Abstract
Introduction:
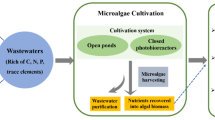
Huge amounts of wastewater are generated during food process, and usually contain high nutrient concentration. The present study investigated the feasibility of dairy and poultry wastewaters as growth media for Chlorella sp. T4 cultivation for concomitant nutrient removal and biomass propagation for biofuel production.
Methods:
Microalgae Chlorella sp. T4 was cultivated in poultry and dairy wastewater collected at different stage of wastewater treatment to study the growth, physiological respond, nutrient removal efficiency and biochemical composition.
Results:
The strains showed phycoremediation potential resulting to high nitrogen and phosphorus removal efficiency in dairy and poultry wastewater ranging from 85–95% and 35–93%, respectively. High biomass yield of 1.28 ± 0.1 g L−1 was obtained in poultry wastewater compared to 0.85 ± 0.02 g L−1 obtained in dairy wastewater. The biomass contained significant amounts of lipids (16.2–25.7 % Dry wt.), carbohydrates (20.7–33.1 % Dry wt.), and proteins (24.5–34.6 % Dry wt.), regardless of the wastewater type. The fatty acid analysis revealed that palmitic (16:0), oleic (18:1), and linoleic (18:2) acids were the major fatty acids accumulated by Chlorella sp. T4 when cultivated in poultry and dairy wastewater. Biodiesel properties of lipids extracted from the cell grown in poultry and dairy wastewater complied with most of the international standards by ASTM D6751 and EN 14214.
Conclusion:
The results of this study revealed that Chlorella sp. T4 is a potential candidate for dairy and poultry wastewater treatment, with a significant accumulation of lipid, protein and carbohydrates for use in biofuel production.
Graphical Abstract



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Daneshvar, E., Antikainen, L., Koutra, E., Kornaros, M., Bhatnagar, A.: Investigation on the feasibility of Chlorella vulgaris cultivation in a mixture of pulp and aquaculture effluents: treatment of wastewater and lipid extraction. Bioresour. Technol. 255, 104–110 (2018)
Razzak, S.A., Ali, S.A.M., Hossain, M.M., deLasa, H.: Biological CO2 fixation with production of microalgae in wastewater–a review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 76, 379–390 (2017)
Hena, S., Znad, H., Heong, K.T., Judd, S.: Dairy farm wastewater treatment and lipid accumulation by Arthrospira platensis. Water Res. 128, 267–277 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.10.057
Mishra, S., Mohanty, K.: Comprehensive characterization of microalgal isolates and lipid-extracted biomass as zero-waste bioenergy feedstock: An integrated bioremediation and biorefinery approach. Bioresour. Technol. 273, 177–184 (2019)
Gumbi, S., Majeke, B., Olaniran, A.O., Mutanda, T.: Isolation, identification and high-throughput screening of neutral lipid producing indigenous microalgae from South African aquatic habitats. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 182(1), 382–399 (2017)
Odjadjare, E.C., Mutanda, T., Olaniran, A.O.: Potential biotechnological application of microalgae: a critical review. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 37(1), 37–52 (2017)
Odjadjare, E.C., Mutanda, T., Chen, Y.-F., Olaniran, A.O.: Evaluation of Pre-chlorinated wastewater effluent for microalgal cultivation and biodiesel production. Water 10(8), 977 (2018)
Qin, L., Wang, Z., Sun, Y., Shu, Q., Feng, P., Zhu, L., Xu, J., Yuan, Z.: Microalgae consortia cultivation in dairy wastewater to improve the potential of nutrient removal and biodiesel feedstock production. Environ. Sci. Poll. Res. 23(9), 8379–8387 (2016)
Mohd Udaiyappan, A.F., Abu Hasan, H., Takriff, M.S., Sheikh Abdullah, S.R.: A review of the potentials, challenges and current status of microalgae biomass applications in industrial wastewater treatment. J. Water Process Engin. 20, 8–21 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2017.09.006
Knothe, G.: “Designer” biodiesel: optimizing fatty ester composition to improve fuel properties. Energy Fuels 22(2), 1358–1364 (2008)
Mandotra, S., Kumar, P., Suseela, M., Nayaka, S., Ramteke, P.: Evaluation of fatty acid profile and biodiesel properties of microalga Scenedesmus abundans under the influence of phosphorus, pH and light intensities. Bioresour. Technol. 201, 222–229 (2016)
Ferreira, A., Marques, P., Ribeiro, B., Assemany, P., de Mendonça, H.V., Barata, A., Oliveira, A.C., Reis, A., Pinheiro, H.M., Gouveia, L.: Combining biotechnology with circular bioeconomy: from poultry, swine, cattle, brewery, dairy and urban wastewaters to biohydrogen. Environmental research 164, 32–38 (2018)
Raposo, M.F.d.J., Oliveira, S.E., Castro, P.M., Bandarra, N.M., Morais, R.M.: On the utilization of microalgae for brewery effluent treatment and possible applications of the produced biomass. J. Inst. Brew. 116(3), 285–292 (2010)
Ummalyma, S.B., Sukumaran, R.K.: Cultivation of microalgae in dairy effluent for oil production and removal of organic pollution load. Bioresour. Technol. 165, 295–301 (2014)
Kothari, R., Prasad, R., Kumar, V., Singh, D.: Production of biodiesel from microalgae Chlamydomonas polypyrenoideum grown on dairy industry wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 144, 499–503 (2013)
Stanier, R.Y., Kunisawa, R., Mandel, M., Cohen-Bazire, G.: Purification and properties of unicellular blue-green algae (order Chroococcales). Bacteriological reviews 35(2), 171 (1971)
Porra, R., Thompson, W., Kriedemann, P.: Determination of accurate extinction coefficients and simultaneous equations for assaying chlorophylls a and b extracted with four different solvents: verification of the concentration of chlorophyll standards by atomic absorption spectroscopy. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Bioenergetics 975(3), 384–394 (1989)
Gupta, S.K., Ansari, F.A., Shriwastav, A., Sahoo, N.K., Rawat, I., Bux, F.: Dual role of Chlorella sorokiniana and Scenedesmus obliquus for comprehensive wastewater treatment and biomass production for bio-fuels. Journal of cleaner production 115, 255–264 (2016)
White, S., Anandraj, A., Bux, F.: PAM fluorometry as a tool to assess microalgal nutrient stress and monitor cellular neutral lipids. Bioresour. Technol. 102(2), 1675–1682 (2011)
Bradford, M.M.: A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72(1–2), 248–254 (1976)
Yemm, E.W., Willis, A.J.: The estimation of carbohydrates in plant extracts by anthrone. Biochem. J. 57(3), 508–514 (1954). doi:https://doi.org/10.1042/bj0570508
Kassim, M.A., Bhattacharya, S.: Dilute alkaline pretreatment for reducing sugar production from Tetraselmis suecica and Chlorella sp. biomass. Process Biochem. 51(11), 1757–1766 (2016). doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2015.11.027
Talebi, A.F., Tabatabaei, M., Chisti, Y.: BiodieselAnalyzer: a user-friendly software for predicting the properties of prospective biodiesel. Biofuel Res. J. 1(2), 55–57 (2014)
Marcilhac, C., Sialve, B., Pourcher, A.-M., Ziebal, C., Bernet, N., Béline, F.: Digestate color and light intensity affect nutrient removal and competition phenomena in a microalgal-bacterial ecosystem. Water Res. 64, 278–287 (2014)
Cuellar-Bermudez, S.P., Aleman-Nava, G.S., Chandra, R., Garcia-Perez, J.S., Contreras-Angulo, J.R., Markou, G., Muylaert, K., Rittmann, B.E., Parra-Saldivar, R.: Nutrients utilization and contaminants removal. A review of two approaches of algae and cyanobacteria in wastewater. Algal Res. 24, 438–449 (2017)
Oliveira, A.C., Barata, A., Batista, A.P., Gouveia, L.: Scenedesmus obliquus in poultry wastewater bioremediation. Environmental technology, 1–10 (2018)
Udaiyappan, A.F.M., Hasan, H.A., Takriff, M.S., Abdullah, S.R.S.: A review of the potentials, challenges and current status of microalgae biomass applications in industrial wastewater treatment. Journal of Water Process Engineering 20, 8–21 (2017)
Larsdotter, K.: Wastewater treatment with microalgae-a literature review. Vatten 62(1), 31 (2006)
Cai, T., Park, S.Y., Li, Y.: Nutrient recovery from wastewater streams by microalgae: status and prospects. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 19, 360–369 (2013)
Hwang, J.-H., Kabra, A.N., Kim, J.R., Jeon, B.-H.: Photoheterotrophic microalgal hydrogen production using acetate- and butyrate-rich wastewater effluent. Energy. 78, 887–894 (2014). doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2014.10.086
Damm, E., Nomura, D., Martin, A., Dieckmann, G.S., Meiners, K.M.: DMSP and DMS cycling within Antarctic sea ice during the winter–spring transition. Deep Sea Res. Part II. 131, 150–159 (2016). doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsr2.2015.12.015
Daneshvar, E., Zarrinmehr, M.J., Koutra, E., Kornaros, M., Farhadian, O., Bhatnagar, A.: Sequential cultivation of microalgae in raw and recycled dairy wastewater: microalgal growth, wastewater treatment and biochemical composition. Bioresour. Technol. 273, 556–564 (2019)
Jais, N., Mohamed, R., Al-Gheethi, A., Hashim, M.A.: The dual roles of phycoremediation of wet market wastewater for nutrients and heavy metals removal and microalgae biomass production. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 19(1), 37–52 (2017)
Mendonça, H.V., de Melo Ribeiro, C.B., Borges, A.C., Bastos, R.R.: R.: Removal of nitrogen and phosphorus from dairy wastewater by flooded systems built operating in batches. Environmental & Water-An Interdisciplinary Journal of Applied Science 7(2), 75–87 (2012)
Kothari, R., Pathak, V.V., Kumar, V., Singh, D.P.: Experimental study for growth potential of unicellular alga Chlorella pyrenoidosa on dairy waste water: An integrated approach for treatment and biofuel production. Biores. Technol. 116, 466–470 (2012). doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.03.121
Chen, G.-Q., Chen, F.: Growing phototrophic cells without light. Biotechnol. Lett. 28(9), 607–616 (2006)
Zhu, L., Wang, Z., Shu, Q., Takala, J., Hiltunen, E., Feng, P., Yuan, Z.: Nutrient removal and biodiesel production by integration of freshwater algae cultivation with piggery wastewater treatment. Water Res. 47(13), 4294–4302 (2013)
Markou, G., Vandamme, D., Muylaert, K.: Microalgal and cyanobacterial cultivation: the supply of nutrients. Water Res. 65, 186–202 (2014)
Han, L., Pei, H., Hu, W., Jiang, L., Ma, G., Zhang, S., Han, F.: Integrated campus sewage treatment and biomass production by Scenedesmus quadricauda SDEC-13. Bioresour. Technol. 175, 262–268 (2015)
Chen, Z., Shao, S., He, Y., Luo, Q., Zheng, M., Zheng, M., Chen, B., Wang, M.: Nutrients removal from piggery wastewater coupled to lipid production by a newly isolated self-flocculating microalga Desmodesmus sp. PW1. Biores. Technol. 302, 122806 (2020). doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.122806
Ji, M.-K., Yun, H.-S., Park, Y.-T., Kabra, A.N., Oh, I.-H., Choi, J.: Mixotrophic cultivation of a microalga Scenedesmus obliquus in municipal wastewater supplemented with food wastewater and flue gas CO2 for biomass production. Journal of environmental management 159, 115–120 (2015)
Wang, Y., Guo, W., Yen, H.-W., Ho, S.-H., Lo, Y.-C., Cheng, C.-L., Ren, N., Chang, J.-S.: Cultivation of Chlorella vulgaris JSC-6 with swine wastewater for simultaneous nutrient/COD removal and carbohydrate production. Bioresour. Technol. 198, 619–625 (2015)
Knothe, G.: Fuel Properties of Highly Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Methyl Esters. Prediction of Fuel Properties of Algal Biodiesel. Energy Fuels. 26(8), 5265–5273 (2012). doi:https://doi.org/10.1021/ef300700v
Mutanda, T., Ramesh, D., Karthikeyan, S., Kumari, S., Anandraj, A., Bux, F.: Bioprospecting for hyper-lipid producing microalgal strains for sustainable biofuel production. Bioresour. Technol. 102(1), 57–70 (2011)
Acknowledgements
The authors hereby acknowledge the National Research Foundation (South Africa) and the University of KwaZulu-Natal for providing financial assistance.
Funding
National Research Foundation, South Africa (Grant No: 94043 and 92803).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.G., T.M. and A.O. conceived and designed the project; S.G. and A.O. designed the experiments; S.G. performed the experiments; A.O. contributed reagents and materials; S.G., T.M. and A.O. wrote the manuscript; all the authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gumbi, S.T., Mutanda, T. & Olaniran, A.O. Nutrient Removal from Dairy and Poultry Wastewater with Simultaneous Biomass and Biodiesel Production by Chlorella sp. T4 Isolated from a Freshwater Stream in South Africa. Waste Biomass Valor 12, 6931–6943 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-021-01492-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-021-01492-0