Abstract
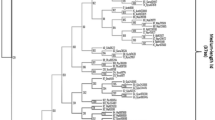
The application of bioinformatics in lipase research has the potential to discover robust members from different genomic/metagenomic databses. In this study, we explored the diversity and distribution of alkaliphilic lipases in archaea domain and metagenome data sets through phylogenetic survey. Reconstructed ancestral sequence of alkaphilic lipase was used to search the homologous alkaliphilic lipases among the archaea and metagenome public databases. Our investigation revealed a total 21 unique sequences of new alkaliphilic lipases in the archaeal and environmental metagenomic protein databases that shared significant sequence similarity to the bacterial alkaliphilic lipases. Most of the identified new members of alkaliphilic lipases belong to class Haloarchaea. The searched list of homologs also comprised of one characterized lipase from alkalohyperthermophilic Archaeoglobus fulgidus. All the newly identified alkaliphilic lipase members showed conserved pentapeptide [X-His-Ser-X-Gly] motif, a key feature of lipase family. Furthermore, detailed analysis of all these new sequences showed homology either with thermostable or alkalophilic lipases. The reconstructed ancestral sequence-based searches increased the sensitivity and efficacies to detect remotely homologous sequences. We hypothesize that this study can enrich our current knowledge on lipases in designing more potential thermo-alkaliphilic lipases for industrial applications.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abol Fotouh DM, Bayoumi RA, Mohamed Hassan A (2016) Production of thermoalkaliphilic lipase from Geobacillus thermoleovorans DA2 and application in leather industry. Enzym Res 2016:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/9034364
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Brenner S (1988) The molecular evolution of genes and proteins: a tale of two serines. Nature 334:528–530
Chen CK, Lee GC, Ko TP, Guo RT, Huang LM, Liu HJ, Ho YF, Shaw JF, Wang AH (2009) Structure of the alkalohyperthermophilic Archaeoglobusfulgidus lipase contains a unique C-terminal domain essential for long-chain substrate binding. J Mol Biol 390:672–685
Collins LJ, Poole AM, Penny D (2003) Using ancestral sequences to uncover potential gene homologues. Appl Bioinform 2:S85–S95
Cunningham CW, Omland KE, Oakley TH (1998) Reconstructing ancestral character states: a critical reappraisal. Trends Ecol Evol 13:361–366
Demirjian DC, Moris F, Cassidy CS (2001) Enzymes from extremophiles. Curr Opin Chem Biol 5:144–151
Derewenda Z, Derewenda U (1991) Relationships among serine hydrolases: evidence for a common structural motif in triacylglyceride lipases and esterases. Biochem Cell Biol 69:842–851
Duflos M, Goutx M, Van Wambeke F (2009) Determination of lipid degradation by marine lipase-producing bacteria: critical evaluation of lipase activity assays. Lipids 44:1113–1124
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res 32:1792–1797
Elias I, Tuller T (2007) Reconstruction of ancestral genomic sequences using likelihood. J Comput Biol 14:216–237
Haki GD, Rakshit SK (2003) Developments in industrially important thermostable enzymes: a review. Bioresour Technol 89:17–34
Hasan F, Shah AA, Hameed A (2006) Industrial applications of microbial lipases. Enzym Microb Technol 39:235–251
Huang Y, Niu B, Gao Y, Fu L, Li W (2010) CD-HIT Suite: a web server for clustering and comparing biological sequences. Bioinformatics 26:680–682
Ingham AB, Pemberton JM (1995) A lipase of Aeromonas hydrophila showing nonhemolytic phospholipase C activity. Curr Microbiol 31:28–33
Jeong ST, Kim HK, Kim SJ, Chi SW, Pan JG, Oh TK, Ryu SE (2002) Novel zinc-binding center and a temperature switch in the Bacillus stearothermophilus L1 lipase. J Biol Chem 277:17041–17047
Jones DT, Taylor WR, Thornton JM (1992) The rapid generation of mutation data matrices from protein sequences. Comput Appl Biosci 8:275–282
Kadri T, Rouissi T, Magdouli S, Brar SK, Hegde K, Khiari Z, Daghrir R, Lauzon JM (2018) Production and characterization of novel hydrocarbon degrading enzymes from Alcanivorax borkumensis. Int J Biol Macromol. 112:230–240
Koshi JM, Goldstein RA (1996) Probabilistic reconstruction of ancestral protein sequences. J Mol Evol 42:313–320
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K (2018) MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 35:1547–1549
Lesuisse E, Schanck K, Colson C (1993) Purification and preliminary characterization of the extracellular lipase of Bacillus subtilis 168, an extremely basic pH-tolerant enzyme. Eur J Biochem 216:155–160
Littlechild JA (2015) Archaeal enzymes and applications in industrial biocatalysts, Archaea 2015:10
Lobb B, Kurtz D, Moreno-Hagelsieb G, Doxey AC (2015) Remote homology and the functions of metagenomic dark matter. Front Genet 6:234
Margesin R, Schinner F (2001) Potential of halotolerant and halophilic microorganisms for biotechnology. Extremophiles 5:73–83
Meghwanshi GK, Vashishtha A (2018) Biotechnology of fungal lipases. In: Fungi and their role in sustainable development: current perspectives. Springer Nature Singapore pp 383–411
Ollis DL, Cheah E, Cygler M, Dijkstra B, Frolow F, Franken SM et al. (1992) The alpha/beta hydrolase fold. Protein Eng 5:197–211
Oren A (2002) Diversity of halophilic microorganisms: environments, phylogeny, physiology, and applications. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 28:56–63
Ozcan B, Ozyilmaz G, Cokmus C, Caliskan M (2009) Characterization of extracellular esterase and lipase activities from five halophilic archaeal strains. J Ind Microbiol Biotechno 36:105–110
Sanchez-Porro C, Martin S, Mellado E, Ventosa A (2003) Diversity of moderately halophilic bacteria producing extracellular hydrolytic enzymes. J Appl Microbio l94:295–300
Saw JH, Spang A, Zaremba-Niedzwiedzka K, Juzokaite L, Dodsworth JA, Murugapiran SK, Colman DR, Takacs-Vesbach C, Hedlund BP, Guy L, Ettema TJ (2015) Exploring microbial dark matter to resolve the deep archaeal ancestry of eukaryotes. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 2:370
Saxena RK, Agarwal L, Meghwanshi GK (2005) Diversity of fungal and yeast lipases: present and future scenario for the 21st century. In: Microbial diversity: current perspectives and potential applications. I.K. International Pvt. Ltd 791–814. ISBN 9788188237432
Sharma PK, Kumar R, Kumar R, Mohammad O, Singh R, Kaur J (2011) Engineering of a metagenome derived lipase towards thermal tolerance: effect of aspargine to lysine mutation on the protein surface. Gene 491:264–271
Sharma PK, Kumar R, Garg P, Kaur J (2015) Insights into controlling role of substitution mutation, E315G on thermostability of a lipase cloned from metagenome of hot spring soil. 3Biotech 4:189–196
Shu ZY, Jiang H, Lin RF, Jiang YM, Lin L, Huang JZ (2010) Technical methods to improve yield, activity and stability in the development of microbial lipases. J Mol Catal B: Enzym 62:1–8
Treichel H, de Oliveira D, Mazutti MA, Di Luccio M, Oliveira JV (2010) A review on microbial lipases production. Food Bioprocess Tech 3:182–196
Verma S, Meghwanshi GK, Kumar R (2018) Structural homogeneity in microbial lipases. Microbiol Curr Res 2:12–13
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to Dr. Athar Alam from Umeå University, Sweden, for his help to improve the language of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest for publishing this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Verma, S., Kumar, R. & Meghwanshi, G.K. Identification of new members of alkaliphilic lipases in archaea and metagenome database using reconstruction of ancestral sequences. 3 Biotech 9, 165 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-019-1693-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-019-1693-9