Abstract
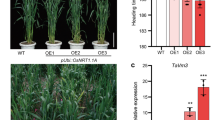
Metallothioneins (MTs) are small, cysteine-rich, metal-binding proteins that may be involved in metal homeostasis and detoxification in both plants and animals. OsMT1a, encoding a type 1 metallothionein, was isolated via suppression subtractive hybridization from Brazilian upland rice (Oryza sativa L. cv. Iapar 9). Expression analysis revealed that OsMT1a predominantly expressed in the roots, and was induced by dehydration. Interestingly, the OsMT1a expression was also induced specifically by Zn2+ treatment. Both transgenic plants and yeasts harboring OsMT1a accumulated more Zn2+ than wild type controls, suggesting OsMT1a is most likely to be involved in zinc homeostasis. Transgenic rice plants overexpressing OsMT1a demonstrated enhanced tolerance to drought. The examination of antioxidant enzyme activities demonstrated that catalase (CAT), peroxidase (POD) and ascorbate peroxidase (APX) were significantly elevated in transgenic plants. Furthermore, the transcripts of several Zn2+-induced CCCH zinc finger transcription factors accumulated in OsMT1a transgenic plants, suggesting that OsMT1a not only participates directly in ROS scavenging pathway but also regulates expression of the zinc finger transcription factors via the alteration of Zn2+ homeostasis, which leads to improved plant stress tolerance.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abeles FB, Biles CL (1991) Characterization of peroxidases in lignifying peach fruit endocarp. Plant Physiol 95:269–273. doi:10.1104/pp.95.1.269
Aebi HE (1983) Catalase. In: Bergmeyer H (ed) Methods of enzymatic analysis, VCH Verlagsgesellschaft mbH, Weinheim, pp 273–282
Akashi K, Nishimura N, Ishida Y, Yokota A (2004) Potent hydroxyl radical-scavenging activity of drought-induced type-2 metallothionein in wild watermelon. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 323:72–78. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.08.056
Apel K, Hirt H (2004) Reactive oxygen species: metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55:373–399
Arrigoni O, De GL, Tommasi F, Liso R (1992) Changes in the ascorbate system during seed development of Vicia faba L. Plant Physiol 99:235–238. doi:10.1104/pp.99.1.235
Bhalerao R, Keskitalo J, Sterky F, Erlandsson R, Bjorkbacka H, Birve SJ, Karlsson J, Gardestrom P, Gustafsson P, Lundeberg J, Jansson S (2003) Gene expression in autumn leaves. Plant Physiol 131:430–442. doi:10.1104/pp.012732
Bor M, Özdemir F, Türkan I (2003) The effect of salt stress on lipid peroxidation and antioxidants in leaves of sugar beet Beta vulgaris L. and wild beet Beta maritima L. Plant Sci 164:77–84
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Bremner I, Beattie JH (1990) Metallothionein and the trace minerals. Annu Rev Nutr 10:63–83. doi:10.1146/annurev.nu.10.070190.000431
Brkljacic JM, Samardzic JT, Timotijevic GS, Maksimovic VR (2004) Expression analysis of buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum Moench) metallothionein-like gene (MT3) under different stress and physiological conditions. J Plant Physiol 161:741–746. doi:10.1078/0176-1617-01211
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N (1987) Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162:156–159. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(87)90021-2
Chyan CL, Lee TT, Liu CP, Yang YC, Tzen JT, Chou WM (2005) Cloning and expression of a seed-specific metallothionein-like protein from sesame. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 69:2319–2325. doi:10.1271/bbb.69.2319
Clemens S (2001) Molecular mechanisms of plant metal tolerance and homeostasis. Planta 212:475–486. doi:10.1007/s004250000458
Clendennen SK, May GD (1997) Differential gene expression in ripening banana fruit. Plant Physiol 115:463–469. doi:10.1104/pp.115.2.463
Cobbett C, Goldsbrough P (2002) Phytochelatins and metallothioneins: roles in heavy metal detoxification and homeostasis. Annu Rev Plant Biol 53:159–182. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.53.100301.135154
de Azevedo Neto AD, Prisco JT, Eneas-Filho J, Medeiros JV, Gomes-Filho E (2005) Hydrogen peroxide pre-treatment induces salt-stress acclimation in maize plants. J Plant Physiol 162:1114–1122
de Framond AJ (1991) A metallothionein-like gene from maize (Zea mays). Cloning and characterization. FEBS Lett 290:103–106. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(91)81236-2
Domenech J, Mir G, Huguet G, Capdevila M, Molinas M, Atrian S (2005) Plant metallothionein domains: functional insight into physiological metal binding and protein folding. Biochimie 88(6):583–593
Evans IM, Gatehouse LN, Gatehouse JA, Robinson NJ, Croy RR (1990) A gene from pea (Pisum sativum L.) with homology to metallothionein genes. FEBS Lett 262:29–32. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(90)80145-9
Foley RC, Singh KB (1994) Isolation of a Vicia faba metallothionein-like gene: expression in foliar trichomes. Plant Mol Biol 26:435–444. doi:10.1007/BF00039552
Gietz RD, Schiestl RH (1991) Applications of high efficiency lithium acetate transformation of intact yeast cells using single-stranded nucleic acids as carrier. Yeast 7:253–263. doi:10.1002/yea.320070307
Guo WJ, Bundithya W, Goldsbrough PB (2003) Characterization of the Arabidopsis metallothionein gene family: tissue-specific expression and induction during senescence and in response to copper. New Phytol 159:369–381. doi:10.1046/j.1469-8137.2003.00813.x
Hall JL (2002) Cellular mechanisms for heavy metal detoxification and tolerance. J Exp Bot 53:1–11. doi:10.1093/jexbot/53.366.1
Hamer DH (1986) Metallothionein. Annu Rev Biochem 55:913–951
Hasegawa S (1963) Upland rice. In: Togari Y (ed) Crop science, a treatise, vol 1. Yokendo, Tokyo, pp 1–124
Hsieh HM, Liu WK, Huang PC (1995) A novel stress-inducible metallothionein-like gene from rice. Plant Mol Biol 28:381–389. doi:10.1007/BF00020388
Hsieh HM, Liu WK, Chang A, Huang PC (1996) RNA expression patterns of a type 2 metallothionein-like gene from rice. Plant Mol Biol 32:525–529. doi:10.1007/BF00019104
Hudspeth RL, Hobbs SL, Anderson DM, Rajasekaran K, Grula JW (1996) Characterization and expression of metallothionein-like genes in cotton. Plant Mol Biol 31:701–705. doi:10.1007/BF00042243
Kawasaki S, Borchert C, Deyholos M, Wang H, Brazille S, Kawai K, Galbraith D, Bohnert HJ (2001) Gene expression profiles during the initial phase of salt stress in rice. Plant Cell 13:889–905
Kim SH, Hong JK, Lee SC, Sohn KH, Jung HW, Hwang BK (2004) CAZFP1, Cys2/His2-type zinc-finger transcription factor gene functions as a pathogen-induced early-defense gene in Capsicum annuum. Plant Mol Biol 55:883–904
Koh M, Kim HJ (2001) The effect of metallothionein on the activity of enzymes involved in removal of reactive oxygen species. Bull Korean Chem Soc 22:362–366
Lane BG, Kajioka R, Kennedy TD (1987) The wheat germ Ec protein is a zinc-containing metallothionein. Biochem Cell Biol 65:1001–1005
Ledger SE, Gardner RC (1994) Cloning and characterization of five cDNAs for genes differentially expressed during fruit development of kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa var. deliciosa). Plant Mol Biol 25:877–886. doi:10.1007/BF00028882
Lee J, Shim D, Song WY, Hwang I, Lee Y (2004) Arabidopsis metallothioneins 2a and 3 enhance resistance to cadmium when expressed in Vicia faba guard cells. Plant Mol Biol 54:805–815. doi:10.1007/s11103-004-0190-6
Liu X, Bai X, Wang X, Chu C (2007) OsWRKY71, a rice transcription factor, is involved in rice defense response. J Plant Physiol 164:969–979
Mahajan S, Tuteja N (2005) Cold, salinity and drought stresses: an overview. Arch Biochem Biophys 444:139–158. doi:10.1016/j.abb.2005.10.018
Margoshes M, Vallee BL (1957) A cadmium protein from equine kidney cortex. J Chem Soc 79:4813–4819. doi:10.1021/ja01574a064
Matsumura H, Nirasawa S, Terauchi R (1999) Technical advance: transcript profiling in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings using serial analysis of gene expression (SAGE). Plant J 20:719–726. doi:10.1046/j.1365-313X.1999.00640.x
Mejare M, Bulow L (2001) Metal-binding proteins and peptides in bioremediation and phytoremediation of heavy metals. Trends Biotechnol 19:67–73. doi:10.1016/S0167-7799(00)01534-1
Merrifield ME, Ngu T, Stillman MJ (2004) Arsenic binding to Fucus vesiculosus metallothionein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 324:127–132. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.09.027
Miller JD, Arteca RN, Pell EJ (1999) Senescence-associated gene expression during ozone-induced leaf senescence in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 120:1015–1024
Mir G, Domenech J, Huguet G, Guo WJ, Goldsbrough P, Atrian S, Molinas M (2004) A plant type 2 metallothionein (MT) from cork tissue responds to oxidative stress. J Exp Bot 55:2483–2493. doi:10.1093/jxb/erh254
Mittova V, Tal M, Volokita M, Guy M (2002) Salt stress induces up-regulation of an efficient chloroplast antioxidant system in the salt-tolerant wild tomato species Lycopersicon pennellii but not in the cultivated species. Physiol Plant 115:393–400
Navabpour S, Morris K, Allen R, Harrison E, Mackerness S, Buchanan-Wollaston V (2003) Expression of senescence-enhanced genes in response to oxidative stress. J Exp Bot 54:2285–2292. doi:10.1093/jxb/erg267
Oztur ZN, Talame V, Deyholos M, Michalowski CB, Galbraith DW, Gozukirmizi N, Tuberosa R, Bohnert HJ (2002) Monitoring large-scale changes in transcript abundance in drought- and salt-stressed barley. Plant Mol Biol 48:551–573. doi:10.1023/A:1014875215580
Pastori GM, Foyer CH (2002) Common components, networks, and pathways of cross-tolerance to stress. The central role of “redox” and abscisic acid-mediated controls. Plant Physiol 129:460–468
Polle A, Rennenberg H (1993) Significance of antioxidants in plan adaption to environmental stress. In: Mansfield T, Fowden L, Stoddard F (eds) Plant adaptation to environmental stress. Chapman & Hall, London, pp 263–273
Rabbani MA, Maruyama K, Abe H, Khan MA, Katsura K, Ito Y, Yoshiwara K, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2003) Monitoring expression profiles of rice genes under cold, drought, and high-salinity stresses and abscisic acid application using cDNA microarray and RNA gel-blot analyses. Plant Physiol 133:1755–1767. doi:10.1104/pp.103.025742
Rauser WE (1999) Structure and function of metal chelators produced by plants: the case for organic acids, amino acids, phytin, and metallothioneins. Cell Biochem Biophys 31:19–48. doi:10.1007/BF02738153
Reid SJ, Ross GS (1997) Up-regulation of two cDNA clones encoding metallothionein-like proteins in apple fruit during cool storage. Physiol Plantarum 100:183–189. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3054.1997.tb03471.x
Robinson NJ, Tommey AM, Kuske C, Jackson PJ (1993) Plant metallothioneins. Biochem J 295(Pt 1):1–10
Robinson NJ, Wilson JR, Turner JS (1996) Expression of the type 2 metallothionein-like gene MT2 from Arabidopsis thaliana in Zn(2+)-metallothionein-deficient Synechococcus PCC 7942: putative role for MT2 in Zn2+ metabolism. Plant Mol Biol 30:1169–1179. doi:10.1007/BF00019550
Roosens NH, Bernard C, Leplae R, Verbruggen N (2004) Evidence for copper homeostasis function of metallothionein (MT3) in the hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens. FEBS Lett 577:9–16. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2004.08.084
Sairam RK, Rao KV, Srivastava GC (2002) Differential response of wheat genotypes to long-term salinity stress in relation to oxidative stress, antioxidant activity and osmolyte concentration. Plant Sci 163:1037–1046
Sakamoto H, Maruyama K, Sakuma Y, Meshi T, Iwabuchi M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2004) Arabidopsis Cys2/His2-type zinc-finger proteins function as transcription repressors under drought, cold, and high-salinity stress conditions. Plant Physiol 136:2734–2746. doi:10.1104/pp.104.046599
Schor-Fumbarov T, Goldsbrough PB, Adam Z, Tel-Or E (2005) Characterization and expression of a metallothionein gene in the aquatic fern Azolla filiculoides under heavy metal stress. Planta 223:69–76. doi:10.1007/s00425-005-0070-6
Segal DJ, Stege JT, Barbas CFIII (2003) Zinc fingers and a green thumb: manipulating gene expression in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:163–168. doi:10.1016/S1369-5266(03)00007-4
Takatsuji H (1999) Zinc-finger proteins: the classical zinc finger emerges in contemporary plant science. Plant Mol Biol 39:1073–1078. doi:10.1023/A:1006184519697
Togawa HA (1939) On the identification of drought resistance of upland rice varieties by the seedling types. Agric Hortic 14:2729–2738
Vaidyanathan H, Sivakumar P, Chakrabarty R, Thomas G (2003) Scavenging of reactive oxygen species in NaCl-stressed rice (Oryza sativa L.): differential response in salt-tolerant and sensitive varieties. Plant Sci 165:1411–1418
Wong HL, Sakamoto T, Kawasaki T, Umemura K, Shimamoto K (2004) Down-regulation of metallothionein, a reactive oxygen scavenger, by the small GTPase OsRac1 in rice. Plant Physiol 135:1447–1456. doi:10.1104/pp.103.036384
Wu YR, Wang QY, Ma YM, Chu CC (2005) Isolation and expression analysis of salt up-regulated ESTs in upland rice using PCR-based subtractive suppression hybridization method. Plant Sci 168:847–853. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2004.10.020
Yu LH, Umeda M, Liu JY, Zhao NM, Uchimiya H (1998) A novel MT gene of rice plants is strongly expressed in the node portion of the stem. Gene 206:29–35. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00577-5
Zhou J, Goldsbrough PB (1994) Functional homologs of fungal metallothionein genes from Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 6:875–884
Zhou GK, Xu YF, Liu JY (2005) Characterization of a rice class II metallothionein gene: tissue expression patterns and induction in response to abiotic factors. J Plant Physiol 162:686–696. doi:10.1016/j.jplph.2004.11.006
Zimeri AM, Dhankher OP, McCaig B, Meagher RB (2005) The plant MT1 metallothioneins are stabilized by binding cadmiums and are required for cadmium tolerance and accumulation. Plant Mol Biol 58:839–855. doi:10.1007/s11103-005-8268-3
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from Chinese Academy of Sciences (grant numbers: KSCX2-YW-N-010 & KSCX2-YW-N-056), and National Science Foundation of China (grant numbers: 30825029 & 30621001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Zhao Yang and Yaorong Wu have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Z., Wu, Y., Li, Y. et al. OsMT1a, a type 1 metallothionein, plays the pivotal role in zinc homeostasis and drought tolerance in rice. Plant Mol Biol 70, 219–229 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-009-9466-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-009-9466-1