Abstract
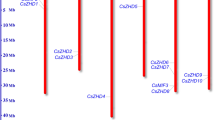
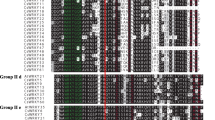
YTH domain-containing RNA-binding proteins are involved in post-transcriptional regulation and play important roles in the growth and development as well as abiotic stress responses of plants. However, YTH genes have not been previously studied in cucumber (Cucumis sativus). In this study, a total of five YTH genes (CsYTH1–CsYTH5) were identified in cucumber, which could be mapped on three out of the seven cucumber chromosomes. All CsYTH proteins had highly conserved C-terminal YTH domains, and two of them (CsYTH1 and CsYTH4) harbored extra CCCH and P/Q/N-rich domains. The phylogenesis, conserved motifs and exon–intron structure of YTH genes from cucumber, Arabidopsis and rice were also analyzed. The phylogenetically closely clustered YTHs shared similar gene structures and conserved motifs. An analysis of the cis-acting regulatory elements in the upstream region of these genes resulted in the identification of many cis-elements related to stress, hormone and development. Expression analysis based on the transcriptome data showed that some CsYTHs had development- or tissue-specific expression. In addition, their expression levels were altered under various stresses such as salt, drought, cold, and abscisic acid (ABA) treatments. These findings lay the foundation for the functional analysis of CsYTHs in the future.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Addepalli B, Hunt AG (2007) A novel endonuclease activity associated with the Arabidopsis ortholog of the 30-kDa subunit of cleavage and polyadenylation specificity factor. Nucleic Acids Res 35:4453–4463
Adhikari S, Xiao W, Zhao YL, Yang YG (2016) m6A: signaling for mRNA splicing. RNA Biol 13:756
Altunoglu YC, Baloglu P, Yer EN, Pekol S, Baloglu MC (2016) Identification and expression analysis of LEA gene family members in cucumber genome. Plant Growth Regul 80:225–241
Ambrosone A, Costa A, Leone A, Grillo S (2012) Beyond transcription: RNA-binding proteins as emerging regulators of plant response to environmental constraints. Plant Sci 182:12–18
Bailey TL, Boden M, Buske FA, Frith M, Grant CE, Clementi L, Ren J, Li WW, Noble WS (2009) MEME SUITE: tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res 37:W202–W208
Baloglu MC, Eldem V, Hajyzadeh M, Unver T (2014) Genome-wide analysis of the bZIP transcription factors in cucumber. PLoS One 9:e96014
Cannon SB, Mitra A, Baumgarten A, Young ND, May G (2004) The roles of segmental and tandem gene duplication in the evolution of large gene families in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol 4:10
Chakrabarti M, Hunt AG (2015) CPSF30 at the interface of alternative polyadenylation and cellular signaling in plants. Biomolecules 5:1151–1168
Du H, Zhao Y, He J, Zhang Y, Xi H, Liu M, Ma J, Wu L (2016) YTHDF2 destabilizes m6A-containing RNA through direct recruitment of the CCR4-NOT deadenylase complex. Nat Commun 7:12626
Eddy SR (2011) Accelerated profile HMM searches. PLoS Comput Biol 7:e1002195
Fu Y, Dominissini D, Rechavi G, He C (2014) Gene expression regulation mediated through reversible m6A RNA methylation. Nat Rev Genet 15:293–306
Harigaya Y, Tanaka H, Yamanaka S, Tanaka K, Watanabe Y, Tsutsumi C, Chikashige Y, Hiraoka Y, Yamashita A, Yamamoto M (2006) Selective elimination of messenger RNA prevents an incidence of untimely meiosis. Nature 442:45–50
Hartmann AM, Nayler O, Schwaiger FW, Obermeier A, Stamm S (1999) The interaction and colocalization of Sam68 with the splicing-associated factor YT521-B in nuclear dots is regulated by the Src family kinase p59(fyn). Mol Biol Cell 10:3909–3926
Harvey R, Dezi V, Pizzinga M, Willis AE (2017) Post-transcriptional control of gene expression following stress: the role of RNA-binding proteins. Biochem Soc Trans 45:1007–1014
Hsu PJ, Zhu Y, Ma H, Cui Y, Shi X, Luo G, Lu Z, Shi H, Dai Q, Clark M et al (2017a) YTHDC2 regulates spermatogenesis through promoting the translation of N 6-methyladenosine-modified RNA. FASEB J 31:595.10
Hsu PJ, Zhu Y, Ma H, Guo Y, Shi X, Liu Y, Qi M, Lu Z, Shi H, Wang J et al (2017b) Ythdc2 is an N 6-methyladenosine binding protein that regulates mammalian spermatogenesis. Cell Res 27:1115–1127
Hu L, Yang Y, Jiang L, Liu S (2016) The catalase gene family in cucumber: genome-wide identification and organization. Genet Mol Biol 39:408–415
Hunt AG (2014) The Arabidopsis polyadenylation factor subunit CPSF30 as conceptual link between mRNA polyadenylation and cellular signaling. Curr Opin Plant Biol 21:128–132
Imai Y, Matsuo N, Ogawa S, Tohyama M, Takagi T (1998) Cloning of a gene, YT521, for a novel RNA splicing-related protein induced by hypoxia/reoxygenation. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 53:33–40
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874
Li D, Zhang H, Hong Y, Huang L, Li X, Zhang Y, Ouyang Z, Song F (2014) Genome-wide identification, biochemical characterization, and expression analyses of the YTH domain-containing RNA-binding protein family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Mol Biol Rep 32:1169–1186
Li A, Chen YS, Ping XL, Yang X, Xiao W, Yang Y, Sun HY, Zhu Q, Baidya P, Wang X et al (2017a) Cytoplasmic m6A reader YTHDF3 promotes mRNA translation. Cell Res 27:444–447
Li X, Han H, Chen M, Yang W, Liu L, Li N, Ding X, Chu Z (2017b) Overexpression of OsDT11, which encodes a novel cysteine-rich peptide, enhances drought tolerance and increases ABA concentration in rice. Plant Mol Biol 93:21–34
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−∆∆CT method. Methods 25:402–408
Mehrotra R, Bhalothia P, Bansal P, Basantani MK, Bharti V, Mehrotra S (2014) Abscisic acid and abiotic stress tolerance—different tiers of regulation. J Plant Physiol 171:486–496
Nayler O, Hartmann AM, Stamm S (2000) The ER repeat protein YT521-B localizes to a novel subnuclear compartment. J Cell Biol 150:949–962
Nicholas KB, Nicholas HBJ, Deerfield DWI (1995) GeneDoc: analysis and visualization of genetic variation. Embnew News 4:14
Sharma S, Kaur C, Singla-Pareek SL, Sopory SK (2016) OsSRO1a Interacts with RNA binding domain-containing protein (OsRBD1) and functions in abiotic stress tolerance in yeast. Front Plant Sci 7:62
Sheth U, Parker R (2003) Decapping and decay of messenger RNA occur in cytoplasmic processing bodies. Science 300:805–808
Shi H, Wang X, Lu Z, Zhao BS, Ma H, Hsu PJ, Liu C, He C (2017) YTHDF3 facilitates translation and decay of N6-methyladenosine-modified RNA. Cell Res 27:315–328
Sievers F, Wilm A, Dineen D, Gibson TJ, Karplus K, Li W, Lopez R, McWilliam H, Remmert M, Soding J et al (2011) Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol Syst Biol 7:539
Stoilov P, Rafalska I, Stamm S (2002) YTH: a new domain in nuclear proteins. Trends Biochem Sci 27:495–497
Vishwakarma K, Upadhyay N, Kumar N, Yadav G, Singh J, Mishra RK, Kumar V, Verma R, Upadhyay RG, Pandey M et al (2017) Abscisic acid signaling and abiotic stress tolerance in plants: a review on current knowledge and future prospects. Front Plant Sci 8:161
Wang N, Yue Z, Liang D, Ma F (2014a) Genome-wide identification of members in the YTH domain-containing RNA-binding protein family in apple and expression analysis of their responsiveness to senescence and abiotic stresses. Gene 538:292–305
Wang X, Lu Z, Gomez A, Hon GC, Yue Y, Han D, Fu Y, Parisien M, Dai Q, Jia G et al (2014b) N 6-methyladenosine-dependent regulation of messenger RNA stability. Nature 505:117–120
Wang J, Pan C, Wang Y, Ye L, Wu J, Chen L, Zou T, Lu G (2015) Genome-wide identification of MAPK, MAPKK, and MAPKKK gene families and transcriptional profiling analysis during development and stress response in cucumber. BMC Genom 16:386
Wang N, Guo T, Sun X, Jia X, Wang P, Shao Y, Liang B, Gong X, Ma F (2017a) Functions of two Malus hupehensis (Pamp.) Rehd. YTPs (MhYTP1 and MhYTP2) in biotic- and abiotic-stress responses. Plant Sci 261:18–27
Wang N, Guo T, Wang P, Sun X, Shao Y, Jia X, Liang B, Gong X, Ma F (2017b) MhYTP1 and MhYTP2 from apple confer tolerance to multiple abiotic stresses in Arabidopsis thaliana. Front Plant Sci 8:1367
Wu B, Xu J, Su S, Liu H, Gan J, Ma J (2017) Structural insights into the specific recognition of DSR by the YTH domain containing protein Mmi1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 491:310–316
Xiao W, Adhikari S, Dahal U, Chen YS, Hao YJ, Sun BF, Sun HY, Li A, Ping XL, Lai WY et al (2016) Nuclear m6A reader YTHDC1 regulates mRNA splicing. Mol Cell 61:507–519
Xu C, Wang X, Liu K, Roundtree IA, Tempel W, Li Y, Lu Z, He C, Min J (2014) Structural basis for selective binding of m6A RNA by the YTHDC1 YTH domain. Nat Chem Biol 10:927–929
Yang Y, Sun BF, Xiao W, Yang X, Sun HY, Zhao YL, Yang YG (2015) Dynamic m6A modification and its emerging regulatory role in mRNA splicing. Sci Bull 60:21–32
Zhang J, Addepalli B, Yun KY, Hunt AG, Xu R, Rao S, Li QQ, Falcone DL (2008) A polyadenylation factor subunit implicated in regulating oxidative signaling in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS One 3:e2410
Zhang Z, Theler D, Kaminska KH, Hiller M, de la Grange P, Pudimat R, Rafalska I, Heinrich B, Bujnicki JM, Allain FH et al (2010) The YTH domain is a novel RNA binding domain. J Biol Chem 285:14701–14710
Zhou Y, He P, Xu Y, Liu Q, Yang Y, Liu S (2017a) Overexpression of CsLEA11, a Y3SK2-type dehydrin gene from cucumber (Cucumis sativus), enhances tolerance to heat and cold in Escherichia coli. AMB Express 7:182
Zhou Y, Hu L, Wu H, Jiang L, Liu S (2017b) Genome-wide identification and transcriptional expression analysis of cucumber superoxide dismutase (SOD) family in response to various abiotic stresses. Int J Genomics 2017:7243973
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the Key Project of Youth Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province (20171ACB21025), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31460522 and 31660578).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Yong Zhou declares that he has no conflict of interest. Lifang Hu declares that she has no conflict of interest. Lunwei Jiang declares that he has no conflict of interest. Shiqiang Liu declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human subjects or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Yong Zhou and Lifang Hu contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Y., Hu, L., Jiang, L. et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of YTH domain-containing RNA-binding protein family in cucumber (Cucumis sativus). Genes Genom 40, 579–589 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-018-0659-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-018-0659-3