Abstract
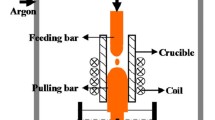
Beta-solidifying TiAl alloy has great potential in the field of aero-industry as a cast alloy. In the present work, the influence of cooling rate during mushy zone on solidification behavior of Ti–44Al–4Nb–2Cr–0.1B alloy was investigated. A vacuum induction heating device combining with temperature control system was used. The Ti–44Al–4Nb–2Cr–0.1B alloy solidified from superheated was melted to β phase with the cooling rates of 10, 50, 100, 200, 400 and 700 K·min−1, respectively. Results show that with the increase in cooling rate from 10 to 700 K·min−1, the colony size of α2/γ lamella decreases from 1513 to 48 μm and the solidification segregation significantly decreases. Also the content of residual B2 phase within α2/γ lamellar colony decreases with the increase in cooling rate. In addition, the alloy in local interdendritic regions would solidify in a hypo-peritectic way, which can be attributed to the solute redistribution and enrichment of Al element in solidification.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appel F, Paul JDH, Oehring M. Gamma Titanium Aluminide Alloys: Science and Technology. Weinheim: Wiley; 2011.
Kim YW, Dimiduk DM. Progress in the understanding of gamma titanium aluminides. JOM. 1991;43(8):40.
Clemens H, Mayer S. Design, processing, microstructure, properties, and applications of advanced intermetallic TiAl alloys. Adv Eng Mater. 2013;15(4):191.
Clemens H, Wallgram W, Kremmer S, Guther V, Otto A, Bartels A. Design of novel β-solidifying TiAl alloys with adjustable β/B2-phase fraction and excellent hot-workability. Adv Eng Mater. 2008;10(8):707.
Hu D, Yang C, Huang A, Dixon M, Hecht U. Grain refinement in beta-solidifying Ti44Al8Nb1B. Intermetallics. 2012;23(4):49.
Schwaighofer E, Clemens H, Mayer S, Lindemann J, Klose J, Smarsly W, Guther V. Microstructural design and mechanical properties of a cast and heat-treated intermetallic multi-phase γ-TiAl based alloy. Intermetallics. 2014;44(1):128.
Liu Y, Hu R, Kou HC, Wang J, Zhang TB, Li JS, Zhang J. Solidification characteristics of high Nb-containing γ-TiAl-based alloys with different aluminum contents. Rare Met. 2015;34(6):381.
Yang J, Wang JN, Xia QF, Wang Y. Effect of cooling rate on the grain refinement of TiAl-based alloys by rapid heat treatment. Mater Lett. 2000;46(4):193.
Perdrix F, Trichet MF, Bonnentien JL, Cornet M, Bigot J. Influence of cooling rate on microstructure and mechanical properties of a Ti-48Al alloy. Intermetallics. 1999;7(12):1323.
Liu ZG, Chai LH, Chen YY. Effect of cooling rate and Y element on the microstructure of rapidly solidified TiAl alloys. J Alloys Compd. 2010;504(8):S491.
Xu XJ, Lin JP, Teng ZK, Wang YL, Chen GL. On the microsegregation of Ti–45Al–(8–9) Nb–(W, B, Y) alloy. Mater Lett. 2007;61(2):369.
Chen GL, Xu XJ, Teng ZK, Lin JP, Wang YL. Microsegregation in high Nb containing TiAl alloy ingots beyond laboratory scale. Intermetallics. 2007;15(5):625.
Kim YW, Kim SL, Dimiduk D, Woodward C. Development of beta gamma alloys: opening robust processing and greater application potential for TiAl-based alloys. Structural aluminides for elevated temperatures. TMS 2008 Annual Meeting & Exhibition. Warrendale: The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society; 2008. 215.
Schmoelzer T, Liss KD, Zickler GA, Watson IJ, Droessler LM, Wallgram W, Buslaps T, Studer A, Clemens H. Phase fractions, transition and ordering temperatures in TiAl–Nb–Mo alloys: an in-and ex situ study. Intermetallics. 2010;18(8):1544.
Imayev RM, Imayev VM, Oehring M, Appel F. Alloy design concepts for refined gamma titanium aluminide based alloys. Intermetallics. 2007;15(4):451.
Hecht U, Witusiewicz V, Drevermann A, Zollinger J. Grain refinement by low boron additions in niobium-rich TiAl-based alloys. Intermetallics. 2008;16(8):969.
Oehring M, Stark A, Paul JDH, Lippmann T, Pyczak F. Microstructural refinement of boron-containing β-solidifying γ-titanium aluminide alloys through heat treatments in the β phase field. Intermetallics. 2013;32(1):12.
Hu D, Yang C, Huang A, Dixon M, Hecht U. Solidification and grain refinement in Ti45Al2Mn2Nb1B. Intermetallics. 2012;22(3):68.
Huang ZW. Inhomogeneous microstructure in highly alloyed cast TiAl-based alloys, caused by microsegregation. Scr Mater. 2005;52(10):1021.
Sun HL, Huang ZW, Zhu DG, Jiang XS. Dendrite core grain refining and interdendritic coarsening behaviour in W-containing γ-TiAl based alloys. J Alloys Compd. 2013;552(3):213.
Xu XJ, Lin JP, Wang YL, Gao JF, Lin Z, Chen GL. Microstructure and tensile properties of as-cast Ti-45Al–(8–9) Nb–(W, B, Y) alloy. J Alloys Compd. 2006;414(1):131.
Johnson DR, Inui H, Muto S, Omiya Y, Yamanaka T. Microstructural development during directional solidification of α-seeded TiAl alloys. Acta Mater. 2006;54(4):1077.
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51401168) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 3102014JCQ01026).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, P., Kou, HC., Yang, JR. et al. Solidification microstructure characteristics of Ti–44Al–4Nb–2Cr–0.1B alloy under various cooling rates during mushy zone. Rare Met. 35, 35–41 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-015-0633-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-015-0633-z