Abstract
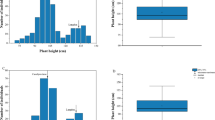
Semi-dwarfism is an agronomically important trait in breeding for stable high yields and for resistance to damage by wind and rain (lodging resistance). Many QTLs and genes causing dwarf phenotype have been found in maize. However, because of the yield loss associated with these QTLs and genes, they have been difficult to use in breeding for dwarf stature in maize. Therefore, it is important to find the new dwarfing genes or materials without undesirable characters. The objectives of this study were: (1) to figure out the inheritance of semi-dwarfism in mutants; (2) mapping dwarfing gene or QTL. Maize inbred lines ‘18599’ and ‘DM173’, which is the dwarf mutant derived from the maize inbred line ‘173’ through 60Co-γ ray irradiation. F2 and BC1F1 population were used for genetic analysis. Whole genome resequencing-based technology (QTL-seq) were performed to map dwarfing gene and figured out the SNP markers in predicted region using dwarf bulk and tall bulk from F2 population. Based on the polymorphic SNP markers from QTL-seq, we were fine-mapping the dwarfing gene using F2 population. In F2 population, 398 were dwarf plants and 135 were tall plants. Results of χ2 tests indicated that the ratio of dwarf plants to tall plants was fitted to 3:1 ratio. Furthermore, the χ2 tests of BC1F1 population showed that the ratio was fitted to 1:1 ratio. Based on QTL-seq, the dwarfing gene was located at the region from 111.07 to 124.56 Mb of chromosome 9, and we named it rht-DM. Using traditional QTL mapping with SNP markers, the rht-DM was narrowed down to 400 kb region between SNP-21 and SNP-24. The two SNPs were located at 0.43 and 0.11 cM. Segregation analysis of F2 and BC1F1 indicated that the dwarfing gene was likely a dominant gene. This dwarfing gene was located in the region between 115.02 and 115.42 Mb on chromosome 9.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe A, Kosugi S, Yoshida K, Natsume S, Takagi H, Kanzaki H, Matsumura H, Yoshida K, Mitsuoka C, Tamiru M, Innan H, Cano L, Kamoun S, Terauchi R (2012) Genome sequencing reveals agronomically important loci in rice using MutMap. Nat Biotech 30(2):174–178
Cao Y, Wang G, Wang S, Wei Y, Lu J, Xie Y, Dai J (2000) Construction of a genetic map and location of quantitative trait loci for dwarf trait in maize by RFLP markers. Chin Sci Bull 45(3):247–250
Das S, Upadhyaya HD, Bajaj D, Kujur A, Badoni S, Laxmi; Kumar V, Tripathi S, Gowda CLL, Sharma S, Singh S, Tyagi AK, Parida SK (2015) Deploying QTL-seq for rapid delineation of a potential candidate gene underlying major trait-associated QTL in chickpea. DNA Res 22(3):193–203
Das S, Singh M, Srivastava R, Bajaj D, Saxena MS, Rana JC, Bansal KC, Tyagi AK, Parida SK (2016) mQTL-seq delineates functionally relevant candidate gene harbouring a major QTL regulating pod number in chickpea. DNA Res 23(1):53–65
Doebley J, Stec A, Hubbard L (1997) The evolution of apical dominance in maize. Nature 386(6624):485
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1990) Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 12:13–15
Fekih R, Takagi H, Tamiru M, Abe A, Natsume S, Yaegashi H, Sharma S, Sharma S, Kanzaki H, Matsumura H, Saitoh H, Mitsuoka C, Utsushi H, Uemura A, Kanzaki E, Kosugi S, Yoshida K, Cano L, Kamoun S, Terauchi R (2013) MutMap+: genetic mapping and mutant identification without crossing in rice. PLoS One 8(7):e68529
Fujioka S, Yamane H, Spray CR, Gaskin P, Macmillan J, Phinney BO, Takahashi N (1988) Qualitative and quantitative analyses of Gibberellins in vegetative shoots of normal, dwarf-1, dwarf-2, dwarf-3, and dwarf-5 seedlings of Zea mays L.. Plant Physiol 88(4):1367–1372
Glover DV (1970) Location of a gene in maize conditioning a reduced plant stature1. Crop Sci 10(5):611–612
Harberd NP, Freeling M (1989) Genetics of dominant gibberellin-insensitive dwarfism in maize. Genetics 121(4):827–838
Johnson EC, Fischer KS, Edmeades GO, Palmer AFE (1986) Recurrent selection for reduced plant height in lowland tropical Maize1. Crop Sci 26(2):253–260
Khush GS (2001) Green revolution: the way forward. Nat Rev Genet 2(10):815–822
Kosambi DD (1943) The esitmation of map distances from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12(1):172–175
Lawit SJ, Wych HM, Xu D, Kundu S, Tomes DT (2010) Maize DELLA Proteins dwarf plant8 and dwarf plant9 as modulators of plant development. Plant Cell Physiol 51(11):1854–1868
Li H, Durbin R (2009) Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows–Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 25(14):1754–1760
Li Y, Wang T (2010) Germplasm base of maize breeding in China and formation of foundation parents. J Maize Sci 18(5):1–8
Li H, Wang Y, Li X, Gao Y, Wang Z, Zhao Y, Wang M (2011) A GA-insensitive dwarf mutant of Brassica napus L. correlated with mutation in pyrimidine box in the promoter of GID1. Mol Biol Rep 38(1):191–197
Li XP, Zhou ZJ, Ding JQ, Wu YB, Zhou B, Wang RX, Ma JL, Wang SW, Zhang XC, Xia ZL, Chen JF, Wu JY (2016) Combined linkage and association mapping reveals QTL and candidate genes for plant and ear height in maize. Front Plant Sci 7:833
Liu T, Zhang J, Wang M, Wang Z, Li G, Qu L, Wang G (2007) Expression and functional analysis of ZmDWF4, an ortholog of Arabidopsis DWF4 from maize (Zea mays L.). Plant Cell Rep 26(12):2091–2099
Lu H, Lin T, Klein J, Wang S, Qi J, Zhou Q, Sun J, Zhang Z, Weng Y, Huang S (2014) QTL-seq identifies an early flowering QTL located near flowering locus T in cucumber. Theor Appl Genet 127(7):1491–1499
Monna L, Kitazawa N, Yoshino R, Suzuki J, Masuda H, Maehara Y, Tanji M, Sato M, Nasu S, Minobe Y (2002) Positional cloning of rice semidwarfing gene, sd-1: rice “Green Revolution Gene” encodes a mutant enzyme involved in gibberellin synthesis. DNA Res 9(1):11–17
Multani DS, Briggs SP, Chamberlin MA, Blakeslee JJ, Murphy AS, Johal GS (2003) Loss of an MDR transporter in compact stalks of maize br2 and Sorghum dw3 Mutants. Science 302(5642):81–84
Neuffer MG, Coe EH, Wessler SR (1997) Mutants of maize. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring
Ogawa M, Kusano T, Koizumi N, Katsumi M, Sano H (1999) Gibberellin-responsive genes: high level of transcript accumulation in leaf sheath meristematic tissue from Zea mays L.. Plant Mol Biol 40(4):645–657
Peng J, Richards DE, Hartley NM, Murphy GP, Devos KM, Flintham JE, Beales J, Fish LJ, Worland AJ, Pelica F, Sudhakar D, Christou P, Snape JW, Gale MD, Harberd NP (1999) ‘Green revolution’ genes encode mutant gibberellin response modulators. Nature 400(6741):256–261
Qin X, Feng F, Li Y, Xu S, Siddique KHM, Liao Y (2016) Maize yield improvements in China: past trends and future directions. Plant Breed 135(2):166–176
Qiu ZG, Yang H, Yuan L, Zhang YQ, Zhang CB, Tang L, Rong TZ, Cao MJ (2015) Identificaiton and genetic analysis of a new dwarf mutant in maize. Acta Agri Boreali Sin 30(6):112–118
Salvi S, Tuberosa R (2005) To clone or not to clone plant QTLs: present and future challenges. Trends Plant Sci 10(6):297–304
Spray CR, Kobayashi M, Suzuki Y, Phinney BO, Gaskin P, MacMillan J (1996) The dwarf-1 (dt) mutant of Zea mays blocks three steps in the gibberellin-biosynthetic pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci 93(19)10515–10518
Takagi H, Abe A, Yoshida K, Kosugi S, Natsume S, Mitsuoka C, Uemura A, Utsushi H, Tamiru M, Takuno S, Innan H, Cano LM, Kamoun S, Terauchi R (2010) QTL-seq: rapid mapping of quantitative trait loci in rice by whole genome resequencing of DNA from two bulked populations. Plant J 74(1):174–83
Tao Y, Zheng J, Xu Z, Zhang X, Zhang K, Wang G (2004) Functional analysis of ZmDWF1, a maize homolog of the Arabidopsis brassinosteroids biosynthetic DWF1/DIM gene. Plant Sci 167(4):743–751
Van Ooijen J (2006) JoinMap 4, Software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps in experimental populations
Wang K, Li M, Hakonarson H (2010a) ANNOVAR: functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res 38(16):e164–e164
Wang YJ, Miao N, Shi YT, Deng DX, Bian YL (2010b) Genetic analysis of a dominant dwarf mutant in maize. Acta Agri Boreali Sin 25(5):90–93
Wang S, Basten C, Zeng Z (2012) Windows QTL Cartographer v2.5
Weng J, Xie C, Hao Z, Wang J, Liu C, Li M, Zhang D, Bai L, Zhang S, Li X (2011) Genome-wide association study identifies candidate genes that affect plant height in Chinese elite maize (Zea mays L.) inbred lines. PLoS One 6(12):e29229
Winkler RG, Helentjaris T (1995) The maize Dwarf3 gene encodes a cytochrome P450-mediated early step in Gibberellin biosynthesis. Plant Cell 7(8):1307–1317
Zheng W, Wang Y, Wang L, Ma Z, Zhao J, Wang P, Zhang L, Liu Z, Lu X (2016) Genetic mapping and molecular marker development for Pi65(t), a novel broad-spectrum resistance gene to rice blast using next-generation sequencing. Theor Appl Genet 129(5):1035–1044
Zhu XD, Xiong ZM, Min SK, Qian Q, Zeng DL, Zhang XH, YAN HH (1997) Inheritance of poly-gene controlling dwarfism of indica rice 83N1041 and its prospective value in breeding program. Acta Agri Zhejiangensis 9(2):66–70
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by funding from National Key Technology Research and Development Program of China (2016YFD0102104), the Project of Innovation Ability Improvement, Sichuan province, China (2017QNJJ-002, 2016ZYPZ-003), National Key Technology Support Program of China (2014BAD01B01-4), and Applied Basic Research Programs of Science and Technology Department, Sichuan Province, China (2016JY0071).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QC and GRY designed the experiments; QC, JS and WPD performed the experiments and analyzed the data; QC and LYX wrote the manuscript; JZ, YJ and XLX revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Q., Song, J., Du, WP. et al. Identification and genetic mapping for rht-DM, a dominant dwarfing gene in mutant semi-dwarf maize using QTL-seq approach. Genes Genom 40, 1091–1099 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-018-0716-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-018-0716-y