Abstract
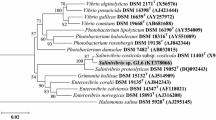
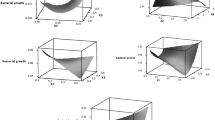
Caffeine is an important naturally occurring compound that can be degraded by bacteria. Excessive caffeine consumption is known to have some adverse effects. We isolated a new bacterium from agriculture soil. The bacterium was tested for its ability to utilise caffeine as the sole carbon and nitrogen source. The isolate was Gram-negative and was identified as Leifsonia sp. strain SIU based on 16S rRNA gene sequencing. It showed 97.16 % of 0.3 g/L caffeine degradation in 48 h when caffeine was used as a sole carbon and nitrogen source. The bacterial growth and degradation at 0.3 g/L caffeine concentration occurred optimally, using 5 g/L sucrose, 0.4 g/L ammonium chloride, at a temperature between 25 and 30 °C and pH of 6.0–7.0. The Luong model best describes the kinetics of the strain growth. The values for the maximum specific growth rate (μ max ), the Monod half saturation constant (K S ), the maximum substrate inhibitory concentration and n are 0.049 h−1, 0.0021 mg/L, 25.0 g/L and 1.562, respectively. These bacterial features make it an ultimate means for caffeine bioremediation. This is the first report of caffeine degradation by Leifsonia sp. strain SIU.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal R, Mahanty B, Dasu VV (2009) Modeling growth of Cellulomonas cellulans NRRL B 4567 under substrate inhibition during cellulase production. Chem Biochem Eng Q 23:213–218
Aiba S, Shoda M, Nagalani M (1968) Kinetics of product inhibition in alcohol fermentation. Biotechnol Bioeng 10:845–864
Alden L, Demoling F, Bååth E (2001) Rapid method of determining factors limiting bacterial growth in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:1830–1838
Asano Y, Komeda T, Yamada H (1993) Microbial production of theobromine from caffeine. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 57:1286–1289
Asano Y, Komeda T, Yamada H (1994) Enzymes involved in theobromine production from caffeine by a Pseudomonas putida no. 352. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 58:2303–2304
Ashihara H, Crozier A (2001) Caffeine, a well known but little mentioned compound in plant science. Trends Plant Sci 6:407–413
Babu VRS, Patra S, Thakur MS, Karanth NG, Varadaraj MC (2005) Degradation of caffeine by Pseudomonas alcaligenes CFR 1708. Enzyme Microb Technol 37:617–624
Bailey RA, Bechet GR (1997) Further evidence of the effects of ratoon stunting disease on production under irrigated and rainfed conditions. Proc S Afr Sugar Technol Assoc 71:97–101
Batish DR, Singh HP, Kaur M, Kohli RK, Yadav SS, Kaohli RK (2008) Caffeine affects adventitious rooting and causes biochemical changes in the hypocotyl cuttings of mung bean (Phaseolus aureus Roxb.). Acta Physiol Plant 30:401–405
Brumbley SM, Petrasovits LA, Hermann SR, Young AJ, Crof BJ (2006) Recent advances in the molecular biology of Leifsonia xyli subsp. xyli, causal organism of ratoon stunting disease. Aust Plant Path 35:681–689
Cappucino JG, Sherman N (2005) Microbiology: A Loboratory Manual 7th Edition. Pearson Education, Inc, San Francisco, pp 45–47
Devereux R, Wilkinson SS (2004) Amplification of ribosomal RNA sequences. In: Akkermans ADL, van Elsas JD, de Bruijn FJ (eds) Molecular Microbial Ecology Manual, 2nd edn. Kluwer Academic, Dodrecht, pp 1–17
Dlugosz L, Belanger K, Hellenbrand K, Holford TR, Leaderer B, Bracken MB (1996) Maternal caffeine consumption and spontaneous abortion: a prospective cohort study. Epidemiology 7:250–255
El-Mched F, Olama Z, Holail H (2013) Optimization of the environmental and physiological factors affecting microbial caffeine degradation and its application in caffeinated products. Basic Res J Microbiol 1:17–27
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Fenster L, Eskenazi B, Windham GC, Swan SH (1991) Caffeine consumption during pregnancy and fetal growth. Am J Public Heal 81:458–461
Friedman J, Waller GR (1983a) Caffeine hazards and their prevention in germinating seeds of coffee (Coffea arabica L.). J Chem Ecol 9:1099–1106
Friedman J, Waller GR (1983b) Seeds as allelopathic agents. J Chem Ecol 9:1107–1115
Frischknecht PM, Ulmer DJ, Baumann TW (1986) Purine alkaloid formation in buds and developing leaflets of Coffea arabica: expression of an optimal defense strategy. Phytochemistry 25:613–616
Gibson AM, Morgan RM, Nikitin AG (2009) The effect of caffeine on the bacterial populations in a freshwater aquarium system. Student Summer Scholars. Paper 31
Gokulakrishnan S, Gummadi SN (2006) Kinetics of cell growth and caffeine utilization by Pseudomonas sp. GSC 1182. Process Biochem 41:1417–1421
Gokulakrishnan S, Chandraraj K, Gummadi SN (2005) Microbial and enzymatic methods for the removal of caffeine. Enzyme Microb Technol 37:225–232
Gokulakrishnan S, Chandraraj K, Gummadi SN (2007) A preliminary study of caffeine degradation by Pseudomonas sp. GSC 1182. Int J Food Microbiol 113:346–350
Green PJ, Suls J (1996) The effects of caffeine on ambulatory blood pressure, heart rate, and mood in coffee drinkers. J Behav Med 19:111–128
Gummadi SN, Ganesh KB, Devarai S (2009) Enhanced degradation of caffeine by immobilized cells of Pseudomonas sp. in agar–agar matrix using statistical approach. Biochem Eng J 44:136–141
Gummadi SN, Bhavya B, Ashok N (2012) Physiology, biochemistry and possible applications of microbial caffeine degradation. Appl Microbiol 93:545–554
Hakil M, Voisinet F, Viniegra-González G, Augur C (1999) Caffeine degradation in solid state fermentation by Aspergillus tamarii: effects of additional nitrogen sources. Process Biochem 35:103–109
Haldane JBS (1930) Enzymes. Longmans, Green, London
Infante RC, Fernandez A, Gauthier R, David M, Rivard GE (1993) Fetal loss associated with caffeine intake before and during pregnancy. J Am Med Assoc 270:2940–2943
Jukes TH, Cantor CR (1969) “Evolution of protein molecules,”. In: Munro HN (ed) In mammalian protein metabolism. Academic Press, New York, pp 21–132
Lakshmi V, Das N (2010) Caffeine degradation by yeasts isolated from caffeine contaminated samples. Int J Sci Nat 1:47–52
Lakshmi V, Nilanjana D (2013a) Caffeine degradation by yeasts isolated from caffeine contaminated samples. Int J Eng Sci Technol 1:47–52
Lakshmi V, Nilanjana D (2013b) Biodegradation of Caffeine by Trichosporon asahii Isolated from caffeine Contaminated Soil. Int J Eng Sci Technol 1:1–10
Lorist MM, Tops M (2003) Caffeine, fatigue, and cognition. Brain Cogn 53:82–94
Luong JHT (1987) Generalization of Monod kinetics for analysis of growth data with substrate inhibition. Biotechnol Bioeng 29:242–248
Madyastha KM, Sridhar GR (1998) A novel pathway for the metabolism of caffeine by a mixed culture consortium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 249:178–181
Madyastha KM, Sridhar GR, Vadiraja BB, Madhavi YS (1999) Purification and partial characterization of caffeine oxidase—a novel enzyme from a mixed culture consortium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 263:460–464
Mazzafera P (2002) Degradation of caffeine by microorganisms and potential use of decaffeinated coffee husk and pulp in animal feeding. Sci Agric 59:815–821
Mazzafera P, Olsson O, Sandberg G (1996) Degradation of caffeine and related methyl xanthines by Serratia marcescens isolated from soil under coffee cultivation. Microb Ecol 31:199–207
Mohanty SK (2013) A. Genetic characterization of the caffeine C-8 oxidation pathway in Pseudomonas sp. CBB1 B. Validation of caffeine dehydrogenase as a suitable enzyme for a rapid caffeine diagnostic test. pp 1–201
Mohanty SK, Yu CL, Das S, Louie TM, Gakhar L, Subramanian M (2012) Delineation of the caffeine C-8 oxidation pathway in Pseudomonas sp. strain CBB1 via characterization of a new trimethyl acid monooxygenase and genes involved in trimethyluric acid metabolism. J Bacteriol 194:3872–3882
Mohapatra BR, Harris N, Nordin R, Mazumder A (2006) Purification and characterization of a novel caffeine oxidase from Alcaligenes species. J Biotechnol 125:319–327
Nathanson JA (1984) Caffeine and related methylxanthines: possible naturally occuring pesticides. Science 226:184–187
Nayak S, Harshitha MJ, Maithili SC, Anilkumar HS, Rao CV (2012) Isolation and characterization of caffeine degrading bacteria from coffee pulp. Indian J Biotechnol 11:86–91
Page RDM (1996) TreeView: an application to display phylogenetic trees on personal computers. Comput Appl Biosci 12:357–358
Perzborn M, Syldatk C, Rudat J (2013) Enzymatical and microbial degradation of cyclic dipeptides (diketopiperazines). AMB Express 3:51–63
Roussos S, Hannibal L, Aquiahuatl MA, Hernandes MRT, Marakis S (1994) Caffeine degradation by Penicillium verrucosum in solid state fermentation of coffee pulp: critical effects of additional inorganic and organic nitrogen sources. J Food Sci Technol 31:316–319
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Bacterial cell maintenance. Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, vol 1. Cold Spring Harbor laboratory Press, New York
Singh RK, Kumar S, Kumar A (2008) Biodegradation kinetic studies for the removal of p-cresol from wastewater using Gliomastix indicus MTCC 3869. Biochem Eng J 40:293–303
Smith A (2002) Effects of caffeine on human behavior. Food Chem Toxicol 40:1243–1255
Srisuphan W, Bracken MB (1986) Caffeine consumption during pregnancy and association with late spontaneous abortion. Am J Obst Gyne 155:14–20
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
White PA, Rasmussen JB (1998) The genotoxic hazards of domestic wastes in surface waters. Mutat Res 410:223–236
Woolfolk CA (1975) Metabolism of N-methylpurines by a Pseudomonas putida strain isolated by enrichment on caffeine as the sole source of carbon and nitrogen. J Bacteriol 123:1088–1106
Yu CL, Kale Y, Gopishetty S, Louie TM, Subramanian M (2008) A novel caffeine dehydrogenase in Pseudomonas sp. strain CBB1 oxidizes caffeine to trimethyluric acid. J Bacteriol 190:772–776
Yu CL, Louie TM, Summers R, Kale Y, Gopishetty S, Subramanian M (2009) Two distinct pathways for metabolism of theophylline and caffeine are coexpressed in Pseudomonas putida CBB5. J Bacteriol 191:4624–4632
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ibrahim, S., Shukor, M.Y., Syed, M.A. et al. Characterisation and growth kinetics studies of caffeine-degrading bacterium Leifsonia sp. strain SIU. Ann Microbiol 66, 289–298 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-015-1108-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-015-1108-z