Abstract
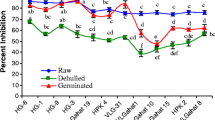
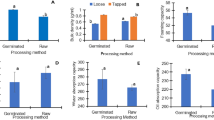
Horsegram is an underutilized pulse, traditionally used for treating various disorders like kidney stones, diabetes and joint pain. The present study was undertaken to optimize the soaking and germination conditions, to decrease the anti-nutritional factors and at the same time maintaining the nutritional properties of horsegram. Horsegram seeds were soaked for 6, 12 and 18 h followed by germination for 0, 24 and 48 h under different illumination conditions i.e., light and dark respectively. The soaked and germinated samples were dried in laboratory drier at 55 °C until constant moisture was achieved and was further analyzed for various quality attributes. Almost all the physicochemical and functional characteristics were significantly affected by both soaking and germination, whereas, germination done in light and dark conditions, exerted significant effect on the ascorbic acid content, total protein, total phenols, antioxidant activity and tannin content only. Based on the quality attributes, it was found that treatment having 18 h soaking and 48 h germination in the presence of light was the best where maximum decrease in the anti-nutritional factors was observed. Moreover, there was an increase in ascorbic acid, total protein content and a decrease in the anti-nutritional factors such as oxalate and tannin content. Thus, it is concluded that 18 h soaking and 48 h germination in the presence of light can be considered as the optimum conditions to increase the nutritional content of horsegram flour, which can further be utilized for the preparation of different value-added food products.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
AACC (2005) Approved methods of the AACC. American Association of Cereal Chemists, St. Paul
Adedeji OE, Oyinloye OD, Ocheme OB (2014) Effects of germination time on the functional properties of maize flour and the degree of gelatinization of its cookies. Afr J Food Sci 8:42–47. doi:10.5897/ajfs2013.1106
Anderson R, Cronshaw J (1970) Sieve-plate pores in tobacco and bean. Planta 91:173–180. doi:10.1007/bf00385475
AOAC (2005) Official methods of analysis, 18th edn. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Washington
Brand-Williams W, Cuvelier M, Berset C (1995) Use of a free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. Food Sci Technol LEB 28:25–30. doi:10.1016/s0023-6438(95)80008-5
Chandra S, Singh S, Kumari D (2015) Evaluation of functional properties of composite flours and sensorial attributes of composite flour biscuits. J Food Sci Technol Mys. doi:10.1007/s13197-014-1427-2
Embaby HE-S (2010) Effect of heat treatments on certain antinutrients and in vitro protein digestibility of peanut and sesame seeds. Food Sci Technol Res 17:31–38. doi:10.3136/fstr.17.31
Gat Y, Ananthanarayan L (2015) Physicochemical, phytochemical and nutritional impact of fortified cereal-based extrudate snacks. Nutrafoods 14:141–149. doi:10.1007/s13749-015-0036-7
Ghumman A, Kaur A, Singh N (2016) Impact of germination on flour, protein and starch characteristics of lentil (Lens culinari) and horsegram (Macrotyloma uniflorum L.) lines. LWT Food Sci Technol 65:137–144. doi:10.1016/j.lwt.2015.07.075
Jung T, Kim W-S, Choi CK (2005) Crystal structure and morphology control of calcium oxalate using biopolymeric additives in crystallization. J Cryst Growth 279:154–162. doi:10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2005.02.010
Kadam SS, Salunkhe DK, Maga JA (1985) Nutritional composition, processing, and utilization of horsegram and moth bean. CRC Crit Rev Food Sci 22:1–26. doi:10.1080/10408398509527407
Kajihausa O, Fasasi R, Atolagbe Y (2014) Effect of different soaking time and boiling on the proximate composition and functional properties of sprouted sesame seed flour. Niger Food J 32:8–15. doi:10.1016/s0189-7241(15)30112-0
Khattak AB, Zeb A, Bibi N (2008) Impact of germination time and type of illumination on carotenoidcontent, protein solubility and in vitro protein digestibility of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) sprouts. Food Chem 109:797–801. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.01.046
Kumar NR, Reedy AN, Rao KN (1979) Levels of phenolic substances on the leachionted in cicezo seed. J Exp Biol 17:114–116
Kuo FE, Taylor AF (2004) A potential natural treatment for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: evidence from a national study. Am J Public Health 94:1580–1586. doi:10.2105/ajph.94.9.1580
Marconi E, Ruggeri S, Cappelloni M et al (2000) Physicochemical, nutritional, and microstructural characteristics of chickpeas (Cicer arietinum L.) and common beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) following microwave cooking. J Agric Food Chem 48:5986–5994. doi:10.1021/jf0008083
Martincabrejas M, Diaz M, Aguilera Y et al (2008) Influence of germination on the soluble carbohydrates and dietary fibre fractions in non-conventional legumes. Food Chem 107:1045–1052. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2007.09.020
Modgil R, Mankotia K, Gupta R, Malhotra SR, Tanwar B (2012) Carbohydrates, minerals, antinutritional constituents and in vivo protein quality of domestically processed cow peas (Vigna ungiculata). Legume Res 35(3):214–219
Modgil R, Joshi R, Tanwar B (2016) Effect of domestic processing on physico chemical and nutritional quality of fenugreek cultivars. Asian J Dairy Food Res 35:338–340. doi:10.18805/ajdfr.v35i4.6637
Moorthy SN, Ramanujam T (1986) Variation in properties of starch in cassava varieties in relation to age of the crop. Starch Stärke 38:58–61. doi:10.1002/star.19860380206
Mubarak AE (2005) Nutritional composition and antinutritional factors of mung bean seeds (Phaseolus aureus) as affected by some home traditional processes. Food Chem 89:489–495. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2004.01.007
Murugkar DA, Gulati P, Gupta C (2013) Effect of sprouting on physical properties and functional and nutritional components of multi-nutrient mixes. Int J Food Nutr Sci 2(2):2–15
Narsih, Yunianta, Harijon (2012) The study of germination and soaking time to improve nutritional quality of sorghum seed. Int Food Res J 4:1429–1432
Nath JP, Rao MSN (1981) Functional properties of guar proteins. J Food Sci 46:1255–1259. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2621.1981.tb03034.x
Pal RS, Bhartiya A, ArunKumar R, Kant L, Aditya JP, Bisht JK (2016) Impact of dehulling and germination on nutrients, antinutrients, and antioxidant properties in horsegram. J Food Sci Technol Mysore 53:337–347
Parmar N, Singh N, Kaur A, Thakur S (2017) Comparison of color, anti-nutritional factors, minerals, phenolic profile and protein digestibility between hard-to-cook and easy-to-cook grains from different kidney bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) accessions. J Food Sci Technol 54:1023–1034
Pérez-Balibrea S, Moreno DA, García-Viguera C (2008) Influence of light on health-promoting phytochemicals of broccoli sprouts. J Sci Food Agric 88:904–910. doi:10.1002/jsfa.3169
Prasad SK, Singh MK (2015) Horse gram-an underutilized nutraceutical pulse crop: a review. J Food Sci Technol Mysore 52:2489–2499
Reddy N, Pierson M (1994) Reduction in antinutritional and toxic components in plant foods by fermentation. Food Res Int 27:281–290. doi:10.1016/0963-9969(94)90096-5
Sadasivam S, Manickam AC (1991) Biochemical method for agricultural sciences. Wiley Eastern Limited, New Dehli
Silva HC, Braga GL (1982) Effect of soaking and cooking on the oligosaccharide content of dry beans (Phaseolus vulgaris, L.). J Food Sci 47:924–925
Singh AK, Rehal J, Kaur A, Jyot G (2013) Enhancement of Attributes of Cereals by Germination and Fermentation: A Review. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition 55:1575–1589. doi:10.1080/10408398.2012.706661
Singh B, Singh JP, Shevkani K, Singh N, Kaur A (2016) Bioactive constituents in pulses and their health benefits. J Food Sci Technol 54:858–870
Singleton VL, Rossi JA (1965) Colorimetry of total phenolics with phosphomolybdic–phosphotungstic acid reagents. Am J Enol Vitic 16(3):144–158
Smirnoff N (2000) Ascorbic acid: metabolism and functions of a multi-facetted molecule. Curr Opin Plant Biol 3:229–235. doi:10.1016/S1369-5266(00)80070-9
Sosulski FW (1962) The centrifuge method for determining flour absorption in hard red spring wheats. Cereal Chem 39:344–347
Sreerama YN, Sashikala VB, Pratape VM, Singh V (2012) Nutrients and antinutrients in cowpea and horsegram flours in comparison to chickpea flour: evaluation of their flour functionality. Food Chem 131:462–468. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.09.008
Stuart BH (2004) Infrared spectroscopy: fundamentals and applications. Wiley, Hoboken
Urbano G, Aranda P, Vilchez A et al (2005) Effects of germination on the composition and nutritive value of proteins in Pisum sativum, L. Food Chem 93:671–679. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2004.10.045
Vidal-Valverde CF, Frias J, Sierra I et al (2002) New functional legume foods by germination: effect on the nutritive value of beans, lentils and peas. Eur Food Res Technol 215:472–477. doi:10.1007/s00217-002-0602-2
Wang JC, Kinsella JE (1976) Functional properties of alfalfa leaf protein: foaming. J Food Sci 41:498–501. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2621.1976.tb00655.x
Williams PC, Nakoul H, Singh KB (1983) Relationship between cooking time and some physical characteristics in chickpeas (Cicer arietinum L.). J Sci Food Agric 34:492–496. doi:10.1002/jsfa.2740340510
Xiong J, Wang Y, Xue Q, Wu X (2011) Synthesis of highly stable dispersions of nanosized copper particles using l-ascorbic acid. Green Chem 13:900. doi:10.1039/c0gc00772b
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the Department of Food Technology and Nutrition, School of Agriculture, Lovely Professional University, Phagwara (Punjab) for providing infrastructural facility and financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Handa, V., Kumar, V., Panghal, A. et al. Effect of soaking and germination on physicochemical and functional attributes of horsegram flour. J Food Sci Technol 54, 4229–4239 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-017-2892-1
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-017-2892-1