Abstract
Metallothioneins (MTs) are cysteine-rich proteins required for heavy metal tolerance in animals and fungi. Recent results indicate that plants also possess functional metallothionein genes. Here we report the cloning and characterization of five metallothionein genes fromArabidopsis thaliana. The position of the single intron in each gene is conserved. The proteins encoded by these genes can be divided into two groups (MT1 and MT2) based on the presence or absence of a central domain separating two cysteine-rich domains. Four of the MT genes (MT1a,MT1c,MT2a andMT2b) are transcribed inArabidopsis. Several lines of evidence suggest that the fifth gene,MT1b, is inactive. There is differential regulation of the MT gene family. MT1 mRNA is expressed highly in roots, moderately in leaves and is barely detected in inflorescences and siliques. MT2a and MT2b mRNAs are more abundant in leaves, inflorescences and in roots from mature plants, but are also detected in roots of young plants, and in siliques. MT2a mRNA is strongly induced in seedlings by CUSO4, whereas MT2b mRNA is relatively abundant in this tissue and levels increase only slightly upon exposure to copper.MT1a andMT1c are located within 2 kb of each other and have been mapped to chromosome 1.MT1b andMT2b map to separate loci on chromosome V, andMT2a is located on chromosome III. The locations of these MT genes are different from that ofCAD1, a gene involved in cadmium tolerance inArabidopsis.
Similar content being viewed by others
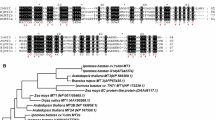
References
Buchanan-Wollaston V (1994) Isolation of cDNA clones for genes that are expressed during leaf senescence inBrassica napus. Identification of a gene encoding a senescence-specific metallothionein-like protein. Plant Physiol 105:839–846
Cherian MG, Chan HM (1993) Biological functions of metallothionein—a review. In: Metallothionein III, Suzuki, KT, Imura N, Kimura M (eds) Metallothionein III, Birkhäuser Verlag, Basel, pp 87–109
Davanloo P, Rosenberg AH, Dunn JJ, Studier, FW (1984) cloning and expression of the gene for bacteriophage T7 RNA Polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:2035–2039
De Framond AJ (1991) A metallothionein-like gene from maize (Zea mays): cloning and characterization. FEBS Lett 290:103–106
De Miranda JR, Thomas MA, Thurman DA, Tomsett AB (1990) Metallothionein genes from the flowering plantMimulus guttatus. FEBS Lett 260:277–280
Doyle J, Doyle M (1990) Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 12:13–15
Evans IM, Gatehouse LN, Gatehouse JA, Robinson NJ, Croy RRD (1990) A gene from pea (Pisum sativum L.) with homology to metallothionein genes. FEBS Lett 262:29–32
Freedman JH, Slice LW, Dixon D, Fire A, Rubin CS (1993) The novel metallothionein genes ofCaenorhabditis elegans. J Biol Chem 268:2554–2564
Furst D, Hu S, Hackett R, Hamer DH (1988) Copper activates metallothionein gene transcription by altering the conformation of a specific DNA binding protein. Cell 55:1219–1223
Goldsbrough PB, Hatch EM, Huang B, Kosinski WG, Dyer WE, Herrman KM, Weller SC (1990) Gene amplification in glyphosate-tolerant tobacco cells. Plant Sci 72:53–62
Hamer DH (1986) Metallothionein. Annu Rev Biochem 55:913–951
Hamer DH, Thiele DJ, Lemontt JE (1985) Function and autoregulation of yeast copperthionein. Science 228:685–690
Henikoff S (1984) Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene 28:351–359
Howden R, Cobbett CS (1992) Cadmium-sensitive mutants ofArabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol 100:100–107
Howden R, Goldsbrough PB, Andersen CR, Cobbett CS (1995) Cadmium-sensitive,cad1 mutants ofArabidopsis thaliana are phytochelatin-deficient. Plant Physiol 107:1059–1066
Kawashima I, Kennedy TD, Chino M, Lane BG (1992) Wheat Ec metallothionein genes: like mammalian Zn2+ metallothionein genes, wheat Zn2+ metallothionein genes are conspicuously expressed during embryogenesis. Eur J Biochem 209:971–976
Kille P, Winge DR, Harwood JL, Kay J (1991) A plant metallothionein produced inE. coli. FEBS Lett 295:171–175
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map distance from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Lander EC, Green P, Abranhamson J, Barlow A, Daly MJ, Lincoln SE, Newburg L (1987) MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181
Leutwiler LS, Meyerowitz EM, Tobin EM (1986) Structure and expression of three light-harvesting chlorophylla/b-binding protein genes inArabidopsis thaliana. Nucleic Acids Res 14:4051–4064
Lister C, Dean C (1993) Recombinant inbred lines for mapping RFLP and phenotypic markers inArabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 4:745–750
Masters BA, Kelly EJ, Quaife CJ, Brinster RL, and Palmfiter RD (1994) Targeted disruption of metallothionein I and II genes increases sensitivity to cadmium. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:584–588
McGrath JM, Jancso MM, Pichersky E (1993) Duplicate sequences with a similarity to expressed genes in the genome ofArabidopsis thaliana Theor Appl Genet 86:880–888
Mehra RK, Tarbet EB, Gray WR, Winge DR (1988) Metal-specific synthesis of two metallothioneins and γ-glutamyl peptides inCandida glabrata. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:8815–8819
Mehra RK, Garey JR, Winge DR (1990) Selective and tandem amplification of a member of the metallothionein gene family inCandida glabrata. J Biol Chem 265:6369–6375
Mehra RK, Thorvaldsen JL, Macreadie IG, Winge DR (1992) Disruption analysis of metallothionein-encoding genes inCandida glabrata. Gene 114:75–80
Mett VL, Lochhead LP, Reynolds HS (1993) Copper-controllable gene expression system for whole plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:4567–4571
Michalska AE, Choo KHA (1993) Targeting and germ-line transmission of a null mutation at the metallothionein I and II loci in mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:8088–8092
Morris CE, Klement JF, McAllister WT (1986) Cloning and expression of the bacteriophage T3 RNA polymerase gene. Gene 41:193–200
Nam HG, Giraudat J, den Boer B, Moonan F, Loos WDB, Hauge BM, Goodman HM (1989) Restriction fragment length polymorphism linkage map ofArabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 1:699–705
Palmiter RD, Findley SD, Whitmore TE, Durnam DM (1992) MT-III, a brain-specific member of the metallothionein gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:6333–6337
Palmiter RD, Sandgren EP, Koeller DM, Findley SD and Brinster RL (1993) Metallothionein genes and their regulation in trans-genic mice. In: Suzuki KT, Imura N, Kimura M (eds) Metallothionein III: biological roles and medical implications. Birkhauser, Basel, pp 399–406
Quaife CJ, Findley SD, Erickson JC, Froelick GJ, Kelly EJ, Zambrwicz BP, Palmiter RD (1994) Induction of a new metallothionein isoform (MT-IV) occurs during differentiation of stratified squamous epithelia. Biochemistry 33:7250–7259
Richards RI, Heguy A, Karin M (1984) Structural and functional analysis of the human metallothionein-IA gene: differential induction by metal ions and glucocorticoids. Cell 37:263–272
Robinson NJ, Tommey AM, Kuske C, Jackson PJ (1993) Plant metallothioneins. Biochem J 295:1–10
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Gold Spring Harbor, New York
Snowden KC, Gardner RC (1993) Five genes induced by aluminum in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) roots. Plant Physiol 103:855–861
Snustad DP, Haas NA, Kopczak SD, Silflow CD (1992) The small genome of Arabidopsis contains at least nine expressedβ-tubulin genes. Plant Cell 4:549–556
Tabor S, Richardson CC (1985) A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:1074–1078
Thiele DJ (1992) Metal-regulated transcription in eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res 20:1183–1191
Tommey AM, Shi J, Lindsay WP, Urwin PE, Robinson NJ (1991) Expression of the pea genePsMT A inE. coli: metal-binding properties of the expressed protein. FEBS Lett 292:48–52
Zhou J, Goldsbrough PB (1993) An Arabidopsis gene with homology to glutathioneS-transferases is regulated by ethylene. Plant Mol Biol 22:517–523
Zhou J, Goldsbrough PB (1994) Functional homologs of fungal metallothionein genes fromArabidopsis. Plant Cell 6:875–884
Zhou P, Thiele D (1991) Isolation of a metal activated transcription factor fromCandida glabrata by complementation inSaccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:6112–6116
Zhou P, Szczypka MS, Sosinowski T, Thiele DJ (1992) Expression of a yeast metallothionein gene family is activated by a single metalloregulatory transcriptional factor. Mol Cell Biol 12:3766–3775
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by A. Kondorosi
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, J., Goldsbrough, P.B. Structure, organization and expression of the metallothionein gene family inArabidopsis . Molec. Gen. Genet. 248, 318–328 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02191599
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02191599



