–286
Nishino M, Jagannathan JP, Ramaiya NH, Van den Abbeele AD (2010) Revised RECIST guideline version 1.1: what oncologists want to know and what radiologists need to know. AJR Am J Roentgenol 195:281–289
Pentheroudakis G, Kotoula V, De Roock W, Kouvatseas G, Papakostas P, Makatsoris T, Papamichael D, Xanthakis I, Sgouros J, Televantou D, Kafiri G, Tsamandas AC, Razis E, Galani E, Bafaloukos D, Efstratiou I, Bompolaki I, Pectasides D, Pavlidis N, Tejpar S, Fountzilas G (2013) Biomarkers of benefit from cetuximab-based therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer: interaction of EGFR ligand expression with RAS/RAF, PIK3CA genotypes. BMC Cancer 13:49. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-13-49
Perren A, Weng LP, Boag AH, Ziebold U, Thakore K, Dahia PL, Komminoth P, Lees JA, Mulligan LM, Mutter GL, Eng C (1999) Immunohistochemical evidence of loss of PTEN expression in primary ductal adenocarcinomas of the breast. Am J Pathol 155:1253–1260
Perrone F, Lampis A, Orsenigo M, Di Bartolomeo M, Gevorgyan A, Losa M, Frattini M, Riva C, Andreola S, Bajetta E, Bertario L, Leo E, Pierotti MA, Pilotti S (2009) PI3KCA/PTEN deregulation contributes to impaired responses to cetuximab in metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Ann Oncol 20:84–90
Razis E, Briasoulis E, Vrettou E, Skarlos DV, Papamichael D, Kostopoulos I, Samantas E, Xanthakis I, Bobos M, Galanidi E, Bai M, Gikonti I, Koukouma A, Kafiri G, Papakostas P, Kalogeras KT, Kosmidis P, Fountzilas G (2008) Potential value of PTEN in predicting cetuximab response in colorectal cancer: an exploratory study. BMC Cancer 8:234. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-8-234
Razis E, Bobos M, Kotoula V, Eleftheraki AG, Kalofonos HP, Pavlakis K, Papakostas P, Aravantinos G, Rigakos G, Efstratiou I, Petraki K, Bafaloukos D, Kostopoulos I, Pectasides D, Kalogeras KT, Skarlos D, Fountzilas G (2011) Evaluation of the association of PIK3CA mutations and PTEN loss with efficacy of trastuzumab therapy in metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 128(2):447–456. doi:10.1007/s10549-011-1572-5
Sadanandam A, Lyssiotis CA, Homicsko K, Collisson EA, Gibb WJ, Wullschleger S, Ostos LC, Lannon WA, Grotzinger C, Del Rio M, Lhermitte B, Olshen AB, Wiedenmann B, Cantley LC, Gray JW, Hanahan D (2013) A colorectal cancer classification system that associates cellular phenotype and responses to therapy. Nat Med 19(5):619–625. doi:10.1038/nm.3175
Saltz LB, Kies M, Abbruzzesse JL, Azarnia N, Needle M (2003) The presence and intensity of the cetuximab-induced acne-like rash predicts increased survival in studies across multiple malignances. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 22(204):A817
Saltz LB, Meropol NT, Loehrer PJ Sr, Needle MN, Kopit J, Mayer RJ (2004) Phase II trial of cetuximab in patients with refractory colorectal cancer that express the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Clin Oncol 22:1201–1208
Saridaki Z, Tzardi M, Papadaki C, Sfakianaki M, Pega F, Kalikaki A, Tsakalaki E, Trypaki M, Messaritakis I, Stathopoulos E, Mavroudis D, Georgoulias V, Souglakos J (2011) Impact of KRAS, BRAF, PIK3CA mutations, PTEN, AREG, EREG expression and skin rash in ≥2 line cetuximab-based therapy of colorectal cancer patients. PLoS ONE 6(1):e15980. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0015980
Sartore-Bianchi A, Martini M, Molinari F, Veronese S, Nichelatti M, Artale S, Di Nicolantonio F, Saletti P, De Dosso S, Mazzucchelli L, Frattini M, Siena S, Bardelli A (2009) PIK3CA mutations in colorectal cancer are associated with clinical resistance to EGFR-targeted monoclonal antibodies. Cancer Res 69:1851–1857. doi:10.1158/0008-5472
Shen Y, Yang J, Xu Z, Gu DY, Chen JF (2012) Phosphatase and tensin homolog expression related to cetuximab effects in colorectal cancer patients: a meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol 18(21):2712–2718
Skacel M, Skilton B, Pettay JD, Tubbs RR (2002) Tissue microarrays: a powerful tool for high-throughput analysis of clinical specimens: a review of the method with validation data. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 10(1):1–6
Sunpaweravong P, Sunpaweravong S, Puttawibul P, Mitarnun W, Zeng C, Baron AE, Franklin W, Said S, Varella-Garcia M (2005) Epidermal growth factor receptor and cyclin D1 are independently amplified and overexpressed in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 131:111–119
Vallböhmer D, Zhang W, Gordon M, Yang DY, Yun J, Press OA, Rhodes KE, Sherrod AE, Iqbal S, Danenberg KD, Groshen S, Lenz HJ (2005) Molecular determinants of cetuximab efficacy. J Clin Oncol 23:3536–3544
Van Cutsem E, Köhne CH, Hitre E, Zaluski J, Chang Chien CR, Makhson A, D’Haens G, Pintér T, Lim R, Bodoky G, Roh JK, Folprecht G, Ruff P, Stroh C, Tejpar S, Schlichting M, Nippgen J, Rougier P (2009) Cetuximab and chemotherapy as initial treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 360(14):1408–1417
Wang ZH, Gao QY, Fang JY (2012) Loss of PTEN expression as a predictor of resistance to anti-EGFR monoclonal therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer: evidence from retrospective studies. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 69(6):1647–1655
Yoshida M, Shimura T, Sato M, Ebi M, Nakazawa T, Takeyama H, Joh TD, Mueser M, Harstrick A, Verslype C, Chau I, Van Cutsem E (2004) A novel predictive strategy by immunohistochemical analysis of four EGFR ligands in metastatic colorectal cancer treated with anti-EGFR antibodies. N Engl J Med 351(4):337–345
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Ms. Thalia Spinari for tissue collection, Ms. Dimitra Katsala for monitoring the study and Ms. Maria Moschoni for coordinating the data management. The study was supported by a Hellenic Cooperative Oncology Group grant HER_6ER/05.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest, that they have full control of all primary data and that they agree to allow the journal to review their data if requested.
Ethical standard
The translational research protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of “Papageorgiou” Hospital in Thessaloniki (Protocol # 193) and “Hygeia” Hospital in Athens, Greece, under the general title “Association of PTEN and EGFR with cetuximab response in colorectal cancer” and has therefore been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. Waiver of consent was obtained from the IRB for patients included in the study before 2005. All patients included in the study after 2005 provided written informed consent for the provision of biological material for future research studies, before receiving any treatment.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Maria Bai: Deceased.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
432_2014_1626_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Supplementary Figure 1. Percent of PTEN categories evaluated by FISH and IHC according to the line of treatment. (TIFF 81 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Razis, E., Pentheroudakis, G., Rigakos, G. et al. EGFR gene gain and PTEN protein expression are favorable prognostic factors in patients with KRAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer treated with cetuximab. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 140, 737–748 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-014-1626-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-014-1626-2