Abstract
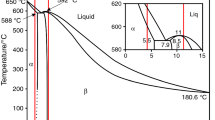
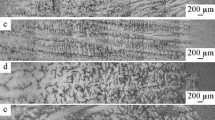
The effect of Al content on the microstructure and solidification characteristics of Ti–Al–Nb–V–Cr alloys in as-cast and isothermally treated states was investigated using X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) equipped with energy dispersive spectroscope (EDS), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The typical solidification characteristics are due to the joint influence of both the crystal temperature range and the solidification path. The wide crystallization temperature range contributes to obtaining coarse dendrites in the as-cast Ti47Al7Nb2.5V1.0Cr (at%) alloy solidifying through the peritectic reaction. The β-solidifying Ti46Al7Nb2.5V1.0Cr (at%) alloy with the narrow crystallization temperature range is attributed to the formation of a homogeneous fine-grained microstructure. However, the crystallization temperature range of Ti48Al7Nb2.5V1.0Cr (at%) alloy is equivalent to that of Ti46Al7Nb2.5V1.0Cr alloy, but it is solidified by peritectic reaction, leading to the formation of finer dendrites.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wu XH. Review of alloy and process development of TiAl alloys. Intermetallics. 2006;14(10):1114.
Yang C, Jiang H, Hu D, Huang A, Dixon M. Effect of boron concentration on phase transformation texture in as-solidified Ti44Al8NbxB. Scripta Mater. 2012;67(1):85.
Hu D, Botten RR. Phase transformations in some TiAl-based alloys. Intermetallics. 2002;10(7):701.
Kim JH, Kim SW, Lee HN, Oh MH, Inui H, Wee DM. Effects of Si and C additions on the thermal stability of directionally solidified TiAl–Nb alloys. Intermetallics. 2005;13(10):1038.
Johnson DR, Chihara K, Inui H, Yamaguchi M. Microstructural control of TiAl–Mo–B alloys by directional solidification. Acta Mater. 1998;46(18):6529.
Qi WJ, Wang SC, Chen XM, Nong D, Zhou Z. Effective nucleation phase and grain refinement mechanism of Al-5Ti-1B master alloy. Chin J Rare Metals. 2013;37(2):179.
Singh AK, Muraleedharan K, Banerjee D. Solidification structure in a cast γ alloy. Scripta Mater. 2003;48(6):767.
Huang L, Liaw PK, Liu CT, Liu Y, Huang JS. Microstructural evolution of (TiAl) + Nb + W + B alloy. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China. 2011;21(10):2192.
Su YQ, Liu C, Li XZ, Guo JJ, Li BS, Jia J, Fu HZ. Microstructure selection during the directionally peritectic solidification of Ti–Al binary system. Intermetallics. 2005;13(3):267.
Zhang YG, Han YF, Chen GL, Guo JT, Wan XJ, Feng T. Intermetallic Compound Structure Material, National Defense. Beijing: Industry Press; 2001. 701.
Wang Y, Liu Y, Yang GY, Li HZ, Tang B. Microstructure of cast γ-TiAl based alloy solidified from β phase region. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China. 2011;21(2):215.
Chen GL, Xu XJ, Teng ZK, Wang YL, Lin JP. Microsegregation in high Nb containing TiAl alloy ingots beyond laboratory scale. Intermetallics. 2007;15(5):625.
Daloz D, Hecht U, Zollinger J, Combeau H, Hazotte A. Microsegregation, macrosegregation and related phase transformations in TiAl alloys. Intermetallics. 2011;19(6):749.
Liu GH, Li XZ, Su YQ, Chen RR, Gou JJ, Fu HZ. Microstructure and microsegregation in directionally solidified Ti−46Al−8Nb alloy. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China. 2012;22(6):1342.
Jung IS, Jang HS, Oh MH, Lee JH, Wee DM. Microstructure control of TiAl alloys containing β stabilizers by directional solidification. Mater Sci Eng A. 2002;329–331(6):13.
Ding XF, Lin JP, Zhang LQ, Su YQ, Hao GJ, Chen GL. A closely-complete peritectic transformation during directional solidification of a Ti-45Al-8.5Nb alloy. Intermetallics. 2011;19(8):1115.
Huang ZW. Inhomogeneous microstructure in highly alloyed cast TiAl-based alloys, caused by microsegregation. Scripta Mater. 2005;52(10):1021.
Johnson DR, Inui H, Muto S, Omiya Y, Yamanaka T. Microstructural development during directional solidification of α-seeded TiAl alloys. Acta Mater. 2006;54(4):1077.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2011CB605503) and the Program of Introducing Talents of Discipline to Universities (No.B08040).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Hu, R., Kou, HC. et al. Solidification characteristics of high Nb-containing γ-TiAl-based alloys with different aluminum contents. Rare Met. 34, 381–386 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-014-0416-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-014-0416-y