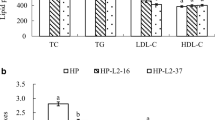
Abstract
Cholesterol-lowering activity is an important health benefit of lactic acid bacteria (LAB). This study aimed to screen LAB strains with cholesterol-lowering activities from salted fermented shrimp and evaluate probiotic characteristics and cholesterol-lowering potentials of these LAB isolates. Among 191 lactic acid strains isolated from traditional salted-fermented shrimp food, FB003 isolate showed the highest cholesterol-lowering activity and investigated as probiotics with cholesterol-lowering ability. Biochemical analysis and 16S rRNA sequencing revealed that this LAB isolate was Lactobacillus plantarum FB003. To screen probiotic trait, L. plantarum FB003 was found to be susceptible to six antibiotics tested and broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity. It also produced various enzymes such as galactosidase, glucosidase, and mannosidase. In addition, this strain showed autoaggregation, and coaggregation capacity for various pathogens. Moreover, it could adhere to Caco-2 cells and be exerted lowering cholesterol effects in Caco-2 cells via an upregulation of PPARα to inhibit NPC1L1 mRNA expression. Strain L. plantarum FB003 might be effective as a candidate probiotic with high cholesterol-lowering activity. The results of the present study suggest that L. plantarum FB003 have an impact on preventing high cholesterol level and may be used as starter culture for shrimp fermentation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mann GV, Spoerry A (1974) Studies of a surfactant and cholesteremia in the Maasai. Am J Clin Nutr 27(5):464–469
Valeriano V, Balolong M, Kang DK (2017) Probiotic roles of Lactobacillus sp. in swine: insights from gut microbiota. J Appl Microbiol 122(3):554–567. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.13364
Angmo K, Kumari A, Bhalla TC (2016) Probiotic characterization of lactic acid bacteria isolated from fermented foods and beverage of Ladakh. LWT-Food Sci Technol 66:428–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2015.10.057
Ishimwe N, Daliri EB, Lee BH, Fang F, Du G (2015) The perspective on cholesterol-lowering mechanisms of probiotics. Mol Nutr Food Res 59(1):94–105. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.201400548
Kumar R, Grover S, Batish VK (2012) Bile salt hydrolase (Bsh) activity screening of Lactobacilli: in vitro selection of indigenous Lactobacillus strains with potential bile salt hydrolysing and cholesterol-lowering ability. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins 4(3):162–172. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-012-9101-3
Jones ML, Tomaro-Duchesneau C, Martoni CJ, Prakash S (2013) Cholesterol lowering with bile salt hydrolase-active probiotic bacteria, mechanism of action, clinical evidence, and future direction for heart health applications. Expert Opin Biol Ther 13(5):631–642. https://doi.org/10.1517/14712598.2013.758706
Liong MT, Shah NP (2005) Optimization of cholesterol removal, growth and fermentation patterns of Lactobacillus acidophilus ATCC 4962 in the presence of mannitol, fructo-oligosaccharide and inulin: a response surface methodology approach. J Appl Microbiol 98(5):1115–1126. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2005.02544.x
Yoon H-s, Ju J-h, Kim H, Lee J, Park H-j, Ji Y, Shin H-k, Do M-S, Lee J-m, Holzapfel W (2011) Lactobacillus rhamnosus BFE 5264 and Lactobacillus plantarum NR74 promote cholesterol excretion through the up-regulation of ABCG5/8 in Caco-2 cells. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins 3(3–4):194–203. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-011-9086-3
Yoon H-S, Ju J-H, Kim H-N, Park H-J, Ji Y, Lee J-E, Shin H-K, Do M-S, Holzapfel W (2013) Reduction in cholesterol absorption in Caco-2 cells through the down-regulation of Niemann-Pick C1-like 1 by the putative probiotic strains Lactobacillus rhamnosus BFE5264 and Lactobacillus plantarum NR74 from fermented foods. Int J Food Sci Nutr 64(1):44–52. https://doi.org/10.3109/09637486.2012.706598
Nakamura F, Ishida Y, Aihara K, Sawada D, Ashida N, Sugawara T, Aoki Y, Takehara I, Takano K, Fujiwara S (2016) Effect of fragmented Lactobacillus amylovorus CP1563 on lipid metabolism in overweight and mildly obese individuals: a randomized controlled trial. Microb Ecol Health Dis 27(1):30312. https://doi.org/10.3402/mehd.v27.30312
Devi SM, Halami PM (2017) Genetic variation of pln loci among probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum group strains with antioxidant and cholesterol-lowering ability. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-017-9336-0
Lee SH, Jung JY, Jeon CO (2015) Bacterial community dynamics and metabolite changes in myeolchi-aekjeot, a Korean traditional fermented fish sauce, during fermentation. Int J Food Microbiol 203:15–22
Jeun YC, Park KS, Kim C, Fowler W, Kloepper J (2004) Cytological observations of cucumber plants during induced resistance elicited by rhizobacteria. Biol Control 29(1):34–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1049-9644(03)00082-3
Jeong JH, Lee CY, Chung DK (2016) Probiotic lactic acid bacteria and skin health. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 56(14):2331–2337. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2013.834874
Tanaka K, Sakai T, Ikeda I, Imaizumi K, Sugano M (1998) Effects of dietary shrimp, squid and octopus on serum and liver lipid levels in mice. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 62(7):1369–1375. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.62.1369
Ooi L-G, Liong M-T (2010) Cholesterol-lowering effects of probiotics and prebiotics: a review of in vivo and in vitro findings. Int J Mol Sci 11(6):2499–2522. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms11062499
Argyri AA, Zoumpopoulou G, Karatzas K-AG, Tsakalidou E, Nychas G-JE, Panagou EZ, Tassou CC (2013) Selection of potential probiotic lactic acid bacteria from fermented olives by in vitro tests. Food Microbiol 33(2):282–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2012.10.005
Lye H-S, Rahmat-Ali GR, Liong M-T (2010) Mechanisms of cholesterol removal by lactobacilli under conditions that mimic the human gastrointestinal tract. Int Dairy J 20(3):169–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.idairyj.2009.10.003
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33(7):1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
Mishra V, Prasad D (2005) Application of in vitro methods for selection of Lactobacillus casei strains as potential probiotics. Int J Food Microbiol 103(1):109–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2004.10.047
Wiegand I, Hilpert K, Hancock RE (2008) Agar and broth dilution methods to determine the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of antimicrobial substances. Nat Protoc 3(2):163–175. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2007.521
EFSA (2012) Guidance on the assessment of bacterial susceptibility to antimicrobials of human and veterinary importance. EFSA J 10:10. https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2012.2740
Bover-Cid S, Holzapfel WH (1999) Improved screening procedure for biogenic amine production by lactic acid bacteria. Int J Food Microbiol 53(1):33–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-1605(99)00152-X
Abe F, Muto M, Yaeshima T, Iwatsuki K, Aihara H, Ohashi Y, Fujisawa T (2010) Safety evaluation of probiotic bifidobacteria by analysis of mucin degradation activity and translocation ability. Anaerobe 16(2):131–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anaerobe.2009.07.006
Bove P, Gallone A, Russo P, Capozzi V, Albenzio M, Spano G, Fiocco D (2012) Probiotic features of Lactobacillus plantarum mutant strains. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 96(2):431–441. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4031-2
Collado MC, Meriluoto J, Salminen S (2008) Adhesion and aggregation properties of probiotic and pathogen strains. Eur Food Res Technol 226(5):1065–1073. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-007-0632-x
Guan L, Cho KH, Lee J-H (2011) Analysis of the cultivable bacterial community in jeotgal, a Korean salted and fermented seafood, and identification of its dominant bacteria. Food Microbiol 28(1):101–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2010.09.001
Huang Y, Wang X, Wang J, Wu F, Sui Y, Yang L, Wang Z (2013) Lactobacillus plantarum strains as potential probiotic cultures with cholesterol-lowering activity. J Dairy Sci 96(5):2746–2753
Michael D, Moss J, Calvente DL, Garaiova I, Plummer S, Ramji D (2016) Lactobacillus plantarum CUL66 can impact cholesterol homeostasis in Caco-2 enterocytes. Benefic Microbes 7(3):443–451. https://doi.org/10.3920/BM2015.0146
Liu DM, Guo J, Zeng XA, Sun DW, Brennan CS, Zhou QX, Zhou JS (2017) The probiotic role of Lactobacillus plantarum in reducing risks associated with cardiovascular disease. Int J Food Sci Technol 52(1):127–136. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.13234
Šušković J, Kos B, Beganović J, Leboš Pavunc A, Habjanič K, Matošić S (2010) Antimicrobial activity–the most important property of probiotic and starter lactic acid bacteria. Food Technol Biotechnol 48(3):296–307
Songisepp E, Kullisaar T, Hütt P, Elias P, Brilene T, Zilmer M, Mikelsaar M (2004) A new probiotic cheese with antioxidative and antimicrobial activity. J Dairy Sci 87(7):2017–2023
Ding W, Shi C, Chen M, Zhou J, Long R, Guo X (2017) Screening for lactic acid bacteria in traditional fermented Tibetan yak milk and evaluating their probiotic and cholesterol-lowering potentials in rats fed a high-cholesterol diet. J Funct Foods 32:324–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2017.03.021
Arena MP, Russo P, Capozzi V, López P, Fiocco D, Spano G (2014) Probiotic abilities of riboflavin-overproducing Lactobacillus strains: a novel promising application of probiotics. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(17):7569–7581. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5837-x
Arai T, Obuchi S, Eguchi K, Seto Y (2016) In vitro investigation of molecules involved in Lactobacillus gasseri SBT2055 adhesion to host intestinal tract components. J Appl Microbiol 120(6):1658–1667. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.13137
Candela M, Seibold G, Vitali B, Lachenmaier S, Eikmanns BJ, Brigidi P (2005) Real-time PCR quantification of bacterial adhesion to Caco-2 cells: competition between bifidobacteria and enteropathogens. Res Microbiol 156(8):887–895
Huang Y, Wang J, Cheng Y, Zheng Y (2010) The hypocholesterolaemic effects of Lactobacillus acidophilus American type culture collection 4356 in rats are mediated by the down-regulation of Niemann-Pick C1-Like 1. Br J Nutr 104(6):807–812. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114510001285
Lim F, Lim S, Ramasamy K (2017) Pediococcus acidilactici LAB4 and Lactobacillus plantarum LAB12 assimilate cholesterol and modulate ABCA1, CD36, NPC1L1 and SCARB1 in vitro. Benefic Microbes 8(1):97–109. https://doi.org/10.3920/BM2016.0048
Kim DH, Jeong D, Kang IB, Kim H, Song KY, Seo KH (2017) Dual function of Lactobacillus kefiri DH5 in preventing high-fat-diet–induced obesity: direct reduction of cholesterol and upregulation of PPARα in adipose tissue. Mol Nutr Food Res. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.201700252
Valasek MA, Clarke SL, Repa JJ (2007) Fenofibrate reduces intestinal cholesterol absorption via PPARα-dependent modulation of NPC1L1 expression in mouse. J Lipid Res 48(12):2725–2735. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.M700345-JLR200
Funding
This study was carried out with the support of the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (NRF-2017R1D1A3B03027816).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Table S1.
Physiological and biochemical characteristics of Lactobacillus plantarum FB003 isolated from jeotgal based on API 50 CH system and additional tests after incubation at 37° C for 24 h (+, positive; −, negative) (DOCX 15 kb)
Table S2.
Enzyme activities of Lactobacillus plantarum FB003 (API ZYM KIT) (DOCX 13 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Le, B., Yang, SH. Identification of a Novel Potential Probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum FB003 Isolated from Salted-Fermented Shrimp and its Effect on Cholesterol Absorption by Regulation of NPC1L1 and PPARα. Probiotics & Antimicro. Prot. 11, 785–793 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-018-9469-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-018-9469-9