Abstract
Background
Megalobrama is economically one of the most important freshwater fish genera in China. However, phylogenetic relationships among M. amblycephala, M. skolkovii, M. hoffmanni and M. pellegrini remain unresolved.
Objective
To explore the genetic diversity and phylogenetic relationship of Megalobrama populations belonging to all four species.
Methods
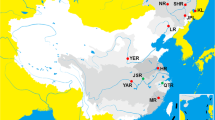
The concatenated sequences of mitochondrial cytochrome b (Cytb) and control region (CR) were used to analyze the genetic variation, genetic differentiation and population expansion of 15 Megalobrama populations.
Results
The study showed that haplotype diversity and nucleotide diversity of M. hoffmanni and M. skolkovii were high, and that M. hoffmanni was the most genetically divergent of the four species. Haplotype network analysis revealed that M. hoffmanni and M. amblycephala formed a monophyletic group each, while M. skolkovii and M. pellegrini clustered together. There was a high genetic differentiation among the four Megalobrama species, and genetic distance among populations was not affected by geographical distance. Additionally, the results indicated that there was gene flow between the Liangzi Lake (LZL) population and Jinsha River Reservoir (JS) population. Also, Zhaoqing (ZQ) population of M. hoffmanni might have experienced a population expansion.
Conclusion
Our study verifies genetic diversity and differentiation of Megalobrama populations, and these findings will represent a significant contribution to the conservation and utilization of germplasm resources of Megalobrama.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al Salameen F, Habibi N, Kumar V, Al Amad S, Dashti J, Talebi L, Al Doaij B (2018) Genetic diversity and population structure of Haloxylon salicornicum moq. in Kuwait by ISSR markers. PLoS ONE 13:e0207369. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0207369
Chen W, Schmidt BV, He S (2018) The potential colonization histories of Opsariichthys bidens (Cyprinidae) in China using Bayesian binary MCMC analysis. Gene 676:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2018.07.019
Chen J, Guo J, Wang ZQ, Wang WM (2020a) Morphological variation among the four Megalobrama species inferred by X-ray photography. Aquac Res 51:3999–4010. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.14743
Chen W, Li C, Chen F, Li Y, Yang J, Li J, Li X (2020b) Phylogeographic analyses of a migratory freshwater fish (Megalobrama terminalis) reveal a shallow genetic structure and pronounced effects of sea-level changes. Gene 737:144478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2020.144478
Cossu P, Scarpa F, Sanna D, Lai T, Dedola GL, Curini-Galletti M, Mura L, Fois N, Casu M (2019) Influence of genetic drift on patterns of genetic variation: The footprint of aquaculture practices in Sparus aurata (Teleostei: Sparidae). Mol Ecol 28:3012–3024. https://doi.org/10.1111/mec.15134
De Lafontaine G, Napier JD, Petit RJ, Hu FS (2018) Invoking adaptation to decipher the genetic legacy of past climate change. Ecology 99:1530–1546. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecy.2382
Diwedi J, Singh AW, Ahlawat S, Sharma R, Arora R, Sharma H, Raja KN, Verma NK, Tantia MS (2020) Comprehensive analysis of mitochondrial DNA based genetic diversity in Indian goats. Gene 756:144910. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2020.144910
Du R, Zhang D, Wang Y, Wang W, Gao Z (2013) Cross-species amplification of microsatellites in genera Megalobrama and Parabramis. J Genet 92:e106–e109. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-013-0308-1
Du M, Yin SW, Niu BZ (2016) Phylogenetic relationships of twenty Gymnothorax species based on cytochrome b sequence data. Genet Mol Res 15:gmr8157. https://doi.org/10.4238/gmr.15028157
Excoffier L, Lischer HE (2010) Arlequin suite ver 3.5: a new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol Ecol Resour 10:564–567. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-0998.2010.02847.x
Farias IP, Ortí G, Sampaio I, Schneider H, Meyer A (2001) The cytochrome b gene as a phylogenetic marker: the limits of resolution for analyzing relationships among cichlid fishes. J Mol Evol 53:89–103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002390010197
García G, Ríos N, Gutiérrez V, Varela JG, Bouza Fernández C, Pardo BG, Portela PM (2014) Promiscuous speciation with gene flow in silverside fish genus Odontesthes (Atheriniformes, Atherinopsidae) from south western Atlantic Ocean basins. PLoS ONE 9:e104659. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0104659
Güler A, Karakoç E, Gökdere G, Doğaç E, Taşkin V (2019) Genetic structure of Mediterranean fruit fly (Diptera: Tephritidae) populations from Turkey revealed by mitochondrial DNA markers. J Genet 98:51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-019-1106-1
Haidar M, Alsaleh H, Haddrill PR (2020) Population genetics of 30 insertion/deletion polymorphisms in the Kuwaiti population. Int J Legal Med 134:985–986. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-019-02180-4
He SP, Liu HZ, Chen YY, Masayuki K, Tsuneo N, Zhong Y (2004) Molecular phylogenetic relationships of Eastern Asian Cyprinidae (Pisces: Cypriniformes) inferred from cytochrome b sequences. Sci China Ser C 47:130–138 (in Chinese, with abstract in English)
Hu X, Luan P, Cao C, Li C, Jia Z, Ge Y, Shang M, Wang S, Meng Z, Tong J, Shi L (2019) Characterization of the mitochondrial genome of Megalobrama terminalis in the Heilong River and a clearer phylogeny of the genus Megalobrama. Sci Rep 9:8509. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-44721-2
Islam MN, Sultana S, Alam MJ (2020) Sequencing and annotation of the complete mitochondrial genome of a threatened labeonine fish. Cirrhinus Reba Genomics Inform 18:e32. https://doi.org/10.5808/GI.2020.18.3.e32
Jondeung A, Karinthanyakit W (2016) Mitochondrial DNA control region of three mackerels, genus Rastrelliger: structure, molecular diversity and phylogenetic relationship. Mitochondrial DNA A DNA Mapp Seq Anal 27:2395–2400. https://doi.org/10.3109/19401736.2015.1028047
Karaiskou N, Gkagkavouzis K, Minoudi S, Botskaris D, Markou K, Kalafatakis S, Antonopoulou E, Triantafyllidis A (2020) Genetic structure and divergence of tench Tinca tinca European populations. J Fish Biol 97:930–934. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfb.14448
Lai R, Zhang X, Li Y, Wu J, Yang D, Wang W (2014) Comparison of mitochondrial genomes of the genus Megalobrama and their phylogenetic analysis. J Fish China 38:1–14 (in Chinese, with abstract in English)
Lei DJ, Zhao G, Xie P, Li Y, Yuan H, Zou M, Niu JG, Ma XF (2017) Analysis of genetic diversity of Leuciscus leuciscus baicalensis using novel microsatellite markers with cross-species transferability. Genet Mol Res 16:gmr16029376. https://doi.org/10.4238/gmr16029376
Leigh J, Bryant D (2015) PopART: full-feature software for haplotype network construction. Methods Ecol Evol 6:1110–1116. https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X.12410
Li N, Chen X, Sun D, Song N, Lin Q, Gao T (2015) Phylogeography and population structure of the red stingray, Dasyatis akajei inferred by mitochondrial control region. Mitochondrial DNA 26:505–513. https://doi.org/10.3109/19401736.2013.861423
Librado P, Rozas J (2009) DnaSP v5: a software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 25:1451–1452. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp187
Lima JS, Ballesteros-Mejia L, Lima-Ribeiro MS, Collevatti RG (2017) Climatic changes can drive the loss of genetic diversity in a Neotropical savanna tree species. Glob Chang Biol 23:4639–4650. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.13685
Liu W, Wang J, Yin DX, Yang M, Wang P, Han QS, Ma QQ, Liu JJ, Wang JX (2016) Genetic diversity and structure of the threatened species Sinopodophyllum hexandrum (Royle) Ying. Genet Mol Res 15:gmr8130. https://doi.org/10.4238/gmr.15028130
Martin SH, Möst M, Palmer WJ, Salazar C, McMillan WO, Jiggins FM, Jiggins CD (2016) Natural selection and genetic diversity in the butterfly Heliconius melpomene. Genetics 203:525–541. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.115.183285
Maw AA, Kawabe K, Shimogiri T, Rerkamnuaychoke W, Kawamoto Y, Masuda S, Okamoto S (2015) Genetic diversity and population structure in native chicken populations from Myanmar, Thailand and laos by using 102 indels markers. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci 28:14–19. https://doi.org/10.5713/ajas.14.0212
Onogi A, Shirai K, Amano T (2017) Investigation of genetic diversity and inbreeding in a Japanese native horse breed for suggestions on its conservation. Anim Sci J 88:1902–1910. https://doi.org/10.1111/asj.12867
Pastukh VM, Gorodnya OM, Gillespie MN, Ruchko MV (2016) Regulation of mitochondrial genome replication by hypoxia: the role of DNA oxidation in D-loop region. Free Radic Biol Med 96:78–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.04.011
Peakall R, Smouse PE (2012) GenAlEx 6.5: genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research–an update. Bioinformatics 28:2537–2539. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts460
Plytycz B, Bigaj J, Panz T, Grzmil P (2018) Asymmetrical hybridization and gene flow between Eisenia andrei and E. fetida lumbricid earthworms. PLoS ONE 13:e0204469. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0204469
Saraswat D, Lakra WS, Nautiyal P, Goswami M, Shyamakant K, Malakar A (2014) Genetic characterization of Clupisoma garua (Hamilton 1822) from six Indian populations using mtDNA cytochrome b gene. Mitochondrial DNA 25:70–77. https://doi.org/10.3109/19401736.2013.782014
Sbisà E, Tanzariello F, Reyes A, Pesole G, Saccone C (1997) Mammalian mitochondrial D-loop region structural analysis: identification of new conserved sequences and their functional and evolutionary implications. Gene 205:125–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0378-1119(97)00404-6
Sun W, Dong H, Gao YB, Su QF, Qian HT, Bai HY, Zhang ZT, Cong B (2015) Genetic variation and geographic differentiation among populations of the nonmigratory agricultural pest Oedaleus infernalis (Orthoptera: Acridoidea) in China. J Insect Sci 15:150. https://doi.org/10.1093/jisesa/iev132
Swofford DL (2003) PAUP*. phylogenetic analysis using parsimony (*and other methods). Version 4. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst197
Tang Q, Liu H, Mayden R, Xiong B (2006) Comparison of evolutionary rates in the mitochondrial DNA cytochrome b gene and control region and their implications for phylogeny of the Cobitoidea (Teleostei: Cypriniformes). Mol Phylogenet Evol 39:347–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2005.08.007
Tibihika PD, Curto M, Alemayehu E, Waidbacher H, Masembe C, Akoll P, Meimberg H (2020) Molecular genetic diversity and differentiation of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus, L. 1758) in East African natural and stocked populations. BMC Evol Biol 20:16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12862-020-1583-0
Xie N, Liu XY, Feng XY, Guo SR (2012) Sequences analysis on mitochondrial Cytochrome b gene fragment of Megalobram spp. Mod Agric Sci Technol 1:290–292 (in Chinese, with abstract in English)
Yang C, Zhu EJ, He QJ, Yi CH, Wang XB, Hu SJ, Wei SJ (2020) Strong genetic differentiation among populations of Cheirotonus gestroi (Coleoptera: Euchiridae) in its native area sheds lights on species conservation. Mitochondrial DNA A DNA Mapp Seq Anal 31:108–119. https://doi.org/10.1080/24701394.2020.1741565
Zhou A, Tian P, Li Z, Li X, Tan X, Zhang Z, Qiu L, He H, Ding W, Li Y (2020) Genetic diversity and differentiation of populations of Chlorops oryzae (Diptera, Chloropidae). BMC Ecol 20:22. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12898-020-00293-8
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31772901) and the Modern Agriculture Industry Technology System Construction Projects of China entitled Staple Freshwater Fishes Industry Technology System (No. CARS-45-08).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
W.M.W. conceived the study and designed the project. J.C. contributed to collecting samples, analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript. W.M.W. modified the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Wang, W. Genetic diversity and genetic differentiation of Megalobrama populations inferred by mitochondrial markers. Genes Genom 43, 1119–1132 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-021-01126-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-021-01126-8