Abstract
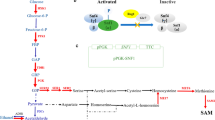
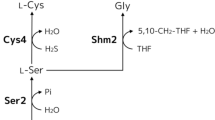
S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM) is an essential metabolite in all living cells, and which plays an important role in cellular functions such as methylation, sulfuration, and polyamine synthesis. The current study was carried out to obtain an industrial strain with overproduction of SAM. The wild-type strain, Saccharomyces cerevisiae CGMCC 1226, was subjected to successive mutagenic with ultraviolet irradiation (UV) coupled with ethionine-resistant screening procedure to achieve a rapid improvement of S-adenosyl-L-methionine production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. A high SAM yield strain, designated as Saccharomyces cerevisiae CGMCC 2842, was successfully selected and exhibited higher SAM synthetase activity which was increased by 2.7-fold in comparison with the wild-type strain. Meanwhile, the production of SAM by Saccharomyces cerevisiae CGMCC 2842 in a 15-L fermentor reached 6.1 g/L after 36 h fed-batch fermentation and was increased by 4.3-fold. In addition, the ethionine-resistant genes of the mutant and wild-type strains were cloned, and analyses of nucleotide sequences suggested that the replacements of amino acid residues could be responsible for the ethionine-resistance.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barra JL, Mautino MR, Rosa AL (1996) A dominant negative of effect of eth-1r, a mutant allele of the Neurospora crassa S-adenosylmethionine synthetase-encoding gene conferring resistance to the methionine toxic analogue ehtionine. Genetics 144:1455–1462
Bradley JD, Flusser D, Katz BP, Schumacher HR Jr, Brandt KD, Chambers MA, Zonay LJ (1994) A randomized, double blind, placebo controlled trial of intravenous loading with S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) followed by oral SAM therapy in patients with knee osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol 21:905–911
Budovskaya YV, Stephan JS, Deminoff SJ, Herman PK (2005) An evolutionary proteomics approach identifies substrates of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:13933–13938
Cantoni GL (1952) The nature of the active methyl donor formed enzymatically from L-methionine and adenosinetriphosphate. J Am Chem Soc 74:2942–2943
Cheng HR, Jiang N (2006) Extremely rapid extraction of DNA from bacteria and yeasts. Biotechnol Lett 28:55–59
Dynesen J, Smits HP, Olsson L, Nielsen J (1998) Carbon catabolite repression of invertase during batch cultivations of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: the role of glucose, fructose, and mannose. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 50:579–582
Fontecave M, Atta M, Mulliez E (2004) S-adenosyl-L-methionine: nothing goes to waste. Trends Biochem Sci 29:243–249
He J, Deng J, Zheng Y, Gu J (2006) A synergistic effect on the production of S-adenosyl-l-methionine in Pichia pastoris by knocking in of S-adenosyl-l-methionine synthase and knocking out of cystathionine-synthase. J Biotechnol 126:519–527
Hosea Blewett HJ (2008) Exploring the mechanisms behind. S-adenosylmethionine (SAMe) in the treatment of osteoarthritis. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 48:458–463
Hu H, Qian JC, Chu J, Wang Y, Zhuang Y, Zhang S (2009) DNA shuffling of methionine adenosyltransferase gene leads to improved S-adenosyl-L-methionine production in Pichia pastoris. J Biotechnol 141:97–103
Huang L, Wei PL, Zang R, Xu ZN, Cen PL (2010) High-throughput screening of high-yield colonies of Rhizopus oryzae for enhanced production of fumaric acid. Ann Microbiol 60:287–292
Jeong-Nam P, Lee KH, Ko KH, Seo KH, Chin JE, Lee HB, Bai S (2004) Expression of ethionine resistance conferring gene in an industrial strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Korean J Microbiol Biotech 32:356–361
Lee SW, Park BS, Choi ES, Oh MK (2010) Overexpression of ethionine resistance gene for maximized production of S-adenosylmethionine in Saccharomyces cerevisiae sake kyokai No. 6. Korean J Chem Eng 27:587–589
Li W, Ye S, Luo KJ, Ge FL, Du LJ, Wu K, Ding CW (2007) Isolation and characterisation of Candida sp. mutants enriched in S-adenosylmethionine (SAM). Ann Microbiol 57:383–387
Lieber CS, Packer L (2002) S-Adenosy-l-methionine: molecular, biological, and clinical aspects-an introduction. Am J Clin Nutr 76(Suppl):1148S–1150S
Linnebank M, Popp J, Smulders Y, Smith D, Semmler A, Farkas M, Kulic L, Cvetanovska G, Blom H, Stoffel-Wagner B, Kölsch H, Weller M, Jessen F (2010) S-Adenosylmethionine Is Decreased in the Cerebrospinal Fluid of Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurodegenerative Dis 7:373–378
Lu SC, Mato JM (2008) S-Adenosy-l-methionine in cell growth, apoptosis and liver cancer. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 23(Suppl):73S–77S
Malkowski MG, Quartley E, Friedman AE, Babulski J, Kon Y, Wolfley J, Said M, Luft JR, Phizicky EM, DeTitta GT, Grayhack EJ (2007) Blocking S-adenosylmethionine synthesis in yeast allows selenomethionine incorporation and multiavelength anomalous dispersion phasing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:6678–6683
Maw GA (1966) Incorporation and distribution of ethionine-sulfur in the protein of ethionine-sensitive and ethionine-resistant yeasts. Arch Biochem Biophys 115:291–301
Newman PE (2000) Alzheimer’s disease revisited. Med Hypotheses 54:774–776
Nguyen M, Gregan A (2002) S-adenosyl-l-methionine and depression. Aust Fam Physician 31:339–343
Santiago TC, Mamoun CB (2003) Genome expression analysis in yeast reveals novel transcriptional regulation by Inositol and Choline and New Regulatory Functions for Opi1p, Ino2p, and Ino4p. J Biol Chem 278:38723–38730
Scarpa S, Fuso A, D'Anselmi F, Cavallaro RA (2003) Presenilin 1 gene silencing by S-adenosylmethionine: a treatment for Alzheimer disease? FEBS Lett 541:145–148
Schlenk F, Zydek CR (1967) The radiopurity of S-adenosylmethionine and S-adenosylethionine preparations. J Labelled Compounds 3:137–143
Schlenk F, Zydek CR, Ehninger DJ, Dainko JL (1965) The production of S-adenosyl-L-methionine and S-adenosyl-L-ethionine by yeast. Enzymologia 29:283–298
Shiomi N, Fukuda H, Fukuda Y, Murata K, Kimura A (1991) Nucleotide sequence and characterization of a gene conferring resisitance to ethionine in yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Ferment Bioeng 4:211–215
Shiomi N, Fukuda H, Murata K, Kimura A (1995) Improvement of S-adenosylmethionine production by integration of the ethionine-resistance gene into chromosomes of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 42:730–733
Shiozaki S, Shimizu S, Yamada H (1984) Unusual intracellular accumulation of S-adenosyl-L-methionine by microorganisms. Agric Biol Chem 48:2293–2300
Shippy RA, Mendez D, Jones K, Cergnul I, Karpiak SE (2004) S-adenosy-l-methioine (SAM-e) for the treatment of depression in people living with HIV/AIDS. BMC Psychiatry 4:38
Sreenivas A, Carman GM (2003) Phosphorylation of the yeast phospholipid synthesis regulatory protein Opi1p by protein kinase A. J Biol Chem 278:20673–20680
Sridhar M, KiranSree N, Venkateswa RL (2002) Effect of UV radiation on thermotolerance, ethanol tolerance and osmotolerance of Saccharomyces cerevisiae VS1 and VS3 strains. Bioresour Technol 83:199–202
Thomas D, Surdin-kejian Y (1991) The synthesis of the two S-adenosyl-L-methionine synthetase is differently regulated in Sacchromyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet 226:224–232
Zhou J, Chu J, Wang YH, Zhang SL, Zhuang YP, Yuan ZY (2008) Purification and properties of Saccharomyces cerevisiae S-adenosylmethionine synthetase expressed in recombinant Pichia pastoris. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 24:789–796
Acknowledgements
This study was sponsored by Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (SBK200921231), the Industrialization of Scientific Research Promotion Projects of Colleges and Universities in Jiangsu Province (JH10-12), the Qing Lan Project (2008) from Jiangsu Province and the “111 Project” from the Ministry of Education of China and the State Administration of Foreign Expert Affairs of China (No. 111-2-07).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Xitao Cao and Minghua Yang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, X., Yang, M., Xia, Y. et al. Strain improvement for enhanced production of S-adenosyl-L-methionine in Saccharomyces cerevisiae based on ethionine-resistance and SAM synthetase activity. Ann Microbiol 62, 1395–1402 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-011-0389-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-011-0389-0