Abstract
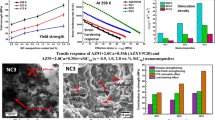
In this work, an attempt has been made to fabricate novel hybrid nanocomposites from Mg-Zn-Yttrium (traceable) alloy with 1.0 wt. percent nano-SiCP (fixed) and 0.5, 1.0, and 1.5 wt. percent nano-hBNP as reinforcing particles. The combined effect of stir-ultrasonication and squeeze casting was applied to mix the nanoparticles in the Mg matrix. The nanocomposite samples were heat-treated at T5 condition. Optical microscopy evaluates the refined grains. SEM pictures represent the uniform nanoparticle dispersion in the Mg matrix. As compared with base alloy, higher dislocation density is observed in the nanocomposite samples which were confirmed by the TEM images. XRD validates the occurrence of SiC and BN phases in the hybrid nanocomposites. The combination of 1.0 wt% SiCP and 1.5 wt% hBNP reinforced hybrid nanocomposite show 31% more microhardness and 42% more tensile strength than the base alloy. Various strengthening models employed to assess the influence of nanoparticles on yield strength, which were then, compared to the experimental yield strength values. Experimental and theoretical yield strength values were found to be in closer agreement.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
This work is part of the ongoing research work. All the data required for this work is included in the manuscript itself.
References
Gupta M, Wong WLE (2015) Magnesium-based nanocomposites: Lightweight materials of the future. Mater Charact 105:30–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2015.04.015
Fan Y, Wu G, Gao H et al (2006) Influence of lanthanum on the microstructure, mechanical property and corrosion resistance of magnesium alloy. J Mater Sci 41:5409–5416. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-006-0256-8
Shen MJ, Wang XJ, Ying T et al (2016) Characteristics and mechanical properties of magnesium matrix composites reinforced with micron/submicron/nano SiC particles. J Alloys Compd 686:831–840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.06.232
Anandajothi M, Vinod B (2020) Tribological behavior of magnesium hybrid composite: effect of amorphous silica-solid waste reinforcement particles to reduce material cost. Silicon. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-020-00769-8
Kumar KCK, Kumar BR, Rao NM (2021) Microstructural, mechanical characterization, and fractography of AZ31/SiC reinforced composites by stir casting method. Silicon. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-021-01180-7
Ramesh S, Anne G, Kumar G et al (2021) Influence of ball burnishing process on equal channel angular pressed Mg-Zn-Si alloy on the evolution of microstructure and corrosion properties. Silicon 13:1549–1560. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-020-00541-y
Rajan K, Bontha R, M R R S et al (2018) Effect of zinc and rare-earth element addition on mechanical, corrosion, and biological properties of magnesium. J Mater Res 33:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2018.311
Huang Y, Xu Y, You S et al (2018) Strengthening and ductilizing of magnesium alloying with heavy rare earth elements. MATEC Web Conf 188
Sivashanmugam N, Harikrishna KL (2020) Influence of rare earth elements in magnesium alloy - A mini review. Mater Sci Forum 979:162–166. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.979.162
Gnanavelbabu A, Sunu Surendran KT, Kumar S (2020) Influence of ultrasonication power on grain refinement, mechanical properties and wear behaviour of AZ91D/nano-Al2O3 composites. Mater Res Express 7:16544. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab64d7
Agarwal P, Kishore A, Kumar V et al (2019) Fabrication and machinability analysis of squeeze cast Al 7075/h-BN/graphene hybrid nanocomposite. Eng Res Express 1:15004. https://doi.org/10.1088/2631-8695/ab26f5
Prasad Reddy A, Vamsi Krishna P, Rao RN (2019) Tribological behaviour of Al6061–2SiC-xGr hybrid metal matrix nanocomposites fabricated through ultrasonically assisted stir casting technique. Silicon 11:2853–2871. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-019-0072-9
Li J, Lü S, Wu S, Gao Q (2018) Effects of ultrasonic vibration on microstructure and mechanical properties of nano-sized SiC particles reinforced Al-5Cu composites. Ultrason Sonochem 42:814–822. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2017.12.038
Madhukar P, Selvaraj N, Rao CSP, Veeresh Kumar GB (2020) Fabrication and characterization two step stir casting with ultrasonic assisted novel AA7150-hBN nanocomposites. J Alloys Compd 815:152464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.152464
Verma P, Kumari P, Ghose J, Pandey V (2019). In: Chattopadhyay J, Singh R, Prakash O (eds) Investigation of mechanical properties and microstructure of pure Al-SiC-nanocomposite casted by stir-squeeze casting process BT - Innovation in materials science and engineering. Springer, Singapore, pp 61–70
Wang XJ, Wang NZ, Wang LY et al (2014) Processing, microstructure and mechanical properties of micro-SiC particles reinforced magnesium matrix composites fabricated by stir casting assisted by ultrasonic treatment processing. Mater Des 57:638–645. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2014.01.022
Madhukar P, Selvaraj N, Gujjala R, Rao CSP (2019) Production of high performance AA7150-1% SiC nanocomposite by novel fabrication process of ultrasonication assisted stir casting. Ultrason Sonochem 58:104665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2019.104665
Drozd Z, Trojanová Z, Arlic U et al (2017) Effect of hexagonal boron nitride and graphite nanoparticles on the mechanical and physical properties of magnesium. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng 219:12017. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899x/219/1/012017
Harichandran R, Selvakumar N (2018) Microstructure and mechanical characterization of (B4C+ h-BN)/Al hybrid nanocomposites processed by ultrasound assisted casting. Int J Mech Sci 144:814–826. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2017.08.039
Vinod B, Ramanathan S, Ananthi V, Selvakumar N (2019) Fabrication and characterization of organic and in-organic reinforced A356 aluminium matrix hybrid composite by improved double-stir casting. Silicon 11:817–829. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-018-9881-5
Liu Z, Han Q, Li J (2011) Ultrasound assisted in situ technique for the synthesis of particulate reinforced aluminum matrix composites. Compos Part B Eng 42:2080–2084. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2011.04.004
HU K, YUAN D, LÜ S, WU S (2018) Effects of nano-SiCp content on microstructure and mechanical properties of SiCp/A356 composites assisted with ultrasonic treatment. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China 28:2173–2180. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(18)64862-9
Soundararajan R, Sivasankaran S, Al-Mufadi FA et al (2019) Investigation on A356-20wt%SiC composites through mechanical stirring and ultra-sonic-assisted cavitation. Mater Res Express 6:96572. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab3082
Yuan D, Yang X, Wu S et al (2019) Development of high strength and toughness nano-SiCp/A356 composites with ultrasonic vibration and squeeze casting. J Mater Process Technol 269:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2019.01.021
Khandelwal A, Mani K, Srivastava N et al (2017) Mechanical behavior of AZ31/Al2O3 magnesium alloy nanocomposites prepared using ultrasound assisted stir casting. Compos Part B Eng 123:64–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2017.05.007
Dieringa H, Katsarou L, Buzolin R et al (2017) Ultrasound assisted casting of an AM60 based metal matrix nanocomposite, its properties, and recyclability. Metals 7(10):388
Barati F, Latifi M, Moayeri far E, et al (2019) Novel AM60-SiO2 nanocomposite produced via ultrasound-assisted casting; production and characterization. Materials (Basel) 12(23):3976
Saboori A, Padovano E, Pavese M, Badini C (2018) Novel magnesium elektron21-AlN nanocomposites produced by ultrasound-assisted casting; microstructure thermal and electrical conductivity. Materials (Basel) 11(1):27
Li Q, Qiu F, Dong B et al (2018) Fabrication, microstructure refinement and strengthening mechanisms of nanosized SiCP/Al composites assisted ultrasonic vibration. Mater Sci Eng A 735:310–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2018.08.060
Dorri Moghadam A, Omrani E, Lopez H et al (2017) Strengthening in hybrid alumina-titanium diboride aluminum matrix composites synthesized by ultrasonic assisted reactive mechanical mixing. Mater Sci Eng A 702:312–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2017.07.022
Lü S, Xiao P, Yuan D et al (2018) Preparation of Al matrix nanocomposites by diluting the composite granules containing nano-SiCp under ultrasonic vibaration. J Mater Sci Technol 34:1609–1617. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2018.01.003
Zhou J, Ren L, Geng X et al (2019) As-cast magnesium AM60-based hybrid nanocomposite containing alumina fibres and nanoparticles: Microstructure and tensile behavior. Mater Sci Eng A 740–741:305–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2017.10.070
Suneesh E, Sivapragash M (2018) Comprehensive studies on processing and characterization of hybrid magnesium composites. Mater Manuf Process 33:1324–1345. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2018.1453155
Poovazhagan L, Kalaichelvan K, Sornakumar T (2016) Processing and performance characteristics of aluminum-nano boron carbide metal matrix nanocomposites. Mater Manuf Process 31:1275–1285. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2015.1026354
Xuan Y, Nastac L (2018) The role of ultrasonic cavitation in refining the microstructure of aluminum based nanocomposites during the solidification process. Ultrasonics 83:94–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultras.2017.06.023
Nie K, Deng K, Wang X, Wu K (2017) Characterization and strengthening mechanism of SiC nanoparticles reinforced magnesium matrix composite fabricated by ultrasonic vibration assisted squeeze casting. J Mater Res 32:2609–2620. https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2017.202
Reddy AP, Krishna PV, Rao RN (2019) Strengthening and mechanical properties of SiC and graphite reinforced Al6061 hybrid nanocomposites processed through ultrasonically assisted casting technique. Trans Indian Inst Met 72:2533–2546. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-019-01723-y
Kim C-S, Sohn I, Nezafati M et al (2013) Prediction models for the yield strength of particle-reinforced unimodal pure magnesium (Mg) metal matrix nanocomposites (MMNCs). J Mater Sci 48:4191–4204. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-013-7232-x
Xuan Y, Jia S, Nastac L (2017) Processing and microstructure characteristics of As-Cast A356 alloys manufactured via ultrasonic cavitation during solidification. High Temp Mater Process 36:381–387. https://doi.org/10.1515/htmp-2016-0147
Jian X, Xu H, Meek T, Han Q (2005) Effect of power ultrasound on solidification of aluminum A356 alloy. Mater Lett 59:190–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2004.09.027
Wang G, Dargusch MS, Qian M et al (2014) The role of ultrasonic treatment in refining the as-cast grain structure during the solidification of an Al–2Cu alloy. J Cryst Growth 408:119–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2014.09.018
Mirza FA, Chen DL (2015) A unified model for the prediction of yield strength in particulate-reinforced metal matrix nanocomposites. Materials 8(8):5138–5153
Trojanová Z, Drozd Z, Minárik P et al (2016) Influence of texture on the thermal expansion coefficient of Mg/BN nanocomposite. Thermochim Acta 644:69–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2016.10.010
Zhou X, Su D, Wu C, Liu L (2012) Tensile mechanical properties and strengthening mechanism of hybrid carbon nanotube and silicon carbide nanoparticle-reinforced magnesium alloy composites. J Nanomater 2012:851862. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/851862
Lin L, Liu Z, Chen L, Li F (2004) Tensile properties and strengthening mechanisms of Mg–Zn–Zr alloys. Met Mater Int 10:507–512. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03027411
Hassan SF, Tan MJ, Gupta M (2008) High-temperature tensile properties of Mg/Al2O3 nanocomposite. Mater Sci Eng A 486:56–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2007.08.045
Srivastava N, Chaudhari GP (2018) Microstructural evolution and mechanical behavior of ultrasonically synthesized Al6061-nano alumina composites. Mater Sci Eng A 724:199–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2018.03.092
Acknowledgements
(i) The authors acknowledge the financial and facility support (Grant number: CRG/2018/001006) provided by Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), Govt. of India.
(ii) The authors acknowledge the facility support (Grant number: EEQ/2017/000382) by Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), Govt. of India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Parthiban K – Materials procurement, Experimental works, Manuscript preparations, Testing and Characterizations.
Poovazhagan Lakshmanan – Supervising the work, Manuscript corrections, Similarity checking and Corrections.
Gnanavelbabu A – Provided facilities for experimentations, Experimental work – Supervising.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parthiban, K., Lakshmanan, P. & Gnanavelbabu, A. Experimental and Theoretical Yield Strength of Silicon Carbide and Hexagonal Boron Nitride Reinforced Mg-Zn Nanocomposites Produced by the Combined Effects of Ultrasonication and Squeeze Casting. Silicon 14, 8993–9007 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-022-01679-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-022-01679-7