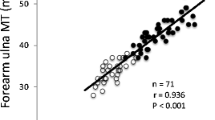
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to examine the applicability of ultrasound muscle thickness (MT) measurements for predicting whole body fat-free mass (FFM) in elderly individuals. Design and setting: Crosssectional study of 77 healthy elderly individuals. Methods: MTs at nine sites of the body and FFM were determined using B-mode ultrasound and dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA), respectively, in 44 women and 33 men aged 52 to 78 yrs. Stepwise multiple regression analysis produced two equations for predicting DXA-based FFM with sex (dummy: woman = 0 and man = 1) and either MTs at the anterior and posterior of thigh and lower leg (Eq1) or the product of MT and limb length (MT×LL) at thigh anterior and posterior, lower leg posterior, and upper arm anterior (Eq2) as independent variables. Results: The R2 and SEE for each of the two equations were 0.929 and 2.5 kg for Eq1 and 0.955 and 2.0 kg for Eq2. The estimated FFM from each of Eq1 (44.4 ± 8.9 kg) and Eq2 (44.4 ± 9.0 kg) did not significantly differ from that of the DXA-based FFM (44.4 ± 9.2 kg), without systematic error. However, the absolute value of the difference between the DXA-based and estimated FFM was significantly greater with Eq1 (2.0 ± 1.5 kg) than with Eq2 (1.5 ± 1.3 kg). Conclusion: The current results indicate that ultrasound MT measurement is useful to predict FFM in the elderly, and its accuracy is improved by using the product of MT and limb length as an independent variable.
Similar content being viewed by others

Références
Landers KA, Hunter GR, Wetzstein CJ, Bamman MM, Weinsier RL. The interrelationship among muscle mass, strength, and the ability to perform physical tasks of daily living in younger and older women. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci, 2001;56, B443–448.
Ball S, Swan PD, DeSimone R. Comparison of anthropometry to dual energy X-ray absorptiometry: a new prediction equation for women. Res Q Exerc Sport, 2004;75, 248–258.
Miyatani M, Kanehisa H, Fukunaga T. Validity of bioelectrical impedance and ultrasonographic methods for estimating the muscle volume of the upper arm. Eur J Appl Physiol, 2000;82, 391–396.
Ishida Y, Kanehisa H, Carroll JF, Pollock ML, Graves JE, Ganzarella L. Distribution of subcutaneous fat and muscle thicknesses in young and middle-aged women. Am J Hum Biol, 1997;9, 247–255.
Miyatani M, Kanehisa H, Azuma K, Kuno S, Fukunaga T. Site-related differences in muscle loss with aging“a cross-sectional survey on the muscle thickness in Japanese men aged 20 to 79 years”. Int J Sport Health Sci, 2003;1, 34–40.
Kanehisa H, Ishiguro N, Takeshita K, Kawakami Y, Kuno S, Miyatani M, Fukunaga T. Effects of gender on age-related changes in muscle thickness in the elderly. Int J Sport Health Sci, 2006;4, 427–434.
Takai Y, Katsumata Y, Kawakami Y, Kanehisa H, Fukunaga T. Ultrasound method for estimating the cross-sectional area of the psoas major muscle. Med Sci Sports Exerc, 2011;43, 2000–2004.
Abe T, Kawakami Y, Kondo M, Fukunaga T. Comparison of ultrasound-measured agerelated, site-specific muscle loss between healthy Japanese and German men. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging, 2011;31, 320–325.
Abe T, Kawakami Y, Bemben MG, Fukunaga T. Comparison of age-related, site-specific muscle loss between young and old active and inactive Japanese women. J Geriatr Phys Ther, 2011;34, 168–173.
Abe T, Bemben MG, Kondo M, Kawakami Y, Fukunaga T. Comparison of skeletal muscle mass to fat-free mass ratios among different ethnic groups. J Nutr Health Aging, 2012;16, 534–538.
Miyatani M, Kanehisa H, Kuno S, Nishijima T, Fukunaga T. Validity of ultrasonograph muscle thickness measurements for estimating muscle volume of knee extensors in humans. Eur J Appl Physiol, 2002;86, 203–208.
Miyatani M, Kanehisa H, Ito M, Kawakami Y, Fukunaga T. The accuracy of volume estimates using ultrasound muscle thickness measurements in different muscle groups. Eur J Appl Physiol, 2004;91, 264–272.
Sanada K, Kearns CF, Midorikawa T, Abe T. Prediction and validation of total and regional skeletal muscle mass by ultrasound in Japanese adults. Eur J Appl Physiol, 2006;96, 24–31.
Abe T, Kondo M, Kawakami Y, Fukunaga T. Prediction equations for body composition of Japanese adults by B-mode ultrasound. Am J Hum Biol, 1994;6, 161–170.
Janssen I, Heymsfield SB, Wang ZM, Ross R. Skeletal muscle mass and distribution in 468 men and women aged 18–88 yr. J Appl Physiol, 2000;89, 81–88.
Visser M, Fuerst T, Lang T, Salamone L, Harris TB. Validity of fan-beam dual-energy Xray absorptiometry for measuring fat-free mass and leg muscle mass. Health, Aging, and Body Composition Study—Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry and Body Composition Working Group. J Appl Physiol, 1999;87, 1513–1520.
Salamone LM, Fuerst T, Visser M, Kern M, Lang T, Dockrell M, Cauley JA, Nevitt M, Tylavsky F, Lohman TG. Measurement of fat mass using DEXA: a validation study in elderly adults. J Appl Physiol, 2000;89, 345–352.
Bland JM, Altman DG. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet, 1986;1, 307–310.
Deurenberg P, van der Kooij K, Evers P, Hulshof T. Assessment of body composition by bioelectrical impedance in a population aged greater than 60 y. Am J Clin Nutr, 1990;51, 3–6.
Roubenoff R, Baumgartner RN, Harris TB, Dallal GE, Hannan MT, Economos CD, Stauber PM, Wilson PW, Kiel DP. Application of bioelectrical impedance analysis to elderly populations. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci, 1997;52, M129–136.
Dupler TL, Tolson H. Body composition prediction equations for elderly men. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci, 2000;55, M180–184.
Kyle UG, Genton L, Karsegard L, Slosman DO, Pichard C. Single prediction equation for bioelectrical impedance analysis in adults aged 20–94 years. Nutrition, 2001;17, 248–253.
Dey DK, Bosaeus I. Comparison of bioelectrical impedance prediction equations for fatfree mass in a population-based sample of 75 y olds: the NORA study. Nutrition, 2003;19, 858–864.
Aleman-Mateo H, Rush E, Esparza-Romero J, Ferriolli E, Ramirez-Zea M, Bour A, Yuchingtat G, Ndour R, Mokhtar N, Valencia ME, Schoeller DA. Prediction of fat-free mass by bioelectrical impedance analysis in older adults from developing countries: a cross-validation study using the deuterium dilution method. J Nutr Health Aging, 2010;14, 418–426.
Abe T, Thiebaud RS, Loenneke JP, Loftin M, Fukunaga T. Prevalence of site-specific thigh sarcopenia in Japanese men and women. Age (Dordr), in press; 2013.
Kanehisa H, Miyatani M, Azuma K, Kuno S, Fukunaga T. Influences of age and sex on abdominal muscle and subcutaneous fat thickness. Eur J Appl Physiol, 2004;91, 534–537.
Kanehisa H, Ikegawa S, Tsunoda N, Fukunaga T. Cross-Sectional Areas of Fat and Muscle in Limbs during Growth and Middle-Age. Int J Sports Med, 1994;15, 420–425.
Ryan AS, Nicklas BJ. Age-related changes in fat deposition in mid-thigh muscle in women: relationships with metabolic cardiovascular disease risk factors. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord, 1999;23, 126–132.
Goodpaster BH, Carlson CL, Visser M, Kelley DE, Scherzinger A, Harris TB, Stamm E, Newman AB. Attenuation of skeletal muscle and strength in the elderly: The Health ABC Study. J Appl Physiol, 2001;90, 2157–2165.
Song MY, Ruts E, Kim J, Janumala I, Heymsfield S, Gallagher D. Sarcopenia and increased adipose tissue infiltration of muscle in elderly African American women. Am J Clin Nutr, 2004;79, 874–880.
Kelley DE, Slasky BS, Janosky J. Skeletal muscle density: effects of obesity and noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Am J Clin Nutr, 1991;54, 509–515.
Lohman TG, Harris M, Teixeira PJ, Weiss L. Assessing body composition and changes in body composition. Another look at dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. Ann N Y Acad Sci, 2000;904, 45–54.
Schoeller DA, Tylavsky FA, Baer DJ, Chumlea WC, Earthman CP, Fuerst T, Harris TB, Heymsfield SB, Horlick M, Lohman TG, Lukaski HC, Shepherd J, Siervogel RM, Borrud LG. QDR 4500A dual-energy X-ray absorptiometer underestimates fat mass in comparison with criterion methods in adults. Am J Clin Nutr, 2005;81, 1018–1025.
Tylavsky F, Lohman T, Blunt BA, Schoeller DA, Fuerst T, Cauley JA, Nevitt MC, Visser M, Harris TB. QDR 4500A DXA overestimates fat-free mass compared with criterion methods. J Appl Physiol, 2003;94, 959–965.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takai, Y., Ohta, M., Akagi, R. et al. Applicability of ultrasound muscle thickness measurements for predicting fat-free mass in elderly population. J Nutr Health Aging 18, 579–585 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-013-0419-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-013-0419-7