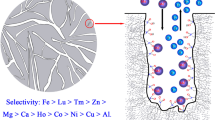
Abstract
Ultra-high purity Yb2O3 is the critical material of many high-tech materials such as laser glass and fiber, in which impurities seriously affect the laser color quality, intensity and power. In order to reduce the influence of impurities on the properties of laser materials, the purification process of Yb2O3 was studied by comparing two kinds of resins (RT-1 and RS-1) using improved ion-exchange chromatography (IEC) method. In this study, through the synergistic improvement of resin structure and eluting system, the environmental pollution caused by ammonia water in the traditional IEC method was reduced, and the requirements of high temperature and pressure were cut. The ion exchange behavior and impurity removal mechanism in the resin column during the loading and eluting process were compared and analyzed. The experimental results show that RS-1 resin is all superior to RT-1 resin in elements selectivity, ion exchange capacity and impurities removal rate. After separation and purification by IEC with RS-1 resin, the total removal rate of rare earth impurities was 77.59% and that of non-rare earth impurities was 95.86% when Yb recovery was more than 70%, both higher than that of RT-1 resin (73.26% and 83.18%). This indicates that the improved IEC method is very effective in separating and removing different metal impurities from Yb2O3. The pilot test results of IEC method separating and purifying Yb2O3 with RS-1 resin show that the purity of Yb2O3 can be increased from 99.9929% to 99.9997% by IEC method. It has exhibited huge potential of preparing ultra-high purity Yb2O3, especially the deep removal of non-rare earth impurities.
Graphical abstract

摘要
超高纯Yb2O3是激光玻璃、光纤等许多高科技材料的关键原料,其中的痕量杂质严重影响激光强度和功率。为了减少杂质对激光材料性能的影响,采用新体系的离子交换色谱法对两种酸性离子交换树脂RT-1和RS-1提纯Yb2O3工艺进行了对比研究。本研究通过树脂结构和淋洗体系的协同改进,减少了传统离子交换提纯过程中氨水对环境的污染,并且不必高温高压的苛刻条件。比较分析了树脂柱在负载和淋洗过程中的离子交换行为和杂质去除机理。实验结果表明,RS-1树脂在离子选择性、离子交换容量和杂质去除率方面均优于RT-1树脂。RS-1树脂经离子交换分离提纯,Yb回收率大于70%时,稀土杂质的总去除率为77.59%,非稀土杂质的总去除率为95.86%,均高于RT-1树脂(73.26%和83.18%)。这表明新体系离子交换色谱法是分离提纯Yb2O3的有效方法。采用RS-1树脂分离提纯Yb2O3的中试结果表明,新体系离子交换色谱法可将Yb2O3纯度由99.9929%提高到99.9997%,在制备超高纯Yb2O3,特别是非稀土杂质的深度去除方面表现出良好的应用前景。










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Henriques MS, Ferreira AC, Cruz A, Ferreira LM, Branco JB, Brázda P, Jurek K, Stora T, Gonçalves AP. Preparation of Yb2O3 submicron-and nano-materials via electrospinning. Ceram Int. 2015;41(9):10795. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.05.017.
Shi D, Zhao Y. Spectroscopic properties and energy transfer of Nd3+/Ho3+-doped Ga2O3-GeO2 glass by codoping Yb3+ ion. J Rare Earths. 2016;4(4):368. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0721(16)60035-2.
Mansour SF, Al-Hazmi F, AlHammad MS, Sadeq MS, Abdo MA. Enhancing the magnetization, dielectric loss and photocatalytic activity of Co–Cu ferrite nanoparticles via the substitution of rare earth ions. J Market Res. 2021;15:2543. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JMRT.2021.09.079.
Song X, Jin D, Zhou D, Xu P, Han K. Er3+/Yb3+ co-doped bismuthate glass and its large-mode-area double-cladding fiber for 1.53 μm laser. J Alloys Compd. 2021;853:157305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.157305.
Reddy CP, Ramaraghavulu R, Kalpana T, Gajendiran J. Energy transfer induced enhancement in NIR luminescence characteristics of Yb3+/Er3+ co-doped sodium zinc bismuth fluorophosphate glasses. Opt Mater. 2020;100:109616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2019.109616.
Xia C, Zhou G, Liu J, Wang C, Han Y, Zhang W, Yuan J. Fabrication and laser performance of Yb3+/Al3+ co-doped photonic crystal fiber synthesized by plasma nonchemical vapor deposition method. Opt Fiber Technol. 2015;25:20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yofte.2015.07.002.
Zheng Y, Lv Q, Wang J, Zhang G, Gao Y, Liu Z. Emission behaviors of Yb2O3 nanoparticles pumped by 980nm laser at different power densities. Opt Laser Technol. 2014;63:39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2014.03.012.
Zhang L, Hu HF. The effect of OH- on IR emission of Nd3+, Yb3+ and Er3+ doped tetraphosphate glasses. J Phys Chem Solids. 2002. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-3697(01)00196-2.
Zhang YM, Li YH, Zhang Y, Hong GY, Yu YN. Effect of Yb3+ concentration on the structures and upconversion luminescence properties of Y2O3:Er3+ ultrafine phosphors. Rare Met. 2008;27(6):603. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0521(08)60190-4.
Wang X, Li K, Yu C, Chen D, Hu L. Effect of Tm2O3 concentration and hydroxyl content on the emission properties of Tm doped silicate glasses. J Lumin. 2014;147:341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2013.11.025.
Leal JJ, Rodríguez E, Nava-Dino CG, Maldonado-Orozco MC, Gaxiola F, Narro-García R. Effect of Ho3+ concentration on the luminescent and thermal stability of tellurite glasses. Mater Res Bull. 2021;144:111483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2021.111483.
Liu HJ, Wang FR, Huang J, Meng J, Ma YJ. Experimental study of 355nm laser damage ignited by Fe and Ce impurities on fused silica surface. Opt Mater. 2019;95:109231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2019.109231.
Li S, Lin Y, Wu Y, Guo Y, Yu H, Miao R, Wang Z, Tian W, Li X. Effect of Fe impurity on performance of La2O3 as a high k gate dielectric. Ceram Int. 2019;45(16):21015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.06.294.
Judge WD, Azimi G. Recent progress in impurity removal during rare earth element processing: a review. Hydrometallurgy. 2020;196:105435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2020.105435.
Da Silva RG, De Morais CA, Teixeira LV, de Oliveira ÉD. Selective removal of impurities from rare earth sulphuric liquor using different reagents. Miner Eng. 2018;127:238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2018.08.007.
Xu GX. Rare Earths. In: Qi YQ, (Eds.) Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press; 1995.728.
Zhou G, Li Q, Sun P, Guan W, Zhang G, Cao Z, Zeng L. Removal of impurities from scandium chloride solution using 732-type resin. J Rare Earths. 2018;36(3):311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jre.2017.09.009.
Li JH, Gao Y, Gao Y, Chen ZF, Wang RX, Xu ZF. Study on aluminum removal through 5-sulfosalicylic acid targeting complexing and D290 resin adsorption. Miner Eng. 2020;147:106175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2019.106175.
Niu F, Xie Z, Fu C, Xu H, Liu D, Zhang X, Yang Y, Shen L. Adsorption–desorption of La3+, Eu3+, and Y3+ by Mg(OH)2-pretreated TP207 resin. JOM. 2020;73(1):32. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-020-04472-2.
Liu F, Chen F, Wang L, Ma S, Wan X, Wang J. Selective separation of rare earths from spent Nd-Fe-B magnets using two-stage ammonium sulfate roasting followed by water leaching. Hydrometallurgy. 2021;203:105626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2021.105626.
General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China Standardization Administration of China, Terms for rare earths, http://openstd.samr.gov.cn/bzgk/gb/newGbInfo?hcno=CB52EDA8B0FC950458B344BC81BC507C, 2015–09–11.
Feng ZY, Wang M, Zhao LS, Xu Y, Zhang YQ, Huang XW. Development status and prospect of rare earth extraction and separation technology. J Chin Soc Rare Earths. 2021;39(3):469.
Feng ZY, Huang XW, Wang M, Zhang GC. Progress and trend of green chemistry in extraction and separation of typical rare earth resources. Chin J Rare Met. 2017;41(5):604. https://doi.org/10.13373/j.cnki.cjrm.XY17030028.
Wan WJ, Xia N, Zhu SM, Liu Q, Gao YC. Synthesis and characterization of a novel soluble hesperetin monoglucoside-copper(II) complex using ion exchange column. Inorg Chim Acta. 2020;512:119857. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ica.2020.119857.
Pan XJ, Dou ZH, Zhang TA, Meng DL, Fan YY. Separation of metal ions and resource utilization of magnesium from saline lake brine by membrane electrolysis. Sepa Purif Technol. 2020;251:117316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117316.
Pan XJ, Dou ZH, Meng DL, Han XX, Zhang TA. Electrochemical separation of magnesium from solutions of magnesium and lithium chloride. Hydrometallurgy. 2020;191:105166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2019.105166.
Meng DL, Zhao QY, Pan XJ, Zhang TA. Preparation of La2O3 by ion-exchange membrane electrolysis of LaCl3 aqueous solution. J Rare Earths. 2019;37(9):1009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jre.2018.11.017.
Meng DL, Zhao QY, Pan XJ, Zhang TA. Clean production of rare earth oxide from rare earth chloride solution by electrical transformation. Hydrometallurgy. 2020;197:105372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2020.105372.
Kifle D, Wibetoe G. Selective liquid chromatographic separation of yttrium from heavier rare earth elements using acetic acid as a novel eluent. J Chromatogr A. 2013;1307:86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2013.07.070.
Technical Committee ISO/TC 201/SC 8, Glow discharge spectroscopy, Surface chemical analysis—Glow discharge mass spectrometry—Operating procedures, ISO/TS 15338:2020-02. https://www.iso.org/standard/70370.html
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2020YFC1909004), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Nos. 2020M680615 and 2021T140581) and the Youth Fund Project of GRINM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, XJ., Yang, ZQ., Xu, Y. et al. Separation and purification of Yb2O3 by ion exchange chromatography and preparation of ultra-high purity Yb2O3. Rare Met. 42, 2725–2735 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-023-02275-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-023-02275-3