Abstract
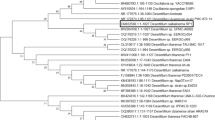
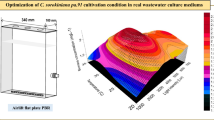
the research aim of this study was to characterize an isolated native strain of Chlorella sp. ACUF_802, well adapted to a high nitrate concentration environment and to investigate its potential to nitrate and phosphate removal from industrial wastewaters with the minimal addition of chemical reagents and energy. The isolated strain was identified and evaluated for its capability to support biomass growth and nutrient removal from synthetic wastewater in batch tests using different concentrations of carbon and nitrogen, different carbon sources and N:P ratios. The strain was isolated via the plating method from the settler of a pilot scale moving bed biofilm reactor performing a nitrification process. The strain was identified using molecular analysis with rDNA primers. Using sodium bicarbonate as carbon source, the batch productivity (71.43 mg L−1 day−1) of the strain Chlorella sp. ACUF_802 was calculated with a logistic model and compared to the values reported in the literature. Assays on the effect of the N:P ratio indicated that the productivity was increased 36% when the N:P ratio was close to 1 (111.96 mg L−1 day−1), but for a complete phosphorus removal a 5:1 N:P ratio with nitrate concentrations ≤125 mg∙L−1 is recommended. The isolated microalgae strain Chlorella sp. ACUF_802 showed versatility to grow in the synthetic industrial wastewaters tested and can be considered as an appropriate organism for nitrogen removal from industrial wastewaters in the presence of an organic or inorganic carbon source.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Raouf N, Al-Homaidan AA, Ibraheem IBM (2012) Microalgae and wastewater treatment. Saudi J Biol Sci 19:257–275
Alachiotis N, Vogiatzi E, Pavlidis P, Stamatakis A (2013) ChromatoGate: a tool for detecting base mis-calls in multiple sequence alignments by semi-automatic chromatogram inspection. Comput Struct Biotechnol J 6(7). https://doi.org/10.5936/csbj.201303001
Ammary B (2004) Nutrients requirements in biological industrial wastewater treatment. Afr J Biotechnol 3(4):236–238
APHA (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 21st edn. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC 1220 pp
Arbib Z, Ruiz J, Álvarez-Díaz P, Garrido C, Barragan J, Perales JA (2013) Photobiotreatment: influence of nitrogen and phosphorus ratio in wastewater on growth kinetics of Scenedesmus obliquus. Int J Phytoremediation 15:774–788
Arbib Z, Ruiz J, Álvarez-Díaz P, Garrido-Pérez C, Perales JA (2014) Capability of different microalgae species for phytoremediation processes: wastewater tertiary treatment, CO2 bio-fixation and low cost biofuels production. Water Res 49:465–474
Battah MG, El-Sayed AB, El-Sayed EW (2013) Growth of the green alga Chlorella vulgaris as affected by different carbon sources. Life Sci J10(1):2075–2081
Boratyn GM, Camacho C, Cooper PS, Coulouris G, Fong A, Ma N, Madden TL, Matten WT, McGinnis SD, Merezhuk Y, Raytselis Y, Sayers EW, Tao T, Ye J, Zaretskaya I (2013) BLAST: a more efficient report with usability improvements. Nucleic Acids Res 41:W29–W33
Bumbak F, Cook S, Zachleder V (2011) Best practices in heterotrophic high-cell-density microalgal processes: achievements, potential and possible limitations. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 91:31–46
Cai T, Park SY, Li Y (2013) Nutrient recovery from wastewater streams by microalgae: status and prospects. Renew Sust Energ Rev 19:360–369
Cerón García M, García Camacho F, Sánchez Mirón A, Fernández Sevilla JM, Chisti Y, Molina Grima E (2006) Mixotrophic production of marine microalga Phaeodactylum tricornutum on various carbon sources. J Microbiol Biotechnol 16(5):689–694
Chi Z, Xie Y, Elloy F, Zheng Y, Hu Y, Chen S (2013) Bicarbonate-based integrated carbon capture and algae production system with alkalihalophilic cyanobacterium. Bioresour Technol 133:513–521
Chinnasamy S, Bhatnagar A, Hunt RW, Das KC (2010) Microalgae cultivation in a wastewater dominated by carpet mill effluents for biofuel applications. Bioresour Technol 101:3097–3105
Craggs R, Sutherland D, Campbell H (2005) Hectare-scale demonstration of high rate algal ponds for enhanced wastewater treatment and biofuel production. J Appl Phycol 24:329–337
Da Silva A, Lourenco SO, Chaloub RM (2009) Effects of nitrogen starvation on the photosynthetic physiology of a tropical marine microalga Rhodomonas sp. (Cryptophyceae). Aquat Bot 91:291–297
De la Noüe J, Laliberete G, Proulx D (1992) Algae and wastewater. J Appl Phycol 4:247–254
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1990) Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 12:13–15
Gani P, Mohamed Sunar N, Matias-Peralta H, Abdul Latiff AA, Mohamad Fuzi SF (2017) Growth of microalgae Botryococcus sp. in domestic wastewater and application of statistical analysis for the optimization of flocculation using alum and chitosan. Prep Biochem Biotechnol 47(4):333–341
Gargano I, Olivieri G, Andreozzi R, Marotta R, Marzocchella A, Pollio A (2016) Biodiesel production in outdoor cultures of Scenedesmus vacuolatus. Chem Eng Trans 49:397–402
Ge S, Champagne P (2016) Nutrient removal, microalgal biomass growth, harvesting and lipid yield in response to centrate wastewater loadings. Water Res 88:604–612
Gong H, Lun S (1996) The kinetics of lysine batch fermentation. Chin J Biotechnol 12:219–225
Gong Q, Feng Y, Knag L, Luo M, Yang J (2014) Effects of light and pH on cell density of Chlorella vulgaris. Energy Procedia 61:2012–2015
Gonzalez LE, Canizares RO, Baena S (1997) Efficiency of ammonia and phosphorus removal from a Colombian agroindustrial wastewater by the microalgae Chlorella vulgaris and Scenedesmus dimorphus. Bioresour Technol 60:259–262
Grobbelaar JU (2007) Photosynthetic characteristics of Spirulina platensis grown in commercial-scale open outdoor raceway ponds: what do the organisms tell us? J Appl Phycol 19:591–598
Gupta PL, Choi HJ, Lee SM (2016) Enhanced nutrient removal from municipal wastewater assisted by mixotrophic microalgal cultivation using glycerol. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:10114–10123
Heeg JS, Wolf M (2015) ITS2 and 18S rDNA sequence-structure phylogeny of Chlorella and allies (Chlorophyta, Trebouxiophyceae, Chlorellaceae). Plant Gene 4:20–28
Hongyang S, Yalei Z, Chunmin Z, Xuefei Z, Jinpeng L (2011) Cultivation of Chlorella pyrenoidosa in soybean processing wastewater. Bioresour Technol 102:9884–9890
Ibisch R, Austnes K, Borchardt D, Boteler B, Leujak W, Lukat E, Rouillard J, Schmedtje U, Solheim AL, Westphal K (2016) European assessment of eutrophication abatement measures across land-based sources, inland, coastal and marine waters. European Topic Centre on Inland, Coastal and Marine Waters (ETC-iCM), UFZ, Magdeburg
Issa AA, Shaieb FA, Al-Sefat RM (2015) Role of cloacal algae in the treatment of wastewater and their biotechnological applications. J Biosci Bioeng 1(3):48–56
Jamaian SS, Bakeri NM, Sunar NM, Gani P (2017) A Verhulst model for microalgae Botryococcus sp. growth and nutrient removal in wastewater. AIP Conf Proc 1870(1). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4995886
Ji F, Wang YK, Li G, Zhou YG, Dong RJ (2015) Isolation of microalgae with growth restriction and nutrient removal from alkaline wastewater. Int J Agric Biol Eng 8(6):62–68
Klausmeier CA, Litchman E, Daufresne T, Levin SA (2004) Optimal nitrogen-to-phosphorus stoichiometry of phytoplankton. Nature 429:171–174
Kobayashi N, Noel EA, Barnes A, Watson A, Rosenberg JN, Erickson G, Oyler GA (2013) Characterization of three Chlorella sorokiniana strains in anaerobic digested effluent from cattle manure. Bioresour Technol 150:377–386
Kong QX, Li L, Martinez B, Chen P, Ruan R (2010) Culture of microalgae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii in wastewater for biomass feedstock production. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 160(1):9–18
Krienitz L, Hegewald EH, Hepperle D, Huss VAR, Rohr T, Wolf M (2004) Phylogenetic relationship of Chlorella and Parachlorella gen. nov. (Chlorophyta, Trebouxiophyceae). Phycologia 43:529–542
Li X, Hu HY, Gan K, Sun YX (2010) Effects of different nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations on the growth, nutrient uptake, and lipid accumulation of a freshwater microalga Scenedesmus sp. Bioresour Technol 101:5494–5500
Li Y, Chen Y, Chen P, Min M, Zhou W, Martinez B, Zhu J, Ruan R (2011) Characterization of a microalga Chlorella sp. well adapted to highly concentrated municipal wastewater for nutrient removal and biodiesel production. Bioresour Technol 102:5138–5144
Li C, Yang H, Xia X, Li Y, Chen L, Zhang M, Zhang L (2013) High efficient treatment of citric acid effluent by Chlorella vulgaris and potential biomass utilization. Bioresour Technol 127:248–255
Liang Y, Sarkany N, Cui Y (2009) Biomass and lipid productivities of Chlorella vulgaris under autotrophic, heterotrophic and mixotrophic growth conditions. Biotechnol Lett 31(7):1043–1049
Lin L, Chan GYS, Jiang BL, Lan CY (2007) Use of ammoniacal nitrogen tolerant microalgae in landfill leachate treatment. Waste Manag 27:1376–1382
Mallick N (2002) Biotechnological potential of immobilized algae for wastewater N, P and metal removal: a review. Biometals 15:377–390
Markou G, Vandamme D, Muylaert K (2014) Microalgal and cyanobacterial cultivation: the supply of nutrients. Water Res 65:186–202
Masojídek J, Torzillo G (2008) Mass cultivation of freshwater microalgae. In: Jørgensen SE and Fath BD (eds) Encyclopedia of ecology. Academic Press, pp 2226–2235
Mata TM, Martins AA, Caetano NS (2010) Microalgae for biodiesel production and other applications: a review. Renew Sust Energ Rev 14:217–232
Mirzaie M, Kalbasi M, Mousavi SM, Ghobadian B (2016) Investigation of mixotrophic, heterotrophic, and autotrophic growth of Chlorella vulgaris under agricultural waste medium. Prep Biochem Biotechnol 46(2):150–156
Moheimani NR, Borowitzka MA, Isdepsky A, FonSing S (2013) Standard methods for measuring growth of algae and their composition. In: Borowitzka MA, Moheimani NR (eds) Algae for biofuels and energy. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 265–284
Nichols H, Bold H (1965) Growth media. In: JR S (ed) Hand B. Physiol. Methods. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 7–24
Nigam S, Rai MP, Sharma R (2011) Effect if nitrogen on growth and lipid content of Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Am J Biochem Biotechnol 7(3):126–131
Okonechnikov K, Golosova O, Fursov M (2012) UGENE team Unipro UGENE: a unified bioinformatics toolkit. Bioinformatics 28:1166–1167
Oswald WJ, Gotaas HB, Golueke CG, Kellen WR (1957) Algae in wastewater treatment. Sewage Ind Waste 29:437–455
Park JBK, Craggs RJ, Shilton AN (2011) Wastewater treatment high rate algal ponds for biofuel production. Bioresour Technol 102(1):35–42
Pérez-Garcia O, Bashan Y (2015) Microalgal heterotrophic and mixotrophic culturing for bio-refining: from metabolic routes to techno-economics. Prokop et al. (eds.) Algal biorefineries, Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-20200-6
Pérez-Garcia O, Escalante FM, de-Bashan LE, Bashan Y (2011) Heterotrophic cultures of microalgae: metabolism and potential products. Water Res 45(1):11–36
Redfield AC (1958) The biological control of chemical factors in the environment. Am Sci 46:205–211
Renuka N, Sood A, Ratha SK, Prasanna R, Ahluwalia AS (2013) Evaluation of microalgal consortia for treatment of primary treated sewage effluent and biomass production. J Appl Phycol 25:1529–1537
Renuka N, Sood A, Prasanna R, Ahluwalia AS (2015) Phycoremediation of wastewaters: a synergistic approach using microalgae for bioremediation and biomass generation. Int J Environ Sci Technol 12:1443–1460
Richmond A (2004) Handbook of microalgal culture: Biotechnol. and Appl. Phycol. Wiley-Blackwell, Oxford
Rindi F (2011) Terrestrial green algae: systematics, biogeography and expected responses to climate change. In: Hodkinson TR, Jones MB, Waldren S, Parnell JAN (eds) Climate change, ecology and systematics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 201–227
Ruiz J, Álvarez P, Arbib Z, Garrido C, Barragán J, Perales JA (2011) Effect of nitrogen and phosphorus concentration on their removal kinetic in treated urban wastewater by Chlorella vulgaris. Int J Phytoremediation 13(9):884–896
Sharma NK, Rai AK (2010) Biodiversity and biogeography of microalgae: progress and pitfalls. Environ Rev 19:1–15
Singh M, Reynolds DL, Das KC (2011) Microalgal system for treatment of effluent from poultry litter anaerobic digestion. Bioresour Technol 102:10841–10848
Su Y, Mennerich A, Urban B (2012) Comparison of nutrient removal capacity and biomass settleability of four highpotential microalgal species. Bioresour Technol 124:157–162
Tan X, Chu H, Zhang Y, Yang L, Zhao F, Zhou X (2014) Chlorella pyrenoidosa cultivation using anaerobic digested starch processing wastewater in an airlift circulation photobioreactor. Bioresour Technol 170:538–548
Tavaré S (1986) Some probabilistic and statistical problems in the analysis of DNA sequences. In: Miura RM (ed) Lectures math. Life Sci., vol 17. American Mathematical Society, Providence (RI), pp 57–86
Vannecke TP, Bernet N, Winkler MK, Santa-Catalina G, Steyer JP, Volcke EI (2016) Influence of process dynamics on the microbial diversity in a nitrifying biofilm reactor: correlation analysis and simulation study. Biotechnol Bioeng 113:1962–1974
Verhulst PF (1838) Notice sur la loi que la population suit dans son accroissement. Corresp Math Phys Publ Par A Quetel 10:113–121
Wagner EC (1940) Titration of ammonia in the presence of boric acid. Ind Eng Chem Anal Ed 5(6):396–398
Wang H, Xiong H, Hui Z, Zeng X (2012) Mixotrophic cultivation of Chlorella pyrenoidosa with diluted primary piggery wastewater to produce lipids. Bioresour Technol 104:215–220
Wang H, Hu Z, Xiao B, Cheng Q, Li F (2013) Ammonium nitrogen removal in batch cultures treating digested piggery wastewater with microalgae Oedogonium sp. Water Sci Technol 68:269–275
White TJ, Bruns TD, Lee SB, Taylor JW (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky JJ, White TJ (eds) PCR protocols and applications—a laboratory manual, Publisher. Academic Press, London, pp 315–322
Wu YH, Hu HY, Yu Y, Zhang TY, Zhu SF, Zhuang LL, Zhang X, Lu Y (2014) Microalgal species for sustainable biomass/lipid production using wastewater as resource: a review. Renew Sust Energ Rev 33:675–688
WWAP (United Nations World Water Assessment Programme) (2015) The United Nations World Water Development Report 2015: water for a sustainable world. UNESCO, Paris
Yang C, Hua Q, Shimizu K (2000) Energetics and carbon metabolism during growth of microalgal cells under photoautotrophic, mixotrophic and cyclic light-autotrophic/dark-heterotrophic conditions. Biochem Eng J 6:87–102
Yang LB, Tan XB, Li D, Chu HQ, Zhou XF, Zhang YL, Yu H (2015) Nutrients removal and lipids production by Chlorella pyrenoidosa cultivation using anaerobic digested starch wastewater and alcohol wastewater. Bioresour Technol 181:54–161
Yapijakis C, Wang LK (2006) Treatment of phosphate industry wastes. In: Wang LK, Hung Y, Lo HH, Yapijakis C (eds) Waste treatment in the process industries. Taylor and Francis Group, LLC, USA, pp 399–451
Yeh KL, Chang JS (2012) Effects of cultivation conditions and media composition on cell growth and lipid productivity of indigenous microalga Chlorella vulgaris ESP-31. Bioresour Technol 105:120–127
Zhang W, Zhang P, Sun H, Chen M, Lu S, Li P (2014a) Effects of various organic carbon sources on the growth and biochemical composition of Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Bioresour Technol 173:52–58
Zhang Q, Wang T, Hong Y (2014b) Investigation of initial pH effects on growth of an oleaginous microalgae Chlorella sp. HQ for lipid production and nutrient uptake. Water Sci Technol 70(4):712–719
Zhu LD, Wang Z, Takala J, Hiltunen E, Qin L, Xu Z, Qin X, Yuan Z (2013) Scale-up potential of cultivating Chlorella zofingiensis in piggery wastewater for biodiesel production. Bioresour Technol 137:318–325
Zippel B, Rijstenbil J, Neu TR (2007) A flow-lane incubator for studying freshwater and marine phototrophic biofilms. J Microbiol Methods 70:336–345
Acknowledgements
The authors thank to Niculina Musat and Julian Hofer for their pertinent comments and proof reading of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the European Commission through the Erasmus Mundus Joint Doctorate “Environmental Technologies for Contaminated Solids, Soils, and Sediments, EteCoS3” (FPA 2010/0009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
(If applicable) N/A. This research did not involve human participants and/or animals.
Informed consent
N/A. This research did not involve human participants.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 357 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moreno Osorio, J.H., Luongo, V., Del Mondo, A. et al. Nutrient removal from high strength nitrate containing industrial wastewater using Chlorella sp. strain ACUF_802. Ann Microbiol 68, 899–913 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-018-1400-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-018-1400-9