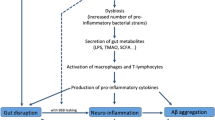
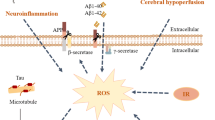
Abstract
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease considered the major cause of dementia in the elderly. The main pathophysiological features of the disease are neuronal loss (mainly cholinergic neurons), glutamatergic excitotoxicity, extracellular accumulation of amyloid beta, and intracellular neurofibrillary tangles. However, other pathophysiological features of the disease have emerged including neuroinflammation and dysregulation of the kynurenine pathway (KP). The intestinal microbiota is a large and diverse collection of microorganisms that play a crucial role in regulating host health. Recently, studies have highlighted that changes in intestinal microbiota contribute to brain dysfunction in various neurological diseases including AD. Studies suggest that microbiota compositions are altered in AD patients and animal models and that these changes may increase intestinal permeability and induce inflammation. Considering that microbiota can modulate the kynurenine pathway and in turn neuroinflammation, the gut microbiome may be a valuable target for the development of new disease-modifying therapies. The present review aims to link the interactions between AD, microbiota, and the KP.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agahi A, Hamidi GA, Daneshvar R, Hamdieh M, Soheili M, Alinaghipour A, Esmaeili Taba SM, Salami M (2018) Does severity of Alzheimer’s disease contribute to its responsiveness to modifying gut microbiota? A double blind clinical trial. Front Neurol 9:662. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2018.00662
Agudelo LZ, Femenía T, Orhan F, Porsmyr-Palmertz M, Goiny M et al (2014) Skeletal muscle PGC-1α1 modulates kynurenine metabolism and mediates resilience to stress-induced depression. Cell 159:33–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2014.07.051
Akbari E, Asemi Z, Daneshvar Kakhaki R, Bahmani F, Kouchaki E, Tamtaji OR, Hamidi GA, Salami M (2016) Effect of probiotic supplementation on cognitive function and metabolic status in Alzheimer’s disease: a randomized, double-blind and controlled trial. Front Aging Neurosci 8:256. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2016.00256
Angevaren M, Aufdemkampe G, Verhaar HJJ, Aleman A, Vanhees L (2008) Physical activity and enhanced fitness to improve cognitive function in older people without known cognitive impairment. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD005381.pub2
Athari Nik Azm S, Djazayeri A, Safa M, Azami K, Ahmadvand B, Sabbaghziarani F, Sharifzadeh M, Vafa M (2018) Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium ameliorate memory and learning deficits and oxidative stress in Abeta (1-42) injected rats. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 43:718–726. https://doi.org/10.1139/apnm-2017-0648
Avila J, Wandosell F, Hernandez F (2010) Role of glycogen synthase kinase-3 in Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis and glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibitors. Expert Rev Neurother 10:703–710. https://doi.org/10.1586/ern.10.40
Bachstetter AD, Xing B, de Almeida L, Dimayuga ER, Watterson DM, van Eldik LJ (2011) Microglial p38alpha MAPK is a key regulator of proinflammatory cytokine up-regulation induced by toll-like receptor (TLR) ligands or beta-amyloid (Abeta). J Neuroinflammation 8:79. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-2094-8-79
Backhed F, Ley RE, Sonnenburg JL, Peterson DA, Gordon JI (2005) Host-bacterial mutualism in the human intestine. Science 307:1915–1920. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1104816
Bauchop T, Mountfort DO (1981) Cellulose fermentation by a rumen anaerobic fungus in both the absence and the presence of rumen methanogens. Appl Environ Microbiol 42:1103–1110
Biesalski HK (2016) Nutrition meets the microbiome: micronutrients and the microbiota. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1372:53–64. https://doi.org/10.1111/nyas.13145
Blaser MJ (2016) Antibiotic use and its consequences for the normal microbiome. Science 352:544–545. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aad9358
Bliss TV, Collingridge GL (1993) A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature 361:31–39. https://doi.org/10.1038/361031a0
Bonda DJ, Mailankot M, Stone JG, Garrett MR, Staniszewska M, Castellani RJ, Siedlak SL, Zhu X, Lee HG, Perry G, Nagaraj RH, Smith MA (2010) Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and 3-hydroxykynurenine modifications are found in the neuropathology of Alzheimer’s disease. Redox Rep 15:161–168. https://doi.org/10.1179/174329210x12650506623645
Bondi MW, Jak AJ, Delano-Wood L, Jacobson MW, Delis DC, Salmon DP (2008) Neuropsychological contributions to the early identification of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychol Rev 18:73–90. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11065-008-9054-1
Bonfili L, Cecarini V, Berardi S, Scarpona S, Suchodolski JS, Nasuti C, Fiorini D, Boarelli MC, Rossi G, Eleuteri AM (2017) Microbiota modulation counteracts Alzheimer’s disease progression influencing neuronal proteolysis and gut hormones plasma levels. Sci Rep 7:2426. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-02587-2
Brandscheid C, Schuck F, Reinhardt S, Schafer KH, Pietrzik CU et al (2017) Altered gut microbiome composition and tryptic activity of the 5xFAD Alzheimer’s mouse model. J Alzheimers Dis 56:775–788. https://doi.org/10.3233/jad-160926
Buoso E, Lanni C, Schettini G, Govoni S, Racchi M (2010) Beta-amyloid precursor protein metabolism: focus on the functions and degradation of its intracellular domain. Pharmacol Res 62:308–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2010.05.002
Campbell BM, Charych E, Lee AW, Moller T (2014) Kynurenines in CNS disease: regulation by inflammatory cytokines. Front Neurosci 8:12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2014.00012
Castellano-Gonzalez G, Jacobs KR, Don E, Cole NJ, Adams S, Lim CK, Lovejoy DB, Guillemin GJ (2019) Kynurenine 3-monooxygenase activity in human primary neurons and effect on cellular bioenergetics identifies new neurotoxic mechanisms. Neurotox Res 35:530–541. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-019-9997-4
Castellano JF, Fletcher BR, Patzke H, Long JM, Sewal A, Kim DH, Kelley-Bell B, Rapp PR (2014) Reassessing the effects of histone deacetylase inhibitors on hippocampal memory and cognitive aging. Hippocampus 24:1006–1016. https://doi.org/10.1002/hipo.22286
Cattaneo A, Cattane N, Galluzzi S, Provasi S, Lopizzo N, Festari C, Ferrari C, Guerra UP, Paghera B, Muscio C, Bianchetti A, Volta GD, Turla M, Cotelli MS, Gennuso M, Prelle A, Zanetti O, Lussignoli G, Mirabile D, Bellandi D, Gentile S, Belotti G, Villani D, Harach T, Bolmont T, Padovani A, Boccardi M, Frisoni GB (2017) Association of brain amyloidosis with pro-inflammatory gut bacterial taxa and peripheral inflammation markers in cognitively impaired elderly. Neurobiol Aging 49:60–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2016.08.019
Cervenka I, Agudelo LZ, Ruas JL (2017) Kynurenines: tryptophan’s metabolites in exercise, inflammation, and mental health. Science 357:eaaf9794. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaf9794
Chatterjee P, Goozee K, Lim CK, James I, Shen K, Jacobs KR, Sohrabi HR, Shah T, Asih PR, Dave P, ManYan C, Taddei K, Lovejoy DB, Chung R, Guillemin GJ, Martins RN (2018) Alterations in serum kynurenine pathway metabolites in individuals with high neocortical amyloid-β load: a pilot study. Sci Rep 8:8008–8008. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-25968-7
Clarke G, Grenham S, Scully P, Fitzgerald P, Moloney RD, Shanahan F, Dinan TG, Cryan JF (2013) The microbiome-gut-brain axis during early life regulates the hippocampal serotonergic system in a sex-dependent manner. Mol Psychiatry 18:666–673. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2012.77
Clarke G, Stilling RM, Kennedy PJ, Stanton C, Cryan JF, Dinan TG (2014) Minireview: gut microbiota: the neglected endocrine organ. Mol Endocrinol 28:1221–1238. https://doi.org/10.1210/me.2014-1108
Cobianchi L, Fornoni A, Pileggi A, Molano RD, Sanabria NY et al (2008) Riboflavin inhibits IL-6 expression and p38 activation in islet cells. Cell Transplant 17:559–566
Crews L, Masliah E (2010) Molecular mechanisms of neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 19:R12–R20. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddq160
Cuello AC, Ferretti MT, Leon WC, Iulita MF, Melis T, Ducatenzeiler A, Bruno MA, Canneva F (2010) Early-stage inflammation and experimental therapy in transgenic models of the Alzheimer-like amyloid pathology. Neurodegener Dis 7:96–98. https://doi.org/10.1159/000285514
De Filippo C, Cavalieri D, Di Paola M, Ramazzotti M, Poullet JB et al (2010) Impact of diet in shaping gut microbiota revealed by a comparative study in children from Europe and rural Africa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:14691–14696. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1005963107
Desbonnet L, Garrett L, Clarke G, Bienenstock J, Dinan TG (2008) The probiotic Bifidobacteria infantis: an assessment of potential antidepressant properties in the rat. J Psychiatr Res 43:164–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2008.03.009
Dingerkus VL, Gaber TJ, Helmbold K, Bubenzer S, Eisert A et al (2012) Acute tryptophan depletion in accordance with body weight: influx of amino acids across the blood-brain barrier. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 119:1037–1045. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-012-0793-z
Dubois B, Hampel H, Feldman HH, Scheltens P, Aisen P, Andrieu S, Bakardjian H, Benali H, Bertram L, Blennow K, Broich K, Cavedo E, Crutch S, Dartigues JF, Duyckaerts C, Epelbaum S, Frisoni GB, Gauthier S, Genthon R, Gouw AA, Habert MO, Holtzman DM, Kivipelto M, Lista S, Molinuevo JL, O'Bryant SE, Rabinovici GD, Rowe C, Salloway S, Schneider LS, Sperling R, Teichmann M, Carrillo MC, Cummings J, Jack CR Jr (2016) Preclinical Alzheimer’s disease: definition, natural history, and diagnostic criteria. Alzheimers Dement 12:292–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2016.02.002
Dumitrescu L, Popescu-Olaru I, Cozma L, Tulba D, Hinescu ME et al (2018) Oxidative stress and the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2018:2406594. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/2406594
Durazzo TC, Mattsson N, Weiner MW (2014) Smoking and increased Alzheimer’s disease risk: a review of potential mechanisms. Alzheimers Dement 10:S122–S145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2014.04.009
Dursun E, Gezen-Ak D, Hanagasi H, Bilgic B, Lohmann E et al (2015) The interleukin 1 alpha, interleukin 1 beta, interleukin 6 and alpha-2-macroglobulin serum levels in patients with early or late onset Alzheimer’s disease, mild cognitive impairment or Parkinson’s disease. J Neuroimmunol 283:50–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2015.04.014
Emery DC, Shoemark DK, Batstone TE, Waterfall CM, Coghill JA, Cerajewska TL, Davies M, West NX, Allen SJ (2017) 16S rRNA next generation sequencing analysis shows bacteria in Alzheimer’s post-mortem brain. Front Aging Neurosci 9:195. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2017.00195
Erny D, Hrabe de Angelis AL, Jaitin D, Wieghofer P, Staszewski O et al (2015) Host microbiota constantly control maturation and function of microglia in the CNS. Nat Neurosci. 18:965–977. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4030
Farina N, Rusted J, Tabet N (2014) The effect of exercise interventions on cognitive outcome in Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review. Int Psychogeriatr 26:9–18. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1041610213001385
Forbes D, Forbes SC, Blake CM, Thiessen EJ, Forbes S (2015) Exercise programs for people with dementia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD006489.pub4
Freewan M, Rees MD, Plaza TSS, Glaros E, Lim YJ, Wang XS, Yeung AWS, Witting PK, Terentis AC, Thomas SR (2013) Human indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase is a catalyst of physiological heme peroxidase reactions: implications for the inhibition of dioxygenase activity by hydrogen peroxide. J Biol Chem 288:1548–1567. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.410993
Fung TC, Olson CA, Hsiao EY (2017) Interactions between the microbiota, immune and nervous systems in health and disease. Nat Neurosci 20:145–155. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4476
Garcez ML, de Carvalho CA, Mina F, Bellettini-Santos T, Schiavo GL, da Silva S, Campos ACBF, Varela RB, Valvassori SS, Damiani AP, Longaretti LM, de Andrade VM, Budni J (2018) Sodium butyrate improves memory and modulates the activity of histone deacetylases in aged rats after the administration of d-galactose. Exp Gerontol 113:209–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2018.10.005
Ghavami SB, Rostami E, Sephay AA, Shahrokh S, Balaii H, Aghdaei HA, Zali MR (2018) Alterations of the human gut Methanobrevibacter smithii as a biomarker for inflammatory bowel diseases. Microb Pathog 117:285–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2018.01.029
Giil LM, Midttun O, Refsum H, Ulvik A, Advani R, Smith AD, Ueland PM (2017) Kynurenine pathway metabolites in Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 60:495–504. https://doi.org/10.3233/jad-170485
Gong B, Pan Y, Vempati P, Zhao W, Knable L, Ho L, Wang J, Sastre M, Ono K, Sauve AA, Pasinetti GM (2013) Nicotinamide riboside restores cognition through an upregulation of proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator 1α regulated β-secretase 1 degradation and mitochondrial gene expression in Alzheimer’s mouse models. Neurobiol Aging 34:1581–1588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2012.12.005
Groot C, Hooghiemstra AM, Raijmakers PGHM, van Berckel BNM, Scheltens P, Scherder EJA, van der Flier WM, Ossenkoppele R (2016) The effect of physical activity on cognitive function in patients with dementia: a meta-analysis of randomized control trials. Ageing Res Rev 25:13–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2015.11.005
Guillemin GJ, Williams KR, Smith DG, Smythe GA, Croitoru-Lamoury J et al (2003) Quinolinic acid in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Adv Exp Med Biol 527:167–176
Hampel H, Vergallo A, Aguilar LF, Benda N, Broich K, Cuello AC, Cummings J, Dubois B, Federoff HJ, Fiandaca M, Genthon R, Haberkamp M, Karran E, Mapstone M, Perry G, Schneider LS, Welikovitch LA, Woodcock J, Baldacci F, Lista S (2018) Precision pharmacology for Alzheimer’s disease. Pharmacol Res 130:331–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2018.02.014
Harach T, Marungruang N, Duthilleul N, Cheatham V, Mc Coy KD, Frisoni G, Neher JJ, Fåk F, Jucker M, Lasser T, Bolmont T (2017) Reduction of Abeta amyloid pathology in APPPS1 transgenic mice in the absence of gut microbiota. Sci Rep 7:41802. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep41802
Harries LW, Bradley-Smith RM, Llewellyn DJ, Pilling LC, Fellows A, Henley W, Hernandez D, Guralnik JM, Bandinelli S, Singleton A, Ferrucci L, Melzer D (2012) Leukocyte CCR2 expression is associated with mini-mental state examination score in older adults. Rejuvenation Res 15:395–404. https://doi.org/10.1089/rej.2011.1302
Heneka MT, Carson MJ, Khoury JE, Landreth GE, Brosseron F, Feinstein DL, Jacobs AH, Wyss-Coray T, Vitorica J, Ransohoff RM, Herrup K, Frautschy SA, Finsen B, Brown GC, Verkhratsky A, Yamanaka K, Koistinaho J, Latz E, Halle A, Petzold GC, Town T, Morgan D, Shinohara ML, Perry VH, Holmes C, Bazan NG, Brooks DJ, Hunot S, Joseph B, Deigendesch N, Garaschuk O, Boddeke E, Dinarello CA, Breitner JC, Cole GM, Golenbock DT, Kummer MP (2015) Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Neurol 14:388–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(15)70016-5
Heneka MT, Kummer MP, Latz E (2014) Innate immune activation in neurodegenerative disease. Nat Rev Immunol 14:463–477. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3705
Henskens M, Nauta IM, van Eekeren MCA, Scherder EJA (2018) Effects of physical activity in nursing home residents with dementia: a randomized controlled trial. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 46:60–80. https://doi.org/10.1159/000491818
Hernandez F, Lucas JJ, Avila J (2013) GSK3 and tau: two convergence points in Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 33(Suppl 1):S141–S144. https://doi.org/10.3233/jad-2012-129025
Hess NC, Dieberg G, McFarlane JR, Smart NA (2014) The effect of exercise intervention on cognitive performance in persons at risk of, or with, dementia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Health Aging Res 3:1–10
Heyes MP, Morrison PF (1997) Quantification of local de novo synthesis versus blood contributions to quinolinic acid concentrations in brain and systemic tissues. J Neurochem 68:280–288
Hill M, Tanguy-Royer S, Royer P, Chauveau C, Asghar K, Tesson L, Lavainne F, Rémy S, Brion R, Hubert FX, Heslan M, Rimbert M, Berthelot L, Moffett JR, Josien R, Grégoire M, Anegon I (2007) IDO expands human CD4+CD25high regulatory T cells by promoting maturation of LPS-treated dendritic cells. Eur J Immunol 37:3054–3062. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.200636704
Howard R, McShane R, Lindesay J, Ritchie C, Baldwin A, Barber R, Burns A, Dening T, Findlay D, Holmes C, Jones R, Jones R, McKeith I, Macharouthu A, O'Brien J, Sheehan B, Juszczak E, Katona C, Hills R, Knapp M, Ballard C, Brown RG, Banerjee S, Adams J, Johnson T, Bentham P, Phillips PPJ (2015) Nursing home placement in the donepezil and memantine in moderate to severe Alzheimer’s disease (DOMINO-AD) trial: secondary and post-hoc analyses. Lancet Neurol 14:1171–1181. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(15)00258-6
Huai W, Zhao R, Song H, Zhao J, Zhang L, Zhang L, Gao C, Han L, Zhao W (2014) Aryl hydrocarbon receptor negatively regulates NLRP3 inflammasome activity by inhibiting NLRP3 transcription. Nat Commun 5:4738. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms5738
Hung CH, Chang YT, Chang YJ (2011) Roles of microorganisms other than Clostridium and Enterobacter in anaerobic fermentative biohydrogen production systems--a review. Bioresour Technol 102:8437–8444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.02.084
Iqbal K, Liu F, Gong C-X, Alonso AC, Grundke-Iqbal I (2009) Mechanisms of tau-induced neurodegeneration. Acta Neuropathol 118:53–69. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-009-0486-3
Jack CR Jr, Knopman DS, Jagust WJ, Petersen RC, Weiner MW, Aisen PS, Shaw LM, Vemuri P, Wiste HJ, Weigand SD, Lesnick TG, Pankratz VS, Donohue MC, Trojanowski JQ (2013) Tracking pathophysiological processes in Alzheimer’s disease: an updated hypothetical model of dynamic biomarkers. Lancet Neurol 12:207–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(12)70291-0
Ji Z, Fan Z, Zhang Y, Yu R, Yang H, Zhou C, Luo J, Ke ZJ (2014) Thiamine deficiency promotes T cell infiltration in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis: the involvement of CCL2. J Immunol 193:2157–2167. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1302702
Jia Y, Li Z, Feng Y, Cui R, Dong Y, Zhang X, Xiang X, Qu K, Liu C, Zhang J (2018) Methane-rich saline ameliorates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury through anti-inflammation, antioxidative, and antiapoptosis effects by regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2018:4756846–4756846. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/4756846
Junges VM, Closs VE, Nogueira GM, Gottlieb MGV (2018) Crosstalk between gut microbiota and central nervous system: a focus on Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Alzheimer Res 15:1179–1190. https://doi.org/10.2174/1567205015666180904155908
Kai K, Hashimoto M, Amano K, Tanaka H, Fukuhara R, Ikeda M (2015) Relationship between eating disturbance and dementia severity in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS One 10:e0133666. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0133666
Kannan V, Brouwer N, Hanisch UK, Regen T, Eggen BJ et al (2013) Histone deacetylase inhibitors suppress immune activation in primary mouse microglia. J Neurosci Res 91:1133–1142. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.23221
Kennedy PJ, Cryan JF, Dinan TG, Clarke G (2014) Irritable bowel syndrome: a microbiome-gut-brain axis disorder? World J Gastroenterol: WJG 20:14105–14125. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i39.14105
Kennedy PJ, Cryan JF, Dinan TG, Clarke G (2017) Kynurenine pathway metabolism and the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Neuropharmacology 112:399–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.07.002
Kim CH, Park J, Kim M (2014) Gut microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids, T cells, and inflammation. Immune Netw 14:277–288. https://doi.org/10.4110/in.2014.14.6.277
Kiss EA, Vonarbourg C, Kopfmann S, Hobeika E, Finke D, Esser C, Diefenbach A (2011) Natural aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligands control organogenesis of intestinal lymphoid follicles. Science 334:1561–1565. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1214914
Lamas B, Richard ML, Leducq V, Pham HP, Michel ML, da Costa G, Bridonneau C, Jegou S, Hoffmann TW, Natividad JM, Brot L, Taleb S, Couturier-Maillard A, Nion-Larmurier I, Merabtene F, Seksik P, Bourrier A, Cosnes J, Ryffel B, Beaugerie L, Launay JM, Langella P, Xavier RJ, Sokol H (2016) CARD9 impacts colitis by altering gut microbiota metabolism of tryptophan into aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligands. Nat Med 22:598–605. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4102
Lambert JC, Ibrahim-Verbaas CA, Harold D, Naj AC, Sims R et al (2013) Meta-analysis of 74,046 individuals identifies 11 new susceptibility loci for Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Genet 45:1452–1458. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2802
Lanoiselee HM, Nicolas G, Wallon D, Rovelet-Lecrux A, Lacour M et al (2017) APP, PSEN1, and PSEN2 mutations in early-onset Alzheimer disease: a genetic screening study of familial and sporadic cases. PLoS Med 14:e1002270. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1002270
LeBlanc JG, Laiño JE, del Valle MJ, Vannini V, van Sinderen D et al (2011) B-group vitamin production by lactic acid bacteria – current knowledge and potential applications. J Appl Microbiol 111:1297–1309. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2011.05157.x
Leblhuber F, Steiner K, Schuetz B, Fuchs D, Gostner JM (2018) Probiotic supplementation in patients with Alzheimer’s dementia - an explorative intervention study. Curr Alzheimer Res 15:1106–1113. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389200219666180813144834
Lee J-H, Wood TK, Lee J (2015) Roles of indole as an interspecies and interkingdom signaling molecule. Trends Microbiol 23:707–718. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2015.08.001
Lee JS, Cella M, McDonald KG, Garlanda C, Kennedy GD et al (2011) AHR drives the development of gut ILC22 cells and postnatal lymphoid tissues via pathways dependent on and independent of Notch. Nat Immunol 13:144–151. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.2187
Levy M, Thaiss CA, Elinav E (2016) Metabolites: messengers between the microbiota and the immune system. Genes Dev 30:1589–1597. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.284091.116
Ley RE, Peterson DA, Gordon JI (2006) Ecological and evolutionary forces shaping microbial diversity in the human intestine. Cell 124:837–848. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2006.02.017
Li CQ, Zheng Q, Wang Q, Zeng QP (2016) Biotic/abiotic stress-driven Alzheimer’s disease. Front Cell Neurosci 10:269. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2016.00269
Lin W, Ding M, Xue J, Leng W (2013) The role of TLR2/JNK/NF-κB pathway in amyloid β peptide-induced inflammatory response in mouse NG108-15 neural cells. Int Immunopharmacol 17:880–884. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2013.09.016
Liu D, Pitta M, Jiang H, Lee J-H, Zhang G, Chen X, Kawamoto EM, Mattson MP (2013a) Nicotinamide forestalls pathology and cognitive decline in Alzheimer mice: evidence for improved neuronal bioenergetics and autophagy procession. Neurobiol Aging 34:1564–1580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2012.11.020
Liu S, Liu Y, Hao W, Wolf L, Kiliaan AJ, Penke B, Rube CE, Walter J, Heneka MT, Hartmann T, Menger MD, Fassbender K (2012) TLR2 is a primary receptor for Alzheimer’s amyloid beta peptide to trigger neuroinflammatory activation. J Immunol 188:1098–1107. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1101121
Liu W, Sheng H, Xu Y, Liu Y, Lu J, Ni X (2013b) Swimming exercise ameliorates depression-like behavior in chronically stressed rats: relevant to proinflammatory cytokines and IDO activation. Behav Brain Res 242:110–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2012.12.041
Long AN, Owens K, Schlappal AE, Kristian T, Fishman PS, Schuh RA (2015) Effect of nicotinamide mononucleotide on brain mitochondrial respiratory deficits in an Alzheimer’s disease-relevant murine model. BMC Neurol 15:19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12883-015-0272-x
Markus CR (2008) Dietary amino acids and brain serotonin function; implications for stress-related affective changes. NeuroMolecular Med 10:247–258. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-008-8039-9
Marlatt MW, Bauer J, Aronica E, van Haastert ES, Hoozemans JJ et al (2014) Proliferation in the Alzheimer hippocampus is due to microglia, not astroglia, and occurs at sites of amyloid deposition. Neural Plast 2014:693851. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/693851
Massudi H, Grant R, Braidy N, Guest J, Farnsworth B, Guillemin GJ (2012) Age-associated changes in oxidative stress and NAD+ metabolism in human tissue. PLoS One 7:e42357–e42357. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0042357
Mayer EA (2011) Gut feelings: the emerging biology of gut-brain communication. Nat Rev Neurosci 12:453–466. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn3071
Mellor AL, Munn DH (2004) IDO expression by dendritic cells: tolerance and tryptophan catabolism. Nat Rev Immunol 4:762–774. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri1457
Mezrich JD, Fechner JH, Zhang X, Johnson BP, Burlingham WJ, Bradfield CA (2010) An interaction between kynurenine and the aryl hydrocarbon receptor can generate regulatory T cells. J Immunol 185:3190–3198. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.0903670
Moloney RD, Desbonnet L, Clarke G, Dinan TG, Cryan JF (2014) The microbiome: stress, health and disease. Mamm Genome 25:49–74. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00335-013-9488-5
Morales-Cruz M, Figueroa CM, Gonzalez-Robles T, Delgado Y, Molina A et al (2014) Activation of caspase-dependent apoptosis by intracellular delivery of cytochrome c-based nanoparticles. J Nanobiotechnol 12:33. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-014-0033-9
Mouchiroud L, Houtkooper Riekelt H, Moullan N, Katsyuba E, Ryu D et al (2013) The NAD+/sirtuin pathway modulates longevity through activation of mitochondrial UPR and FOXO. Signaling Cell 154:430–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.06.016
Nimgampalle M, Kuna Y (2017) Anti-Alzheimer properties of probiotic, Lactobacillus plantarum MTCC 1325 in Alzheimer’s disease induced albino rats. J Clin Diagn Res 11:Kc01–kc05. https://doi.org/10.7860/jcdr/2017/26106.10428
Oberdoerffer P, Michan S, McVay M, Mostoslavsky R, Vann J, Park SK, Hartlerode A, Stegmuller J, Hafner A, Loerch P, Wright SM, Mills KD, Bonni A, Yankner BA, Scully R, Prolla TA, Alt FW, Sinclair DA (2008) SIRT1 redistribution on chromatin promotes genomic stability but alters gene expression during aging. Cell 135:907–918. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2008.10.025
Öhman H, Savikko N, Strandberg TE, Pitkälä KH (2014) Effect of physical exercise on cognitive performance in older adults with mild cognitive impairment or dementia: a systematic review. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 38:347–365. https://doi.org/10.1159/000365388
Ohta S (2014) Molecular hydrogen as a preventive and therapeutic medical gas: initiation, development and potential of hydrogen medicine. Pharmacol Ther 144:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2014.04.006
Oleskin AV, El’-Registan GI, Shenderov BA (2016) Role of neuromediators in the functioning of the human microbiota: “business talks” among microorganisms and the microbiota-host dialogue. Microbiology 85:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261716010082
Ostojic SM (2018) Inadequate production of H2 by gut microbiota and Parkinson disease. Trends Endocrinol Metab 29:286–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2018.02.006
Patel O, Kjer-Nielsen L, Le Nours J, Eckle SB, Birkinshaw R et al (2013) Recognition of vitamin B metabolites by mucosal-associated invariant T cells. Nat Commun 4:2142. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms3142
Perdew GH, Babbs CF (1991) Production of Ah receptor ligands in rat fecal suspensions containing tryptophan or indole-3-carbinol. Nutr Cancer 16:209–218. https://doi.org/10.1080/01635589109514159
Prischmann J (2016) Life and death in Alzheimer’s disease. Minn Med 99:20–21
Rahman A, Ting K, Cullen KM, Braidy N, Brew BJ, Guillemin GJ (2009) The excitotoxin quinolinic acid induces tau phosphorylation in human neurons. PLoS One 4:e6344. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0006344
Ramirez-Bermudez J (2012) Alzheimer’s disease: critical notes on the history of a medical concept. Arch Med Res 43:595–599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arcmed.2012.11.008
Rhee SJ, Walker WA, Cherayil BJ (2005) Developmentally regulated intestinal expression of IFN-gamma and its target genes and the age-specific response to enteric Salmonella infection. J Immunol 175:1127–1136
Ridge PG, Hoyt KB, Boehme K, Mukherjee S, Crane PK, Haines JL, Mayeux R, Farrer LA, Pericak-Vance MA, Schellenberg GD, Kauwe JSK, Adams PM, Albert MS, Albin RL, Apostolova LG, Arnold SE, Asthana S, Atwood CS, Baldwin CT, Barber RC, Barmada MM, Barnes LL, Barral S, Beach TG, Becker JT, Beecham GW, Beekly D, Bennett DA, Bigio EH, Bird TD, Blacker D, Boeve BF, Bowen JD, Boxer A, Burke JR, Burns JM, Buxbaum JD, Cairns NJ, Cantwell LB, Cao C, Carlson CS, Carlsson CM, Carney RM, Carrasquillo MM, Carroll SL, Chui HC, Clark DG, Corneveaux J, Crane PK, Cribbs DH, Crocco EA, Cruchaga C, de Jager PL, DeCarli C, Demirci FY, Dick M, Dickson DW, Doody RS, Duara R, Ertekin-Taner N, Evans DA, Faber KM, Fairchild TJ, Fallon KB, Fardo DW, Farlow MR, Ferris S, Foroud TM, Frosch MP, Galasko DR, Gearing M, Geschwind DH, Ghetti B, Gilbert JR, Goate AM, Graff-Radford NR, Green RC, Growdon JH, Hakonarson H, Hamilton RL, Hamilton-Nelson KL, Hardy J, Harrell LE, Honig LS, Huebinger RM, Huentelman MJ, Hulette CM, Hyman BT, Jarvik GP, Jicha GA, Jin LW, Jun G, Kamboh MI, Karydas A, Katz MJ, Kauwe JSK, Kaye JA, Kim R, Kowall NW, Kramer JH, Kukull WA, Kunkle BW, LaFerla FM, Lah JJ, Larson EB, Leverenz JB, Levey AI, Li G, Lieberman AP, Lin CF, Lipton RB, Lopez OL, Lunetta KL, Lyketsos CG, Mack WJ, Marson DC, Martin ER, Martiniuk F, Mash DC, Masliah E, McCormick WC, McCurry SM, McDavid AN, McKee AC, Mesulam M, Miller BL, Miller CA, Miller JW, Montine TJ, Morris JC, Mukherjee S, Murrell JR, Myers AJ, Naj AC, O'Bryant S, Olichney JM, Pankratz VS, Parisi JE, Partch A, Paulson HL, Perry W, Peskind E, Petersen RC, Pierce A, Poon WW, Potter H, Quinn JF, Raj A, Raskind M, Reiman EM, Reisberg B, Reisch JS, Reitz C, Ringman JM, Roberson ED, Rogaeva E, Rosen HJ, Rosenberg RN, Royall DR, Sager MA, Sano M, Saykin AJ, Schneider JA, Schneider LS, Seeley WW, Smith AG, Sonnen JA, Spina S, St George-Hyslop P, Stern RA, Swerdlow RH, Tanzi RE, Thornton-Wells TA, Trojanowski JQ, Troncoso JC, Tsuang DW, Valladares O, van Deerlin VM, van Eldik LJ, Vardarajan BN, Vinters HV, Vonsattel JP, Wang LS, Weintraub S, Welsh-Bohmer KA, Wendland JR, Wilhelmsen KC, Williamson J, Wingo TS, Winslow AR, Wishnek S, Woltjer RL, Wright CB, Wu CK, Younkin SG, Yu CE, Yu L (2016) Assessment of the genetic variance of late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 41:200.e13–200.e20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2016.02.024
Rudy CC, Hunsberger HC, Weitzner DS, Reed MN (2015) The role of the tripartite glutamatergic synapse in the pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s disease. Aging Dis 6:131–148. https://doi.org/10.14336/ad.2014.0423
Sampson TR, Mazmanian SK (2015) Control of brain development, function, and behavior by the microbiome. Cell Host Microbe 17:565–576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2015.04.011
Savva GM, Wharton SB, Ince PG, Forster G, Matthews FE, Brayne C (2009) Age, neuropathology, and dementia. N Engl J Med 360:2302–2309. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0806142
Scherzer R, Gdalevsky GY, Goldgur Y, Cohen-Luria R, Bittner S, Parola AH (2009) New tryptophanase inhibitors: towards prevention of bacterial biofilm formation. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 24:350–355. https://doi.org/10.1080/14756360802187612
Schipper HM (2011) Apolipoprotein E: implications for AD neurobiology, epidemiology and risk assessment. Neurobiol Aging 32:778–790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2009.04.021
Schwarz MJ, Guillemin GJ, Teipel SJ, Buerger K, Hampel H (2013) Increased 3-hydroxykynurenine serum concentrations differentiate Alzheimer’s disease patients from controls. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 263:345–352. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-012-0384-x
Scott HA, Gebhardt FM, Mitrovic AD, Vandenberg RJ, Dodd PR (2011) Glutamate transporter variants reduce glutamate uptake in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 32:553.e551–553.e511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2010.03.008
Selkoe DJ (2008) Soluble oligomers of the amyloid beta-protein impair synaptic plasticity and behavior. Behav Brain Res 192:106–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2008.02.016
Serrano-Pozo A, Frosch MP, Masliah E, Hyman BT (2011) Neuropathological alterations in Alzheimer disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 1:a006189. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a006189
Sery O, Povova J, Misek I, Pesak L, Janout V (2013) Molecular mechanisms of neuropathological changes in Alzheimer’s disease: a review. Folia Neuropathol 51:1–9
Seyedsadjadi N, Berg J, Bilgin AA, Braidy N, Salonikas C, Grant R (2018) High protein intake is associated with low plasma NAD+ levels in a healthy human cohort. PLoS One 13:e0201968–e0201968. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0201968
Shen L, Ji HF (2015) Associations between homocysteine, folic acid, vitamin B12 and Alzheimer’s disease: insights from meta-analyses. J Alzheimers Dis 46:777–790. https://doi.org/10.3233/jad-150140
Shen L, Liu L, Ji HF (2017) Alzheimer’s disease histological and behavioral manifestations in transgenic mice correlate with specific gut microbiome state. J Alzheimers Dis 56:385–390. https://doi.org/10.3233/jad-160884
Shi LZ, Faith NG, Nakayama Y, Suresh M, Steinberg H, Czuprynski CJ (2007) The aryl hydrocarbon receptor is required for optimal resistance to Listeria monocytogenes infection in mice. J Immunol 179:6952–6962
Singh N, Thangaraju M, Prasad PD, Martin PM, Lambert NA, Boettger T, Offermanns S, Ganapathy V (2010) Blockade of dendritic cell development by bacterial fermentation products butyrate and propionate through a transporter (Slc5a8)-dependent inhibition of histone deacetylases. J Biol Chem 285:27601–27608. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.102947
Smoller JWRS, Lee PH, Neale B, Nurnberger JI, Santangelo S, Sullivan PF, Perlis RH, Purcell SM, Fanous A, Neale MC, Rietschel M, Schulze TG, Thapar A, Anney R, Buitelaar JK, Farone SV, Hoogendijk WJ, Levinson DF, Lesch KP, Riley B, Schachar R, Sonuga-Barke E, Absher D, Agartz I (2013) Identification of risk loci with shared effects on five major psychiatric disorders: a genome-wide analysis. Lancet 381:1371–1379. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(12)62129-1
Sofi F, Valecchi D, Bacci D, Abbate R, Gensini GF, Casini A, Macchi C (2011) Physical activity and risk of cognitive decline: a meta-analysis of prospective studies. J Intern Med 269:107–117. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2796.2010.02281.x
Solfrizzi V, Custodero C, Lozupone M, Imbimbo BP, Valiani V, Agosti P, Schilardi A, D’Introno A, la Montagna M, Calvani M, Guerra V, Sardone R, Abbrescia DI, Bellomo A, Greco A, Daniele A, Seripa D, Logroscino G, Sabbá C, Panza F (2017) Relationships of dietary patterns, foods, and micro- and macronutrients with Alzheimer’s disease and late-life cognitive disorders: a systematic review. J Alzheimers Dis 59:815–849. https://doi.org/10.3233/jad-170248
Solfrizzi V, D'Introno A, Colacicco AM, Capurso C, Todarello O, Pellicani V, Capurso SA, Pietrarossa G, Santamato V, Capurso A, Panza F (2006) Circulating biomarkers of cognitive decline and dementia. Clin Chim Acta 364:91–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2005.06.015
Song H, Park H, Kim Y-S, Kim KD, Lee H-K, Cho DH, Yang JW, Hur DY (2011) l-Kynurenine-induced apoptosis in human NK cells is mediated by reactive oxygen species. Int Immunopharmacol 11:932–938. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2011.02.005
Souza LC, Jesse CR, Del Fabbro L, de Gomes MG, Goes ATR et al (2017) Swimming exercise prevents behavioural disturbances induced by an intracerebroventricular injection of amyloid-β1-42 peptide through modulation of cytokine/NF-kappaB pathway and indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase in mouse brain. Behav Brain Res 331:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2017.05.024
Stockinger B, Meglio PD, Gialitakis M, Duarte JH (2014) The aryl hydrocarbon receptor: multitasking in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol 32:403–432. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-immunol-032713-120245
Sun M, Wu W, Chen L, Yang W, Huang X, Ma C, Chen F, Xiao Y, Zhao Y, Ma C, Yao S, Carpio VH, Dann SM, Zhao Q, Liu Z, Cong Y (2018) Microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids promote Th1 cell IL-10 production to maintain intestinal homeostasis. Nat Commun 9:3555–3555. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-05901-2
Tan MS, Yu JT, Jiang T, Zhu XC, Tan L (2013) The NLRP3 inflammasome in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurobiol 48:875–882. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-013-8475-x
Ting KK, Brew BJ, Guillemin GJ (2009) Effect of quinolinic acid on human astrocytes morphology and functions: implications in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuroinflammation 6:36. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-2094-6-36
Tse JKY (2017) Gut microbiota, nitric oxide, and microglia as prerequisites for neurodegenerative disorders. ACS Chem Neurosci 8:1438–1447. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschemneuro.7b00176
Udan ML, Ajit D, Crouse NR, Nichols MR (2008) Toll-like receptors 2 and 4 mediate Abeta(1-42) activation of the innate immune response in a human monocytic cell line. J Neurochem 104:524–533. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.05001.x
Valladares R, Bojilova L, Potts AH, Cameron E, Gardner C, Lorca G, Gonzalez CF (2013) Lactobacillus johnsonii inhibits indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and alters tryptophan metabolite levels in BioBreeding rats. FASEB J 27:1711–1720. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.12-223339
Van der Leek AP, Yanishevsky Y, Kozyrskyj AL (2017) The kynurenine pathway as a novel link between allergy and the gut microbiome. Front Immunol 8:1374. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2017.01374
Veber D, Mutti E, Galmozzi E, Cedrola S, Galbiati S, Morabito A, Tredici G, la Porta CA, Scalabrino G (2006) Increased levels of the CD40:CD40 ligand dyad in the cerebrospinal fluid of rats with vitamin B12(cobalamin)-deficient central neuropathy. J Neuroimmunol 176:24–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2006.04.002
Vickers JC, Mitew S, Woodhouse A, Fernandez-Martos CM, Kirkcaldie MT et al (2016) Defining the earliest pathological changes of Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Alzheimer Res 13:281–287
Wang L, Yao Y, He R, Meng Y, Li N, Zhang D, Xu J, Chen O, Cui J, Bian J, Zhang Y, Chen G, Deng X (2017) Methane ameliorates spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats: antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic activity mediated by Nrf2 activation. Free Radic Biol Med 103:69–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.12.014
Wang X, Hu X, Yang Y, Takata T, Sakurai T (2016) Nicotinamide mononucleotide protects against β-amyloid oligomer-induced cognitive impairment and neuronal death. Brain Res 1643:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2016.04.060
Wang Y, Qin ZH (2010) Molecular and cellular mechanisms of excitotoxic neuronal death. Apoptosis 15:1382–1402. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-010-0481-0
Westin K, Buchhave P, Nielsen H, Minthon L, Janciauskiene S, Hansson O (2012) CCL2 is associated with a faster rate of cognitive decline during early stages of Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS One 7:e30525. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0030525
Widner B, Leblhuber F, Walli J, Tilz GP, Demel U, Fuchs D (2000) Tryptophan degradation and immune activation in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 107:343–353. https://doi.org/10.1007/s007020050029
Wu GD, Chen J, Hoffmann C, Bittinger K, Chen YY, Keilbaugh SA, Bewtra M, Knights D, Walters WA, Knight R, Sinha R, Gilroy E, Gupta K, Baldassano R, Nessel L, Li H, Bushman FD, Lewis JD (2011) Linking long-term dietary patterns with gut microbial enterotypes. Science 334:105–108. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1208344
Wu LE, Sinclair DA (2016) Restoring stem cells - all you need is NAD. Cell Res 26:971–972. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2016.80
Wu W, Nicolazzo JA, Wen L, Chung R, Stankovic R, Bao SS, Lim CK, Brew BJ, Cullen KM, Guillemin GJ (2013) Expression of tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase and production of kynurenine pathway metabolites in triple transgenic mice and human Alzheimer’s disease brain. PLoS One 8:e59749. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0059749
Yano JM, Yu K, Donaldson GP, Shastri GG, Ann P, Ma L, Nagler CR, Ismagilov RF, Mazmanian SK, Hsiao EY (2015) Indigenous bacteria from the gut microbiota regulate host serotonin biosynthesis. Cell 161:264–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.02.047
Yu JT, Tan L, Hardy J (2014) Apolipoprotein E in Alzheimer’s disease: an update. Annu Rev Neurosci 37:79–100. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-neuro-071013-014300
Zelante T, Iannitti RG, Cunha C, De Luca A, Giovannini G et al (2013) Tryptophan catabolites from microbiota engage aryl hydrocarbon receptor and balance mucosal reactivity via interleukin-22. Immunity 39:372–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2013.08.003
Zhang R, Miller RG, Madison C, Jin X, Honrada R, Harris W, Katz J, Forshew DA, McGrath MS (2013) Systemic immune system alterations in early stages of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuroimmunol 256:38–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2013.01.002
Zhang X, Li N, Shao H, Meng Y, Wang L, Wu Q, Yao Y, Li J, Bian J, Zhang Y, Deng X (2016) Methane limit LPS-induced NF-κB/MAPKs signal in macrophages and suppress immune response in mice by enhancing PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β-mediated IL-10 expression. Sci Rep 6:29359–29359. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep29359
Zhuang ZQ, Shen LL, Li WW, Fu X, Zeng F, Gui L, Lü Y, Cai M, Zhu C, Tan YL, Zheng P, Li HY, Zhu J, Zhou HD, Bu XL, Wang YJ (2018) Gut microbiota is altered in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 63:1337–1346. https://doi.org/10.3233/jad-180176
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq-Brazil) for the first author’s research fellowship at Macquarie University, Sydney, Australia. Prof Guillemin’s research is funded by the Australian Research Council (ARC), the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC), and Macquarie University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garcez, M.L., Jacobs, K.R. & Guillemin, G.J. Microbiota Alterations in Alzheimer’s Disease: Involvement of the Kynurenine Pathway and Inflammation. Neurotox Res 36, 424–436 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-019-00057-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-019-00057-3