Abstract
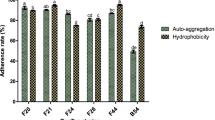
The present study has been focused widely on comparative account of probiotic qualities of Bacillus spp. for safer usage. Initially, 170 heat resistant flora were isolated and selected for non-pathogenic cultures devoid of cytK, hblD, and nhe1 virulence genes. Subsequently, through biochemical tests along with 16S rRNA gene sequencing and fatty acid profiling, the cultures were identified as Bacillus megaterium (AR-S4), Bacillus subtilis (HR-S1), Bacillus licheniformis (Csm1-1a and HN-S1), and Bacillus flexus (CDM4-3c and CDM3-1). The selected cultures showed 70–80 % survival under simulated gastrointestinal condition which was also confirmed through H+-ATPase production. The amount of H+-ATPase increased by more than 2-fold when grown at pH 2 which support for the acid tolerance ability of Bacillus isolates. The study also examined the influence of acidic pH on cellular fatty acid composition of Bacillus spp. A remarkable shift in the fatty acid profile was observed at acidic pH through an increased amount of even numbered fatty acid (C16 and C18) in comparison with odd numbered (C15 and C17). Additionally, the cultures exhibited various probiotic functional properties. Overall, the study increases our understanding of Bacillus spp. and will allow both industries and consumers to choose for well-defined probiotic with possible health benefits.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Maddan TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Belli WA, Marquis RE (1991) Adaptation of Streptococcus mutans and Enterococcus hirae to acid stress in continuous culture. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:1134–1138
Bligh EG, Dyer WJ (1959) A rapid method for total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol 37:911–917
Chaiyawan N, Taveeteptaikul P, Wannissorn B, Ruengsomwong S, Klungsupya P, Buaban W, Itsaranuwat P (2010) Characterization and probiotic properties of Bacillus strains isolated from broiler. Thai J Vet Med 40(2):207–214
Del Re B, Sgorbati B, Miglioli M, Palenzona D (2000) Adhesion, autoaggregation and hydrophobicity of 13 strains of Bifidobacterium longum. Lett Appl Microbiol 31:438–442
EFSA (2005) European Food Safety Authority, Opinion of the scientific committee on a request from EFSA related to a generic approach to the safety assessment by EFSA of microorganisms used in food/feed and the production of food/feed additives. EFSA J 226:1–12
Fakhry S, Sorrentini I, Ricca E, De Felice M, Baccigalupi L (2008) Characterization of spore forming Bacilli isolated from the human gastrointestinal tract. J Appl Microbiol 105:2178–2186
FAO/WHO (2002) Joint FAO/WHO (Food and Agriculture Organization/World Health Organization) working group report on drafting guidelines for the evaluation of probiotics in food. London, Ontario, Canada
Fortier LC, Tourdot-Marechal R, Divie’s C, Lee BH, Guzzo J (2003) Induction of Oenococcus oeni H+-ATPase activity and mRNA transcription under acidic conditions. FEMS Microbiol Lett 222:165–169
Fozo EM, Kajfasz JK, Quivey RG Jr (2004) Low pH-induced membrane fatty acid alterations in oral bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett 238:291–295
From C, Pukall R, Schumann P, Hormazabal V, Granum PE (2005) Toxin producing ability among Bacillus spp. outside the Bacillus cereus group. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:1178–1183
Gilliland SE, Nelson CR, Maxwell C (1985) Assimilation of cholesterol by Lactobacillus acidophilus. Appl Environ Microbiol 49(2):377–381
Giotis ES, McDowell DA, Blair IS, Wilkinson BJ (2007) Role of branched-chain fatty acids in pH stress tolerance in Listeria monocytogenes. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:997–1001
Granum PE, O'Sullivan K, Lund T (1999) The sequence of the non-haemolytic enterotoxin operon from Bacillus cereus. FEMS Microbiol Lett 177:225–229
Guinebretière MH, Broussolle V, Nguyen-The C (2002) Enterotoxigenic profiles of food-poisoning and food-borne Bacillus cereus strains. J Clin Microbiol 40:3053–3056
Havenaar R, Ten Brink B, Huis in’t Veld JHJ (1992) Selection of strains for probiotic use. In: Fuller R (ed) Probiotics. The Scientific Basis Chapman and Hall, London, pp 209–221
Hyronimus B, Le Marrec C, Sassi AH, Deschamps A (2000) Acid and bile tolerance of spore-forming lactic acid bacteria. Int J Food Microbiol 61:193–197
Jonsson H, Strom F, Roos S (2001) Addition of mucin to the growth medium triggers mucus-binding activity in different strains of Lactobacillus reuteri in vitro. FEMS Microbiol Lett 204:19–22
Kullen MJ, Klaenhammer TR (1999) Identification of the pH inducible, proton-translocating F1F0-ATPase (atpBEFHAGDC) operon of Lactobacillus acidophilus by differential display: gene structure, cloning and characterization. Mol Microbiol 33:1152–1161
Kumar S, Nei M, Dudley J, Tamura K (2008) Mega: a biologist-centric software for evolutionary analysis of DNA and protein sequences. Brief Bioinforma 9:299–306
Lee J, Park I, Choi Y, Cho J (2012) Bacillus strains as feed additives: in vitro evaluation of its potential probiotic properties. Rev Colomb Cienc Pecu 25:577–585
Mahler H, Pasi A, Kramer JM, Schulte P, Scoging AC, Baer W, Kraehenbuehl S (1997) Fulminant liver failure associated with the emetic toxin of Bacillus cereus. The New Engl J Med 336:1143–1148
Miwa T, Esaki H, Umemori J, Hino T (1997) Activity of H+-ATPase in ruminal bacteria with special reference to acid tolerance. Appl Environ Microbiol 63(6):2155–2158
Nithya V, Halami PM (2013) Evaluation of the probiotic characteristics of Bacillus species isolated from different food sources. Ann Microbiol 6(1):129–137
O’sullivan E, Condon S (1999) Relationship between acid tolerance, cytoplasmic pH, and ATP and H+-ATPase levels in chemostat cultures of Lactococcus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol 65(6):2287–2293
Otero MC, Ocana VS, Macias ENM (2004) Bacterial surface characteristics applied to selection of probiotic microorganisms. Method Mol Biol 268:435–440
Patel AK, Ahire JJ, Pawar SP, Chaudhari BL, Chincholkar SB (2009) Comparative accounts of probiotic characteristics of Bacillus spp. isolated from food wastes. Food Res Int 42:505–510
Peak KK, Duncan KE, Luna VA, King DS, McCarthy PJ, Cannons AC (2011) Bacillus strain most closely related to Bacillus nealsonii are not effectively circumseribed within the taxonomic species definition. Int J Microbiol. doi:10.1155/2011/673136.
Petrackova D, Vecer J, Svobodova J, Herman P (2010) Long term adaptation of Bacillus subtilis 168 to extreme pH affects chemical and physical properties of the cellular membrane. J Membr Biol 233(1–3):73–83
Prakash R, Sinha PR, Sinha RN, Singh B (1997) Adherence of lactobacilli to epithelial cells and hexadecane for use of probiotics. Ind J Dairy Sci 10:43–47
Raghavendra P, Halami PM (2009) Screening, Selection and characterization of phytic acid degrading lactic acid bacteria from chicken intestine and their probiotic properties. Int J Food Microbiol 133:129–134
Roberts MS, Nakamura LK, Cohan FM (1994) Bacillus mojavensis sp. nov., distinguishable from Bacillus subtilis by sexual isolation, divergence in DNA sequence, and differences in fatty acid composition. Int J Sys Bacteriol 44:256–264
Rosenberg M, Gutnick D, Rosenberg E (1980) Adherence of bacteria to hydrocarbons: a simple method for measuring cell-surface hydrophobicity. FEMS Microbiol Lett 9:29–33
Rowan NJ, Deans K, Anderson JG, Gemmell CG, Hunter IS, Chaithong T (2001) Putative virulence factor expression by clinical and food isolates of Bacillus spp. after growth in reconstituted infant milk formulae. Appl Environ Microbiol 67(9):3873–3881
Ryan PA, MacMillan JD, Zilinskas BA (1997) Molecular cloning and characterization of the genes encoding the L1 and L2 components of hemolysin BL from Bacillus cereus. J Bacteriol 179:2551–2556
Sahadeva RPK, Leong SF, Chua KH, Tan CH, Chan HY, Tong EV, Wong SYW, Chan HK (2011) Survival of commercial probiotic strains to pH and bile. Int Food Res J 18(4):1515–1522
Schillinger U, Yousif NMK, Sesar L, Franz CMAP (2003) Use of group-specific and RAPD-PCR analyses for rapid differentiation of Lactobacillus strains from probiotic yogurts. Curr Microbiol 47:453–456
Sen R, Pal D, Kodali VP, Das S, Ghosh SK (2010) Molecular characterization and in vitro analyses of a sporogenous bacterium with potential probiotic properties. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins 2:152–161
Siegel JP, Smith AR, Novak RJ (1997) Comparison of the cellular fatty acid composition of a bacterium isolated from a human and alleged to be Bacillus sphaericus with that of Bacillus sphaericus isolated from a mosquito larvicide. Appl Environ Microbiol 63(3):1006–1010
Soccol CR, de Souza Vandenberghe LP, Spier MR, Medeiros ABP, Yamaguishi CT, De Dea Lindner J, Pandey A, Thomaz-Soccol V (2010) The Potential of probiotics: a review. Food Technol Biotechnol 48(4):413–434
Sorokulova I (2008) Preclinical testing in the development of probiotics: a regulatory perspective with Bacillus strains as an example. CID 46(Suppl 2):S92–S95
Sowmya R, Sachindra NM (2012) Evaluation of antioxidant activity of carotenoid extract from shrimp processing by products by in-vitro assays and in membrane model system. Food Chem 134:308–314
Xie J, Zhang R, Shang C, Guo Y (2009) Isolation and characterization of a bacteriocin produced by an isolated Bacillus subtilis LFB112 that exhibits antimicrobial activity against domestic animal pathogens. Afr J Biotechnol 8(20):5611–5619
Thirabunyanona M, Thongwittaya N (2012) Protection activity of a novel probiotic strain of Bacillus subtilis against Salmonella enteritidis infection. Res Vet Sci 93:74–81
van Schaik W, Gahan CGM, Hill C (1999) Acid-adapted Listeria monocytogenes displays enhanced tolerance against the lantibiotics nisin and lacticin 3147. J Food Prot 62(5):536–539
Yuk HG, Marshall DL (2004) Adaptation of Escherichia coli O157:H7 to pH alters membrane lipid composition, verotoxin secretion, and resistance to simulated gastric fluid acid. Appl Environ Microbiol 70(6):3500–3505
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the Director, CFTRI, for all the facilities. This study is a part of start-up project funded by SERB-Department of Science and Technology, Government of India, New Delhi.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 59 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shobharani, P., Halami, P.M. Cellular fatty acid profile and H+-ATPase activity to assess acid tolerance of Bacillus sp. for potential probiotic functional attributes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98, 9045–9058 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5981-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5981-3