Abstract
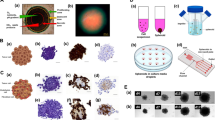
We established an in vitro 3-D model of metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) by culturing MHCC97H cells on molecular scaffolds within a rotating wall vessel bioreactor. Morphological and biochemical analyses revealed that the 3-D HCC model mirrored many clinical pathological features of HCC in vivo, including cancer cell morphology, tissue ultrastructure, protein production and secretion, glucose metabolism, tissue-specific gene expression, and apoptosis. Xenografts into livers of nude mice resulted in tumorigenesis and distant metastasis. This 3-D HCC spheroid is a promising model for HCC tumor biology, anticancer drug screening, and for the establishment of HCC animal models.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim JB. Three-dimensional tissue culture models in cancer biology. Semin Cancer Biol. 2005;15:365–77.
Wang R, Xu J, Juliette L, Castilleja A, Love J, Sung SY, et al. Three -dimensional co-culture models to study prostate cancer growth, progression, and metastasis to bone. Semin Cancer Biol. 2005;15:353–64.
Chang TT, Hughes-Fulford M. Monolayer and spheroid culture of human liver hepatocellular carcinoma cell line cells demonstrate distinct global gene expression patterns and functional phenotypes. Tissue Eng Part A. 2009;15:559–67.
Grun B, Benjamin E, Sinclair J, Timms JF, Jacobs IJ, Gayther SA, et al. Three-dimensional in vitro cell biology models of ovarian and endometrial cancer. Cell Prolif. 2009;42:219–28.
Pampaloni F, Reynaud EG, Stelzer EH. The third dimension bridges the gap between cell culture and live tissue. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:839–45.
Unsworth BR, Lelkes PI. Growing tissues in microgravity. Nat Med. 1998;4:901–7.
Navran S. The application of low shear modeled microgravity to 3-D cell biology and tissue engineering. Biotechnol Annu Rev. 2008;14:275–96.
Santamaría E, Muñoz J, Fernández-Irigoyen J, Prìeto J, Corrales FJ. Toward the discovery of new biomarkers of hepatocellular carcinoma by proteomics. Liver Int. 2007;27:163–73.
Aravalli RN, Steer CJ, Cressman EN. Molecular mechanisms of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2008;48:2047–63.
Blum HE. Hepatocellular carcinoma: therapy and prevention. World J Gastroenterol. 2005;11:7391–400.
Yang Y, Nagano H, Ota H, Morimoto O, Nakamura M, Wada H, et al. Patterns and clinicopathologic features of extrahepatic recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after curative resection. Surgery. 2007;141:196–202.
Miyoshi A, Kitajima Y, Kido S, Shimonishi T, Matsuyama S, Kitahara K, et al. Snail accelerates cancer invasion by upregulating MMP expression and is associated with poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2005;92:252–8.
Tang ZY, Ye SL, Liu YK, Qin LX, Sun HC, Ye QH, et al. A decade’s studies on metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2004;130:187–96.
Li Y, Tian B, Yang J, Zhao L, Wu X, Ye SL, et al. Stepwise metastatic human hepatocellular carcinoma cell model system with multiple metastatic potentials established through consecutive in vivo selection and studies on metastatic characteristics. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2004;130:460–8.
Yan L, Zhao-You T, Sheng-Long Y, Yin-Kun L, Jie C, Qiong X, et al. Establishment of cell clones with different metastatic potential from the metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma cell line MHCC97. World J Gastroenterol. 2001;7:630–6.
Cui JF, Liu YK, Zhang LJ, Shen HL, Song HY, Dai Z, et al. Identification of metastasis candidate proteins among HCC cell lines by comparative proteome and biological function analysis of S100A4 in metastasis in vitro. Proteomics. 2006;6:5953–61.
Tian B, Li Y, Ji XN, Chen J, Xue Q, Ye SL, et al. Basement membrane proteins play an active role in the invasive process of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells with high metastasis potential. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2005;131:80–6.
Li WC, Ye SL, Sun RX, Liu YK, Tang ZY, Kim Y, et al. Inhibition of growth and metastasis of human hepatocellular carcinoma by antisense oligonucleotide targeting signal transducer and activator of transcription3. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:7140–8.
Mueller-Klieser W. Multicellular spheroids. A review on cellular aggregates in cancer research. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1987;113:101–22.
Lopez JB, Balasegaram M, Thambyrajah V, Timor J. The value of liver function tests in hepatocellular carcinoma. Malays J Pathol. 1996;18:95–9.
Tsutsumi M, Sakamuro D, Takada A, Zang SC, Furukawa T, Taniguchi N. Detection of a unique gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase messenger RNA species closely related to the development of hepatocellular carcinoma in humans: a new candidate for early diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 1996;23:1093–7.
Weber G. Enzymology of cancer cells (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1977;296:541–51.
Sun FX, Tang ZY, Lui KD, Ye SL, Xue Q, Gao DM, et al. Establishment of a metastatic model of human hepatocellular carcinoma in nude mice via orthotopic implantation of histologically intact tissues. Int J Cancer. 1996;66:239–43.
Tian J, Tang ZY, Ye SL, Liu YK, Lin ZY, Chen J, et al. New human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell line with highly metastatic potential (MHCC97) and its expressions of the factors associated with metastasis. Br J Cancer. 1999;81:814–21.
Kenny PA, Lee GY, Myers CA, Neve RM, Semeiks JR, Spellman PT, et al. The morphologies of breast cancer cell lines in three-dimensional assays correlate with their profiles of gene expression. Mol Oncol. 2007;1:84–96.
Feder-Mengus C, Ghosh S, Reschner A, Martin I, Spagnoli GC. New dimensions in tumor immunology: what does 3D culture reveal? Trends Mol Med. 2008;14:333–40.
Bissell MJ, Radisky DC, Rizki A, Weaver VM, Petersen OW. The organizing principle: microenvironmental influences in the normal and malignant breast. Differentiation. 2002;70:537–46.
Kim JB, Stein R, O’Hare MJ. Three-dimensional in vitro tissue culture models of breast cancer—a review. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2004;85:281–91.
Yoffe B, Darlington GJ, Soriano HE, Krishnan B, Risin D, Pellis NR, et al. Cultures of human liver cells in simulated microgravity environment. Adv Space Res. 1999;24:829–36.
Khaoustov VI, Darlington GJ, Soriano HE, Krishnan B, Risin D, Pellis NR, et al. Induction of three-dimensional assembly of human liver cells by simulated microgravity. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 1999;35:501–9.
Miyazawa M, Torii T, Toshimitsu Y, Koyama I. Effect of mechanical stress imposition on co-culture of hepatic parenchymal and nonparenchymal cells: possibility of stimulating production of regenerating factor. Transplant Proc. 2005;37:2398–401.
Miyazawa M, Torii T, Toshimitsu Y, Okada K, Koyama I. Hepatocyte dynamics in a three-dimensional rotating bioreactor. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007;22:1959–64.
Dayong Xu, Yun W, Meifu F. Studies on HepG2 growth under simulated microgravity: to establish a method for three-dimensional cultivation in vitro as a research model. Prog Biochem Biophys. 2007;34:146–53.
Arii S, Mise M, Harada T, Furutani M, Ishigami S, Niwano M, et al. Overexpression of matrix metalloproteinase 9 gene in hepatocellular carcinoma with invasive potential. Hepatology. 1996;24:316–22.
Sun JJ, Zhou XD, Liu YK, Tang ZY, Feng JX, Zhou G, et al. Invasion and metastasis of liver cancer: expression of intercellular adhesion molecule 1. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1999;125:28–34.
Hirohashi K, Yamamoto T, Uenishi T, Ogawa M, Sakabe K, Takemura S, et al. CD44 and VEGF expression in extrahepatic metastasis of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology. 2004;51:1121–3.
Osada T, Sakamoto M, Ino Y, Iwamatsu A, Matsuno Y, Muto T, et al. E-cadherin is involved in the intrahepatic metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 1996;24:1460–7.
Liu LX, Jiang HC, Liu ZH, Zhou J, Zhang WH, Zhu AL, et al. Integrin gene expression profiles of human hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2002;8:631–7.
Hayasaka A, Suzuki N, Fujimoto N, Iwama S, Fukuyama E, Kanda Y, et al. Elevated plasma levels of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (92-kd type IV collagenase/gelatinase B) in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 1996;24:1058–62.
Lin RZ, Chou LF, Chien CC, Chang HY. Dynamic analysis of hepatoma spheroid formation: roles of E-cadherin and beta1-integrin. Cell Tissue Res. 2006;324:411–22.
Islam S, Carey TE, Wolf GT, Wheelock MJ, Johnson KR. Expression of N-cadherin by human squamous carcinoma cells induces a scattered fibroblastic phenotype with disrupted cell–cell adhesion. J Cell Biol. 1996;135:1643–54.
Acknowledgement
The authors sincerely thank their colleagues Jun Chen, Ruixia Sun, and Qiong Xue for the kind help in animal experiments. This study was sponsored by grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.30772062 and No.81071902), China National High-Tech Research and Development Program (2006AA02A-308), China National Key Projects for Infectious Disease (2008ZX10002-021 and 2008ZX 10002-017), Shanghai Pujiang Program (No.08PJ140300), and Shanghai Natural Science Foundation (09ZR1406400).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jianhua Tang and Jiefeng Cui contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, J., Cui, J., Chen, R. et al. A three-dimensional cell biology model of human hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro. Tumor Biol. 32, 469–479 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-010-0140-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-010-0140-7