Abstract
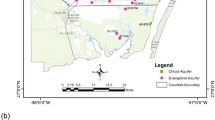
Submarine groundwater discharge (SGD) is a complex hydrological process which occurs at the continent–ocean interface and plays an important role in coastal dynamics. The main objective of this study was to detect groundwater discharge from the sandy freshwater aquifer towards the Atlantic Ocean along the western coast of Buenos Aires Province (Argentina) using multiple methods. 222Rn as a tracer, electrical resistivity tomography (ERT), and hydrogeological information were applied to detect and quantify SGD. 222Rn activity was measured in wells, at the beach (tidal pools and surf zone) and along a transect ~ 200 m from the coastline coincident with geoelectrical measurements. Groundwater depth was measured in wells, and from these data, groundwater contour maps were made. 222Rn activity in wells varies from 16 and 173 dpm/L; at the beach, the values are between 28 and 48 dpm/L; and along the coastline, they oscillate between 1.3 and 20.5 dpm/L. The ERT shows a high resistivity layer close to 3–4 m depth from the sea floor indicating the presence of freshwater. Groundwater contour maps show discharge toward the continental plain to the west and toward the sea to the east. There is no precedent related to the application of these methodologies in the study area which results of interest for the knowledge of the coastal hydrodynamics.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen RG, Pereira LS, Raes D, Martin Smith M (1998) Crop evapotranspiration. Guidelines for computing crop water requirements, FAO irrigation and drainage papers 56. FAO, Rome
Barlow PM, Reichard EG (2010) Saltwater intrusion in coastal regions of North America. Hydrogeol J 18(1):247–260
Bruland KW (1983) Trace elements in seawater. Chemical oceanography, vol 8. Academic Press, London, pp 157–220
Burnett WC, Dulaiova H (2003) Estimating the dynamics of groundwater input into the coastal zone via continuous radon-222 measurements. J Environ Radioact 69(1–2):21–35
Burnett WC, Aggarwal PK, Aureli A, Bokuniewicz H, Cable JE, Charette MA, Kontar E, Krupa S, Kulkarni KM, Loveless A, Moore WS, Oberdorfer JA, Oliveira J, Ozyurt N, Povinec P, Privitera AMG, Rajar R, Ramessur RT, Scholten J, Stieglitz T, Taniguchi M, Turner JV (2006) Quantifying submarine groundwater discharge in the coastal zone via multiple methods. Sci Total Environ 367(2–3):498–543
Cable JE, Burnett WC, Chanton JP, Weatherly GL (1996) Estimating groundwater discharge into the northeastern Gulf of Mexico using radon-222. Earth Planet Sci Lett 144(3–4):591–604
Capone DG, Bautista MF (1985) A groundwater source of nitrate in nearshore marine sediments. Nature 313(5999):214
Carretero S (2011) Comportamiento hidrológico de las dunas costeras en el sector nororiental de la provincia de Buenos Aires [Hydrological behavior of coastal dunes on the northeastern coast of Buenos Aires province]. PhD thesis. Facultad de Ciencias Naturales y Museo, Universidad Nacional de La Plata, La Plata. Argentina. http://sedici.unlp.edu.ar/search/request.php?id_document=ARG-UNLP-TPG-0000002075&request=request. Accessed 10 Mar 2018
Carretero S, Kruse E (2010) Areal exploitation of groundwater in coastal dunes, Buenos Aires, Argentina. In: Paliwal BS (ed) Global groundwater resources and management. Scientific Publishers, India, Jodhpur, pp 385–398
Carretero S, Kruse E (2012) Relationship between precipitation and water-table fluctuation in a coastal dune aquifer: northeastern coast of the Buenos Aires province, Argentina. Hydrogeol J 20:1613–1621
Carretero S, Kruse E (2015) Iron and manganese content in groundwater on the northeastern coast of the Buenos Aires Province, Argentina. Environ Earth Sci 73(5):1983–1995
Carretero S, Dapeña C, Kruse E (2013a) Hydrogeochemical and isotopic characterisation of groundwater in a sand-dune phreatic aquifer on the northeastern coast of the province of Buenos Aires. Isot Environ Health Stud 49(3):399–419
Carretero S, Rapaglia J, Bokuniewicz H, Kruse E (2013b) Impact of sea level rise on saltwater intrusion length into the coastal aquifer, Partido de La Costa, Argentina. Cont Shelf Res 61–62:62–70
Cerdà-Domènech M, Rodellas V, Folch A, Garcia-Orellana J (2017) Constraining the temporal variations of Ra isotopes and Rn in the groundwater end-member: implications for derived SGD estimates. Sci Total Environ 595:849–857
Charette MA, Sholkovitz ER (2006) Trace element cycling in a subterranean estuary: Part 2. Geochemistry of the pore water. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 70(4):811–826
Cho HM, Guebuem K (2016) Determining groundwater Ra end-member values for the estimation of the magnitude of submarine groundwater discharge using Ra isotope tracers. Geophys Res Lett 43(8):3865–3871
Consejo Federal de Inversiones (1989) Evaluación del Recurso Hídrico Subterráneo de la Región Costera Atlántica de la Provincia de Buenos Aires. Regiones 1 y 2. Punta Rasa-Punta Médanos. Provincia de Buenos Aires. Informe Final, Geología y Geomorfología [Evaluation of groundwater resources in the Atlantic Coastal Region of Buenos Aires province. Regions 1 and 2. Punta Rasa-Punta Médanos. Buenos Aires province. Final Report, Geology and Geomorphology]. Consejo Federal de Inversiones, Buenos Aires
deGroot-Hedlin C, Constable S (1990) Occam’s inversion to generate smooth, two dimensional models form magnetotelluric data. Geophysics 55:1613–1624
Forte Lay JA, Aiello JL, Kuba J (1995) Software AGROAGUA v.5.0. AGROAGUA, CIBIOM. CONICET. Buenos Aires
Framiñan MB, Brown OB (1996) Study of the Río de la Plata turbidity front, Part 1: spatial and temporal distribution. Cont Shelf Res 16(10):1259–1282
Johannes RE (1980) The ecological significance of the submarine discharge of groundwater. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 3:365–373
Loke MH (2015) Tutorial: 2-D and 3-D electrical imaging surveys. Geotomo Software, Malaysia
Monti J Jr, Scorca MP (2003) Trends in nitrogen concentration and nitrogen loads entering the South Shore Estuary Reserve from streams and ground-water discharge in Nassau and Suffolk counties, Long Island, New York. US Geological Survey, New York, pp 1952–1997 (No. 2002-4255)
Montluçon D, Sañudo-Wilhelmy SA (2001) Influence of net groundwater discharge on the chemical composition of a coastal environment: flanders Bay, Long Island, New York. Environ Sci Technol 35(3):480–486
Mulligan A, Charette MA (2006) Intercomparison of submarine groundwater discharges estimates from an unconfined sandy coastal aquifer. J Hydrol 327:411–425
New York State, Department of Environmental Conservation Report (2014) Suffolk County: addressing the consequences of development without adequate sewer and septic systems. https://www.dec.ny.gov/lands/97030.html. Accessed 16 Jun 2019
Paytan A, Shellenbarger GG, Street JH, Gonneea ME, Davis K, Young MB, Moore WS (2006) Submarine groundwater discharge: an important source of new inorganic nitrogen to coral reef ecosystems. Limnol Oceanogr 51(1):343–348
Povinec PP, Bokuniewicz H, Burnett WC, Cable J, Charette M, Comanducci JF, Kontar E et al (2008) Isotope tracing of submarine groundwater discharge offshore Ubatuba, Brazil: results of the IAEA-UNESCO SGD project. J Environ Radioact 99(10):1596–1610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2008.06.010
Rapaglia J, Grant C, Bokuniewicz H, Pick T, Scholten J (2015) A GIS typology to locate sites of submarine groundwater discharge. J Environ Radioact 145:10–18
Sasaki Y (1992) Resolution of resistivity tomography inferred from numerical simulation. Geophys Prospect 40:453–464
Sherif MM, Singh VP (1999) Effect of climate change on sea water intrusion in coastal aquifers. Hydrol Process 13(8):1277–1287
SHN (2008) (Servicio de Hidrografía Naval) [Naval Hydrographic Service] Tabla de Mareas [Tide Table]. In: Pub. H-610, Armada Argentina, Buenos Aires
Slomp CP, Van Cappellen P (2004) Nutrient inputs to the coastal ocean through submarine groundwater discharge: controls and potential impact. J Hydrol 295(1–4):64–86
Smith SO, Myott DH (1975) Effect of cesspool discharge on ground-water quality on Long Island, NY. J Am Water Works Assoc 67(8):456–458
Stieglitz T (2005) Submarine groundwater discharge into the near-shore zone of the Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Mar Pollut Bull 51(1–4):51–59
Stieglitz T, Rapaglia J, Bokuniewicz H (2008) Estimation of submarine groundwater discharge from bulk ground electrical conductivity measurements. J Geophys Res Oceans 113:C8
Stieglitz TC, Cook PG, Burnett WC (2010) Inferring coastal processes from regional-scale mapping of 222 radon and salinity: examples from the Great Barrier Reef, Australia. J Environ Radioact 101(7):544–552
Taylor BN, Kuyatt CE (1994) NIST technical note 1297. Guidelines for evaluating and expressing the uncertainty of NIST measurement results, 24
Thornthwaite C, Mather J (1955) The water balance Climatol 8:1–37
Werner AD, Simmons CT (2009) Impact of sea-level rise on sea water intrusion in coastal aquifers. Groundwater 47(2):197–204
Windom HL, Moore WS, Niencheski LF, Jahnke RA (2006) Submarine groundwater discharge: a large, previously unrecognized source of dissolved iron to the South Atlantic Ocean. Mar Chem 102:252–266
Windom H, Moore W, Niencheski F (2007) Influence of groundwater discharge through a coastal sandy barrier in southern Brazil on seawater metal chemistry. A new focus on groundwater–seawater interaction. IAH International Commission on Groundwater. XXI General Assembly, IUGG: 180–188
Winner Jr MD (1975) Ground-water resources of the Cape Hatteras National Seashore, North Carolina: U.S. Geological Survey Hydrologic Investigations Atlas HA-540, 2 sheets
Winner Jr MD, Coble RW (1996) Hydrogeologic framework of the North Carolina coastal plain. Professional Paper 1404- I. https://doi.org/10.3133/pp1404I. Accessed 16 June 2019
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Cooperativa de Provisión de Obras y Servicios Públicos de San Clemente del Tuyú Ltda. for their collaboration. This work was supported by the Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas of Argentina, grant number PIP 0403, 2013–2015, and the Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica, grant number PICT 2013-2117, 2014–2017.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carretero, S., Rapaglia, J., Perdomo, S. et al. A multi-parameter study of groundwater–seawater interactions along Partido de La Costa, Buenos Aires Province, Argentina. Environ Earth Sci 78, 513 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8532-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8532-5