Abstract
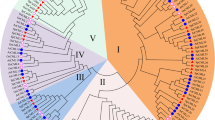
Metallothionein (MT) proteins are low-molecular-weight, cysteine-rich and metal-binding proteins that play important roles in the maintenance of metal homeostasis and detoxification, but their roles in abiotic stress tolerance remain largely unknown. In this study, three MT family genes (CsMT2, CsMT3 and CsMT4) were identified in the cucumber genome. CsMT2, CsMT3 and CsMT4 possessed 14, 10, and 18 Cys residues, which were clustered into 2, 2, and 3 Cys-rich regions, respectively. Phylogenetic analysis of MTs from cucumber, Arabidopsis and soybean revealed that these MTs were clustered into four groups in accordance with the MT types (types 1–4). An analysis of the cis-acting regulatory elements revealed that a series of hormone-, stress-, and development-related cis-elements were present in the promoter regions of CsMT genes. Expression pattern analysis by RT-PCR showed that the CsMT genes exhibited different tissue expression patterns. CsMT2 showed relatively higher expression in stem, leaf, and flower; CsMT3 was mainly expressed in leaf, flower, and fruit, while CsMT4 was highly expressed in fruit and leaf. The qRT-PCR results showed that the CsMT genes were induced by various stress treatments including NaCl, PEG, and ABA, while CsMT4 displayed much higher expression levels in response to these stresses than CsMT2 and CsMT3. Escherichia coli cells expressing CsMT4 exhibited higher salinity and osmotic tolerance compared with control cells, indicating the significant function of CsMT4 to confer tolerance to these stresses. These results lay a foundation for further research on the function of MT family genes in plant stress responses.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn YO, Kim SH, Lee J, Kim H, Lee HS, Kwak SS (2012) Three Brassica rapa metallothionein genes are differentially regulated under various stress conditions. Mol Biol Rep 39:2059–2067
An Z, Li C, Zu Y, Du Y, Andreas W, Roland G et al (2006) Expression of BjMT2, a metallothionein 2 from Brassica juncea, increases copper and cadmium tolerance in Escherichia coli and Arabidopsis thaliana, but inhibits root elongation in Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings. J Exp Bot 57:3575–3582
Ansarypour Z, Shahpiri A (2017) Heterologous expression of a rice metallothionein isoform (OsMTI-1b) in Saccharomyces cerevisiae enhances cadmium, hydrogen peroxide and ethanol tolerance. Braz J Microbiol 48:537–543
Chaturvedi AK, Patel MK, Mishra A, Tiwari V, Jha B (2014) The SbMT-2 gene from a halophyte confers abiotic stress tolerance and modulates ROS scavenging in transgenic tobacco. PLoS One 9:e111379
Chen Y, Zhi J, Li X, Zhang H, Liu H, Xu J (2018) Diversity in cadmium accumulation and resistance associated with various metallothionein genes (type III) in Phytolacca americana L. Int J Biol Macromol 108:704–709
Cobbett CS (2000) Phytochelatins and their roles in heavy metal detoxification. Plant Physiol 123:825–832
Cobbett C, Goldsbrough P (2002) Phytochelatins and metallothioneins: roles in heavy metal detoxification and homeostasis. Annu Rev Plant Biol 53:159–182
Duan L, Yu J, Xu L, Tian P, Hu X, Song X et al (2019) Functional characterization of a type 4 metallothionein gene (CsMT4) in cucumber. Hortic Plant J 5:120–128
Freisinger E (2011) Structural features specific to plant metallothioneins. J Biol Inorg Chem 16:1035–1045
Gautam N, Verma PK, Verma S, Tripathi RD, Trivedi PK, Adhikari B et al (2012) Genome-wide identification of rice class I metallothionein gene: tissue expression patterns and induction in response to heavy metal stress. Funct Integr Genomics 12:635–647
Guo WJ, Bundithya W, Goldsbrough PB (2003) Characterization of the Arabidopsis metallothionein gene family: tissue-specific expression and induction during senescence and in response to copper. New Phytol 159:369–381
Hassinen VH, Tervahauta AI, Schat H, Karenlampi SO (2011) Plant metallothioneins–metal chelators with ROS scavenging activity? Plant Biol 13:225–232
Huang Y, Fang Y, Long X, Liu L, Wang J, Zhu J et al (2018a) Characterization of the rubber tree metallothionein family reveals a role in mitigating the effects of reactive oxygen species associated with physiological stress. Tree Physiol 38:911–924
Huang YY, Gong FY, Shen C, He CT, Fu HL, Wang XS et al (2018b) Cloning, characterization and expression analysis of metallothioneins from Ipomoea aquatica and their cultivar-dependent roles in Cd accumulation and detoxification. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 165:450–458
Jaiswal PS, Mittal N, Randhawa GS (2018) Cyamopsis tetragonoloba type 1 metallothionein (CtMT1) gene is upregulated under drought stress and its protein product has an additional C-X-C motif and unique metal binding pattern. Int J Biol Macromol 119:1324–1334
Jin S, Cheng Y, Guan Q, Liu D, Takano T, Liu S (2006) A metallothionein-like protein of rice (rgMT) functions in E. coli and its gene expression is induced by abiotic stresses. Biotechnol Lett 28:1749–1753
Jin S, Xu C, Li G, Sun D, Li Y, Wang X et al (2017) Functional characterization of a type 2 metallothionein gene, SsMT2, from alkaline-tolerant Suaeda salsa. Sci Rep 7:17914
Kim YO, Patel DH, Lee DS, Song Y, Bae HJ (2011) High cadmium-binding ability of a novel Colocasia esculenta metallothionein increases cadmium tolerance in Escherichia coli and tobacco. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 75:1912–1920
Kim SH, Jeong JC, Ahn YO, Lee HS, Kwak SS (2014) Differential responses of three sweetpotato metallothionein genes to abiotic stress and heavy metals. Mol Biol Rep 41:6957–6966
Kisa D, Ozturk L, Tekin S (2016) Gene expression analysis of metallothionein and mineral elements uptake in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) exposed to cadmium. J Plant Res 129:989–995
Kumar G, Kushwaha HR, Panjabi-Sabharwal V, Kumari S, Joshi R, Karan R et al (2012) Clustered metallothionein genes are co-regulated in rice and ectopic expression of OsMT1e-P confers multiple abiotic stress tolerance in tobacco via ROS scavenging. BMC Plant Biol 12:107
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874
Li Y, Chen YY, Yang SG, Tian WM (2015) Cloning and characterization of HbMT2a, a metallothionein gene from Hevea brasiliensis Muell. Arg differently responds to abiotic stress and heavy metals. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 461:95–101
Li LS, Meng YP, Cao QF, Yang YZ, Wang F, Jia HS et al (2016) Type 1 metallothionein (ZjMT) is responsible for heavy metal tolerance in Ziziphus jujuba. Biochemistry (Mosc) 81:565–573
Liu J, Shi X, Qian M, Zheng L, Lian C, Xia Y et al (2015) Copper-induced hydrogen peroxide upregulation of a metallothionein gene, OsMT2c, from Oryza sativa L. confers copper tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Hazard Mater 294:99–108
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408
Lv Y, Deng X, Quan L, Xia Y, Shen Z (2013) Metallothioneins BcMT1 and BcMT2 from Brassica campestris enhance tolerance to cadmium and copper and decrease production of reactive oxygen species in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Soil 367:507–519
Ma F, Ni L, Liu L, Li X, Zhang H, Zhang A et al (2016) ZmABA2, an interacting protein of ZmMPK5, is involved in abscisic acid biosynthesis and functions. Plant Biotechnol J 14:771–782
Mao H, Yu L, Han R, Li Z, Liu H (2016) ZmNAC55, a maize stress-responsive NAC transcription factor, confers drought resistance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol Biochem 105:55–66
Mekawy AMM, Assaha DVM, Munehiro R, Kohnishi E, Nagaoka T, Ueda A et al (2018) Characterization of type 3 metallothionein-like gene (OsMT-3a) from rice, revealed its ability to confer tolerance to salinity and heavy metal stresses. Environ Exp Bot 147:157–166
Mierek-Adamska A, Znajewska Z, Goc A, Dąbrowska GB (2018) Molecular cloning and characterization of Ipomoea nil metallothioneins. Turk J Bot 42:247–256
Mignolet-Spruyt L, Xu E, Idanheimo N, Hoeberichts FA, Muhlenbock P, Brosche M et al (2016) Spreading the news: subcellular and organellar reactive oxygen species production and signalling. J Exp Bot 67:3831–3844
Mir G, Domenech J, Huguet G, Guo WJ, Goldsbrough P, Atrian S et al (2004) A plant type 2 metallothionein (MT) from cork tissue responds to oxidative stress. J Exp Bot 55:2483–2493
Moyle R, Fairbairn DJ, Ripi J, Crowe M, Botella JR (2005) Developing pineapple fruit has a small transcriptome dominated by metallothionein. J Exp Bot 56:101–112
Nishiuchi S, Liu S, Takano T (2007) Isolation and characterization of a metallothionein-1 protein in Chloris virgata Swartz that enhances stress tolerances to oxidative, salinity and carbonate stress in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol Lett 29:1301–1305
Pagani MA, Tomas M, Carrillo J, Bofill R, Capdevila M, Atrian S et al (2012) The response of the different soybean metallothionein isoforms to cadmium intoxication. J Inorg Biochem 117:306–315
Pan Y, Zhai J, Xiong Y, Li J, Du X, Su C et al (2016) Cucumber metallothionein-like 2 (CsMTL2) exhibits metal-binding properties. Genes 7:106
Pan Y, Zhu M, Wang S, Ma G, Huang X, Qiao C et al (2018) Genome-wide characterization and analysis of metallothionein family genes that function in metal stress tolerance in Brassica napus L. Int J Mol Sci 19:2181
Raghavendra AS, Gonugunta VK, Christmann A, Grill E (2010) ABA perception and signalling. Trends Plant Sci 15:395–401
Tombuloglu H, Semizoglu N, Sakcali S, Kekec G (2012) Boron induced expression of some stress-related genes in tomato. Chemosphere 86:433–438
Xu X, Duan L, Yu J, Su C, Li J, Chen D et al (2018) Characterization analysis and heavy metal-binding properties of CsMTL3 in Escherichia coli. FEBS Open Bio 8:1820–1829
Xue T, Li X, Zhu W, Wu C, Yang G, Zheng C (2009) Cotton metallothionein GhMT3a, a reactive oxygen species scavenger, increased tolerance against abiotic stress in transgenic tobacco and yeast. J Exp Bot 60:339–349
Yamauchi T, Fukazawa A, Nakazono M (2017) METALLOTHIONEIN genes encoding ROS scavenging enzymes are down-regulated in the root cortex during inducible aerenchyma formation in rice. Plant Signal Behav 12:e1388976
Yang Z, Wu Y, Li Y, Ling HQ, Chu C (2009) OsMT1a, a type 1 metallothionein, plays the pivotal role in zinc homeostasis and drought tolerance in rice. Plant Mol Biol 70:219–229
Yang J, Wang Y, Liu G, Yang C, Li C (2011) Tamarix hispida metallothionein-like ThMT3, a reactive oxygen species scavenger, increases tolerance against Cd2+, Zn2+, Cu2+, and NaCl in transgenic yeast. Mol Biol Rep 38:1567–1574
Yang M, Zhang F, Wang F, Dong Z, Cao Q, Chen M (2015) Characterization of a type 1 metallothionein gene from the stresses-tolerant plant Ziziphus jujuba. Int J Mol Sci 16:16750–16762
You J, Chan Z (2015) ROS regulation during abiotic stress responses in crop plants. Front Plant Sci 6:1092
Yuan J, Chen D, Ren Y, Zhang X, Zhao J (2008) Characteristic and expression analysis of a metallothionein gene, OsMT2b, down-regulated by cytokinin suggests functions in root development and seed embryo germination of rice. Plant Physiol 146:1637–1650
Zhang A, Zhang J, Ye N, Cao J, Tan M, Jiang M (2010) ZmMPK5 is required for the NADPH oxidase-mediated self-propagation of apoplastic H2O2 in brassinosteroid-induced antioxidant defence in leaves of maize. J Exp Bot 61:4399–4411
Zhang D, Jiang S, Pan J, Kong X, Zhou Y, Liu Y et al (2014a) The overexpression of a maize mitogen-activated protein kinase gene (ZmMPK5) confers salt stress tolerance and induces defence responses in tobacco. Plant Biol (Stuttg) 16:558–570
Zhang H, Liu Y, Wen F, Yao D, Wang L, Guo J et al (2014b) A novel rice C2H2-type zinc finger protein, ZFP36, is a key player involved in abscisic acid-induced antioxidant defence and oxidative stress tolerance in rice. J Exp Bot 65:5795–5809
Zhou J, Goldsbrough PB (1995) Structure, organization and expression of the metallothionein gene family in Arabidopsis. Mol Gen Genet 248:318–328
Zhou Y, Chu P, Chen H, Li Y, Liu J, Ding Y et al (2012) Overexpression of Nelumbo nucifera metallothioneins 2a and 3 enhances seed germination vigor in Arabidopsis. Planta 235:523–537
Zhou B, Yao W, Wang S, Wang X, Jiang T (2014) The metallothionein gene, TaMT3, from Tamarix androssowii confers Cd2+ tolerance in tobacco. Int J Mol Sci 15:10398–10409
Zhou Y, Hu L, Jiang L, Liu H, Liu S (2017a) Molecular cloning and characterization of an ASR gene from Cucumis sativus. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 130:553–565
Zhou Y, Liu S, Yang Z, Yang Y, Jiang L, Hu L (2017b) CsCAT3, a catalase gene from Cucumis sativus, confers resistance to a variety of stresses to Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Biotec Equip 31:886–896
Zhou Y, Zeng L, Chen R, Wang Y, Song J (2018) Genome-wide identification and characterization of stress-associated protein (SAP) gene family encoding A20/AN1 zinc-finger proteins in Medicago truncatula. Arch Biol Sci 70:87–98
Zimeri AM, Dhankher OP, McCaig B, Meagher RB (2005) The plant MT1 metallothioneins are stabilized by binding cadmiums and are required for cadmium tolerance and accumulation. Plant Mol Biol 58:839–855
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Key Project of Youth Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province (20171ACB21025 and 20181ACB20012), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31660385).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
13205_2019_1929_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Fig. S1. Gene structures of the CsMT genes. The gene structures were determined by aligning the CDS sequences with the corresponding gDNA sequences with the GSDS server. UTRs (untranslated regions), CDSs, and introns showed by green rectangles, blue rectangles, and lines, respectively (TIFF 133 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Y., Liu, J., Liu, S. et al. Identification of the metallothionein gene family from cucumber and functional characterization of CsMT4 in Escherichia coli under salinity and osmotic stress. 3 Biotech 9, 394 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-019-1929-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-019-1929-8