Abstract
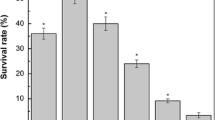
This study aimed to disclose the acid tolerance mechanism of Lactobacillus plantarum by comparing L. plantarum ZDY 2013 with the type strain L. plantarum ATCC 8014 in terms of cell membrane, energy metabolism, and amino acid metabolism. L. plantarum ZDY 2013 had a superior growth performance under acidic condition with 100-fold higher survival rate than that of L. plantarum ATCC 8014 at pH 2.5. To determine the acid tolerance physiological mechanism, cell integrity was investigated through scanning electron microscopy. The study revealed that L. plantarum ZDY 2013 maintained cell morphology and integrity, which is much better than L. plantarum ATCC 8014 under acid stress. Analysis of energy metabolism showed that, at pH 5.0, L. plantarum ZDY 2013 enhanced the activity of Na+/K+-ATPase and decreased the ratio of NAD+/NADH in comparison with L. plantarum ATCC 8014. Similarly, amino acid metabolism of intracellular arginine, glutamate, and alanine was improved in L. plantarum ZDY 2013. Correspondingly, the activity of arginine deiminase and glutamate decarboxylase of L. plantarum ZDY 2013 increased by 1.2-fold and 1.3-fold compared with L. plantarum ATCC 8014 in acid stress. In summary, it is demonstrated that the special physiological behaviors (integrity of cell membrane, enhanced energy metabolism, increased amino acid and enzyme level) of L. plantarum ZDY 2013 can protect the cells from acid stress.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Archibald RM (1944) Determination of citrulline and allantoin and demonstration of citrulline in blood plasma. J Biol Chem 156:121–142
Brinques GB, Ayub MAZ (2011) Effect of microencapsulation on survival of Lactobacillus plantarum in simulated gastrointestinal conditions, refrigeration, and yogurt. J Food Eng 103:123–128
Broadbent JR, Larsen RL, Deibel V, Steele JL (2010) Physiological and transcriptional response of Lactobacillus casei ATCC 334 to acid stress. J Bacteriol 192:2445–2458
Bron PA, Marco M, Hoffer SM, Van Mullekom E, De Vos WM, Kleerebezem M (2004) Genetic characterization of the bile salt response in Lactobacillus plantarum and analysis of responsive promoters in vitro and in situ in the gastrointestinal tract. J Bacteriol 186:7829–7835
Cotter PD, Gahan CG, Hill C (2001) A glutamate decarboxylase system protects Listeria monocytogenes in gastric fluid. Mol Microbiol 40:465–475
Cotter PD, Hill C (2003) Surviving the acid test: Responses of gram-positive bacteria to low pH. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 67:429–453
De Angelis M, Gobbetti M (2004) Environmental stress responses in Lactobacillus: a review. Proteomics 4:106–122
De Angelis M, Mariotti L, Rossi J, Servili M, Fox PF, Rollán G, Gobbetti M (2002) Arginine catabolism by sourdough lactic acid bacteria: Purification and characterization of the arginine deiminase pathway enzymes from Lactobacillus sanfranciscensis CB1. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:6193–6201
De Felipe FL, Kleerebezem M, de Vos WM, Hugenholtz J (1998) Cofactor engineering: a novel approach to metabolic engineering in Lactococcus lactis by controlled expression of NADH oxidase. J Bacteriol 180:3804–3808
De Vries MC, Vaughan EE, Kleerebezem M, de Vos WM (2006) Lactobacillus plantarum—survival, functional and potential probiotic properties in the human intestinal tract. Int Dairy J 16:1018–1028
Duary RK, Batish VK, Grover S (2010) Expression of the atpD gene in probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum strains under in vitro acidic conditions using RT-qPCR. Res Microbiol 161:399–405
Fernández M, Zúñiga M (2006) Amino acid catabolic pathways of lactic acid bacteria. Crit Rev Microbiol 32:155–183
Fernie AR, Carrari F, Sweetlove LJ (2004) Respiratory metabolism: glycolysis, the TCA cycle and mitochondrial electron transport. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7:254–261
Ferrando V, Quiberoni A, Reinhemer J, Suárez V (2015) Resistance of functional Lactobacillus plantarum strains against food stress conditions. Food Microbiol 48:63–71
Fozo EM, Quivey RG (2004) Shifts in the membrane fatty acid profile of Streptococcus mutans enhance survival in acidic environments. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:929–936
Hamon E, Horvatovich P, Marchioni E, Aoudé-Werner D, Ennahar S (2014) Investigation of potential markers of acid resistance in Lactobacillus plantarum by comparative proteomics. J Appl Microbiol 116:134–144
Hernandez-Hernandez O, Muthaiyan A, Moreno FJ, Montilla A, Sanz ML, Ricke S (2012) Effect of prebiotic carbohydrates on the growth and tolerance of Lactobacillus. Food Microbiol 30:355–361
Huang R, Tao X, Wan C et al (2015) In vitro probiotic characteristics of Lactobacillus plantarum ZDY 2013 and its modulatory effect on gut microbiota of mice. J Dairy Sci 98:5850–5861
Johnson BS, Singh NK, Cherry JH, Locy RD (1997) Purification and characterization of glutamate decarboxylase from cowpea. Phytochemistry 46:39–44
Jutfelt F (2006) The intestinal epithelium of salmonids: transepithelial transport, barrier function and bacterial interactions. PhD Thesis, Department of Zoology, Göteborg University
Lechardeur D, Cesselin B, Fernandez A et al (2011) Using heme as an energy boost for lactic acid bacteria. Curr Opin Biotechnol 22:143–149
Lee K, Lee HG, Pi K, Choi YJ (2008) The effect of low pH on protein expression by the probiotic bacterium Lactobacillus reuteri. Proteomics 8:1624–1630
Lin FM, Qiao B, Yuan YJ (2009) Comparative proteomic analysis of tolerance and adaptation of ethanologenic Saccharomyces cerevisiae to furfural, a lignocellulosic inhibitory compound. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:3765–3776
Lin J, Lee IS, Frey J, Slonczewski JL, Foster JW (1995) Comparative analysis of extreme acid survival in Salmonella typhimurium, Shigella flexneri, and Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 177:4097–4104
Marty-Teysset C, de la Torre F, Garel J (2000) Increased production of hydrogen peroxide by Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus upon aeration: involvement of an NADH oxidase in oxidative stress. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:262–267
Mykytczuk NC, Trevors JT, Leduc LG, Ferroni GD (2007) Fluorescence polarization in studies of bacterial cytoplasmic membrane fluidity under environmental stress. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 95:60–82
Parvez S, Malik KA, Ah KS, Kim HY (2006) Probiotics and their fermented food products are beneficial for health. J Appl Microbiol 100:1171–1185
Rallu F, Gruss A, Ehrlich SD, Maguin E (2000) Acid- and multistress-resistant mutants of Lactococcus lactis: Identification of intracellular stress signals. Mol Microbiol 35:517–528
Ryan S, Begley M, Gahan CG, Hill C (2009) Molecular characterization of the arginine deiminase system in Listeria monocytogenes: regulation and role in acid tolerance. Environ Microbiol 11:432
Sanders JW, Leenhouts K, Burghoorn J, Brands JR, Venema G, Kok J (1998) A chloride-inducible acid resistance mechanism in Lactococcus lactis and its regulation. Mol Microbiol 27:299–310
Senouci-Rezkallah K, Schmitt P, Jobin MP (2011) Amino acids improve acid tolerance and internal pH maintenance in Bacillus cereus ATCC14579 strain. Food Microbiol 28:364–372
Shobharani P, Halami PM (2014) Cellular fatty acid profile and H+-ATPase activity to assess acid tolerance of Bacillus sp. for potential probiotic functional attributes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:9045–9058
Teixeira JS, Seeras A, Sanchez-Maldonado AF, Zhang C, Su MS, Gänzle MG (2014) Glutamine, glutamate, and arginine-based acid resistance in Lactobacillus reuteri. Food Microbiol 42:172
Towle D (1984) Regulatory functions of Na++K+-ATPase in marine and estuarine animals. In: Pequeux A (ed) Osmoregulation in estuarine and marine animals. Springer, Berlin, pp 158–170
van de Guchte M, Serror P, Chervaux C, Smokvina T, Ehrlich SD, Maguin E (2002) Stress responses in lactic acid bacteria. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 82:187–216
Wall T, Bth K, Britton RA, Jonsson H, Versalovic J, Roos S (2007) The early response to acid shock in Lactobacillus reuteri involves the ClpL chaperone and a putative Cell Wall-altering esterase. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:3924–3935
Wang WN, Wang AL, Chen L, Liu Y, Sun RY (2002) Effects of pH on survival, phosphorus concentration, adenylate energy charge and Na+-K+ ATPase activities of Penaeus chinensis Osbeck juveniles. Aquat Toxicol 60:75
Wendisch VF, Bott M, Eikmanns BJ (2006) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli and Corynebacterium glutamicum for biotechnological production of organic acids and amino acids. Curr Opin Microbiol 9:268–274
Wu C, Zhang J, Du G, Chen J (2013) Aspartate protects Lactobacillus casei against acid stress. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:4083–4093
Wu C, Zhang J, Wang M, Du G, Chen J (2012) Lactobacillus casei combats acid stress by maintaining cell membrane functionality. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 39:1031–1039
Xu J, Jiang B, Xu S (2003) Rapid determination of glutamate decarboxylase activity from lactic acid bacteria by spectrometric method and its applications. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Tong Bao 31:66–71
Ying W (2008) NAD+/NADH and NADP+/NADPH in cellular functions and cell death: regulation and biological consequences. Antioxid Redox Signal 10:179–206
Zhu X, Dong N, Wang Z, Ma Z, Zhang L, Ma Q, Shan A (2014) Design of imperfectly amphipathic α-helical antimicrobial peptides with enhanced cell selectivity. Acta Biomater 10:244
Acknowledgments
This project was sponsored by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSF31170091, 81760102, 31360377 and 31260363), the Ganpo Talent Engineering 555 Project, the Academic and Technical Leaders Training Program for Major Subjects of Jiangxi Province (P. R. China), the Research Project of Jiangxi Provincial Education Department (GJJ13098; P. R. China), and the Postdoctoral Science Foundation Funded Project of China (M570567).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Disclosures
The manuscript does not contain clinical studies or patient data.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, Y., Tian, X., Huang, R. et al. A physiological comparative study of acid tolerance of Lactobacillus plantarum ZDY 2013 and L. plantarum ATCC 8014 at membrane and cytoplasm levels. Ann Microbiol 67, 669–677 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-017-1295-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-017-1295-x