Abstract
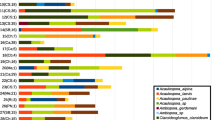
Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge (SMB) is an important herb that has been used in traditional Chinese medicine for centuries. Continuous SMB cropping can result in significant losses of yield and quality of the plant. The purpose of this study was to examine the variations in community structure of soil actinomycetes and fungi under continuous cropping of SMB in Sichuan, China. Four soil samples were analyzed by polymerase chain reaction and denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (PCR-DGGE). The microbial diversity indices (Shannon-Wiener index, richness, and evenness) of the soil actinomycetes decreased along with continuous SMB cropping and rebound at the 3rd year, while that of soil fungi declined. Cluster analysis showed that the similarity between uncultivated soils and cropping soils declined with subsequent cropping periods. Homology search of sequences recovered from the DGGE bands showed that the actinomycete community in the studied soils was dominated by Actinobacteria, while dominant species of the fungal community varied remarkably, including Pleospora, Psathyrella, Pseudozyma, Rhizoctonia, Trichophaea and unclassified groups. Overall, these findings demonstrate that continuous SMB cropping has a significant impact on soil actinomycete and fungal communities.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ben-David EA, Zaady E, Sher Y, Nejidat A (2011) Assessment of the spatial distribution of soil microbial communities in patchy arid and semi-arid landscapes of the Negev Desert using combined PLFA and DGGE analyses. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 76(3):492–503
Bernard E, Larkin RP, Tavantzis S, Erich MS, Alyokhin A, Sewell G, Lannan A, Gross SD (2012) Compost, rapeseed rotation, and biocontrol agents significantly impact soil microbial communities in organic and conventional potato production systems. Appl Soil Ecol 52:29–41
Bever JD, Schultz PA, Pringle A, Morton JB (2001) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi: more diverse than meets the eye, and the ecological tale of why the high diversity of ecologically distinct species of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi within a single community has broad implications for plant ecology. Bioscience 51(11):923–931
Bullock D (1992) Crop rotation. Crit Rev Plant Sci 11(4):309–326
Carlile MJ, Watkinson SC, Gooday GW (2001) The fungi, vol 2. Academic, London
Chen YQ, Dong YH, Wang H, Huang GY, Huo HZ (2011) Effects of different agricultural managements on characteristics of soil microbial community under continuous cropped strawberry (Fragaria ananassa Duchesne). Agric Sci Technol Hunan 12(6):870–875
Chen M, Li X, Yang Q, Chi X, Pan L, Chen N, Yang Z, Wang T, Wang M, Yu S (2012) Soil eukaryotic microorganism succession as affected by continuous cropping of peanut-pathogenic and beneficial fungi were selected. PLoS One 7(7):e40659
Chung TY, Li FY, Chiou WH, Tzen JTC (2012) Magnesium lithospermate B extracted from Salvia miltiorrhiza, a potential substitute for cardiac glycosides. Mini-Rev Org Chem 9(2):163–168
Crookston R, Kurle J, Copeland P, Ford J, Lueschen W (1991) Rotational cropping sequence affects yield of corn and soybean. Agron J 83(1):108–113
Darriba D, Taboada GL, Doallo R, Posada D (2012) jModelTest 2: more models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat Methods 9(8):772–772
García-Amado MA, Bozo-Hurtado L, Astor Y, Suárez P, Chistoserdov A (2011) Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analyses of the vertical distribution and diversity of Vibrio spp. populations in the Cariaco Basin. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 77(2):347–356
Gil SV, Meriles J, Conforto C, Figoni G, Basanta M, Lovera E, March G (2009) Field assessment of soil biological and chemical quality in response to crop management practices. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 25(3):439–448
González-Arenzana L, López R, Santamaría P, López-Alfaro I (2013) Dynamics of lactic acid bacteria populations in Rioja wines by PCR-DGGE, comparison with culture-dependent methods. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol:1–11
González-Chávez MCA, Aitkenhead-Peterson JA, Gentry TJ, Zuberer D, Hons F, Loeppert R (2010) Soil microbial community, C, N, and P responses to long-term tillage and crop rotation. Soil Tillage Res 106(2):285–293
Guindon S, Dufayard JF, Lefort V, Anisimova M, Hordijk W, Gascuel O (2010) New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst Biol 59(3):307–321
Heuer H, Krsek M, Baker P, Smalla K, Wellington E (1997) Analysis of actinomycete communities by specific amplification of genes encoding 16S rRNA and gel-electrophoretic separation in denaturing gradients. Appl Environ Microbiol 63(8):3233–3241
Hilton S, Bennett AJ, Keane G, Bending GD, Chandler D, Stobart R, Mills P (2013) Impact of shortened crop rotation of oilseed rape on soil and rhizosphere microbial diversity in relation to yield decline. PLoS One 8(4):e59859
Hirsch PR, Mauchline TH, Clark IM (2010) Culture-independent molecular techniques for soil microbial ecology. Soil Biol Biochem 42(6):878–887
Ho J, Hong CY (2011) Salvianolic acids: small compounds with multiple mechanisms for cardiovascular protection. J Biomed Sci 18(1):30
Huang X, Chen L, Ran W, Shen Q, Yang X (2011) Trichoderma harzianum strain SQR-T37 and its bio-organic fertilizer could control Rhizoctonia solani damping-off disease in cucumber seedlings mainly by the mycoparasitism. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 91(3):741–755
Hussain Q, Liu Y, Zhang A, Pan G, Li L, Zhang X, Song X, Cui L, Jin Z (2011) Variation of bacterial and fungal community structures in the rhizosphere of hybrid and standard rice cultivars and linkage to CO2 flux. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 78(1):116–128
Kelley K, Long J Jr, Todd T (2003) Long-term crop rotations affect soybean yield, seed weight, and soil chemical properties. Field Crop Res 83(1):41–50
Kirkegaard J, Christen O, Krupinsky J, Layzell D (2008) Break crop benefits in temperate wheat production. Field Crop Res 107(3):185–195
Larkin RP, Honeycutt CW, Olanya OM, Halloran JM, He Z (2012) Impacts of crop rotation and irrigation on soilborne diseases and soil microbial communities. In: Sustainable potato production: global case studies. Springer, Berlin, pp 23–41
Lee JY, Hwang BK (2002) Diversity of antifungal actinomycetes in various vegetative soils of Korea. Can J Microbiol 48(5):407–417
Lin GB (2010) Research on microbial population structure on soil suitability of Salvia miltiorrhiza origin. Dissertation, Chengdu University of TCM
Lin TH, Hsieh CL (2010) Pharmacological effects of Salvia miltiorrhiza (Danshen) on cerebral infarction. Chin Med 5(1):22
Lin YC, Huang CP, Lai HH, Tang WC, Wu CC (2012) The traditional processing method enriches the anti-liver fibrosis active compounds in Salvia miltiorrhiza. Int Proc Chem Biol Environ Eng 40:141
Liu S, Liu S, Zhang Z, Wei H, J-J Qi, J-F Duan (2010) Influence of garlic continuous cropping on rhizosphere soil microorganisms and enzyme activities. Sci Agric Sin 43(5):1000–1006
May LA, Smiley B, Schmidt MG (2001) Comparative denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of fungal communities associated with whole plant corn silage. Can J Microbiol 47(9):829–841
Muyzer G, Smalla K (1998) Application of denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) and temperature gradient gel electrophoresis (TGGE) in microbial ecology. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 73(1):127–141
Ng C, Koon C, Cheung D, Lam M, Leung P, Lau C, Fung K (2011) The anti-hypertensive effect of Danshen (Salvia miltiorrhiza) and Gegen (Pueraria lobata) formula in rats and its underlying mechanisms of vasorelaxation. J Ethnopharmacol 137(3):1366–1372
Nimnoi P, Lumyong S, Pongsilp N (2011) Impact of rhizobial inoculants on rhizosphere bacterial communities of three medicinal legumes assessed by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE). Ann Microbiol 61(2):237–245
Parmeter JR (1970) Rhizoctonia solani, biology and pathology. University of California Press
Qin S, Li J, Chen HH, Zhao GZ, Zhu WY, Jiang CL, Xu LH, Li WJ (2009) Isolation, diversity, and antimicrobial activity of rare actinobacteria from medicinal plants of tropical rain forests in Xishuangbanna, China. Appl Environ Microbiol 75(19):6176–6186
Reysenbach A-L, Giver LJ, Wickham GS, Pace NR (1992) Differential amplification of rRNA genes by polymerase chain reaction. Appl Environ Microbiol 58(10):3417–3418
Rychlik W, Rhoads RE (1989) A computer program for choosing optimal oligonudeotides for filter hybridization, sequencing and in vitro amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 17(21):8543–8551
Saikaly PE, Stroot PG, Oerther DB (2005) Use of 16S rRNA gene terminal restriction fragment analysis to assess the impact of solids retention time on the bacterial diversity of activated sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(10):5814–5822
Singh SK (2012) Spatiotemporal variability in archaeal communities of tropical coastal waters. Ann Microbiol:1–10
Singh SK (2013) Spatiotemporal variability in archaeal communities of tropical coastal waters. Ann Microbiol 63(4):1301–1310
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28(10):2731–2739
Urashima Y, Sonoda T, Fujita Y, Uragami A (2012) Application of PCR-denaturing-gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) method to examine microbial community structure in Asparagus fields with growth inhibition due to continuous cropping. Microbes Environ 27(1):43–48
Van Hop D, Sakiyama Y, Binh CTT, Otoguro M, Hang DT, Miyadoh S, Luong DT, Ando K (2011) Taxonomic and ecological studies of actinomycetes from Vietnam: isolation and genus-level diversity. J Antibiot 64(9):599–606
Wall DH, Bardgett RD, Behan-Pelletier V, Herrick JE, Jones TH, Strong DR (2013) Soil ecology and ecosystem services. Oxford University Press, UK
Wang Y, Zhang Z, Ruan J, Wang Y, Ali S (1999) Investigation of actinomycete diversity in the tropical rainforests of Singapore. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 23(3):178–187
Wu JR, Zhang JC, Shi P, Wu R, Yue XQ, Zhang HP (2013) Bacterial community involved in traditional fermented soybean paste dajiang made in northeast China. Ann Microbiol:1–5
Yang W, Jh J, Jeon MJ, Han X, Shin I (2010) Danshen (Salvia miltiorrhiza) extract inhibits proliferation of breast cancer cells via modulation of Akt activity and p27 level. Phytother Res 24(2):198–204
Zhang CL, Sun Q, Ye Q (2004) Obstacle effect of continuous cropping on Salvia miltiorrhiza growth. Acta Bot Boreali-Occidentalia Sin 25(5):1029–1034
Zhang XL, Pan ZG, Zhou XF, Ni WZ (2007) Autotoxicity and continuous cropping obstacles. Chin J Soil Sci 4:033
Zhang W, Long X, Huo X, Chen Y, Lou K (2013) 16S rRNA-based PCR-DGGE analysis of actinomycete communities in fields with continuous cotton cropping in Xinjiang, China. Microb Ecol 66(2):385–393
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the anonymous reviewers for their critical reading of the manuscript. This research was funded by a Key Project of Shenzhen Emerging Industries (No. JC201104210118A) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.81130070).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jie Tang and Zhiquan Xue contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, J., Xue, Z., Daroch, M. et al. Impact of continuous Salvia miltiorrhiza cropping on rhizosphere actinomycetes and fungi communities. Ann Microbiol 65, 1267–1275 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-014-0964-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-014-0964-2