Abstract
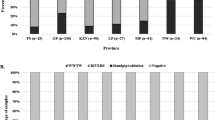
Noroviruses (NoV) and hepatitis A virus (HAV) are the leading causes of non-bacterial gastroenteritis in shellfish consumers worldwide. This study determined the seasonal and geographical distribution of NoV (genogroups I and II) and HAV in live U.S. market oysters. Samples were analyzed to determine the occurrence and levels of NoV and HAV using RT-qPCR and conventional RT-PCR. NoV and HAV were detected in 3.9 and 4.4%, respectively. NoV genogroups I and II were detected, with genogroup II predominating. Sequencing identified genotypes II.4, II.3, and II.7. The GII.4 strain showed ≥98% similarity with 2006–2007 circulating strains, Minerva and Laurens. HAV sequences from the 5′ non-coding region (NCR) of the genome were from genotypes I, II, or III. The incidence of NoV in oysters harvested from Atlantic Coast states was higher than that in oysters from other regions and its occurrence was greatest during the cooler months (December to February). HAV was detected at a higher frequency in shellfish harvested from the Gulf Coast and also predominated during cooler months. The seasonal occurrence of viruses in this study corresponded to the reported incidence of shellfish-associated viral illnesses. This investigation provides an overview of the occurrence and distribution of NoV and HAV in U.S. market shellfish.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ando, T., Noel, J. S., & Fankhauser, R. L. (2000). Genetic classification of Norwalk-like viruses. Journal of Infectious Disease, 181, S336–S348.
Beuret, C., Kohler, D., Baumgartner, A., & Luthi, T. M. (2002). Norwalk-live virus sequences in mineral waters: one year monitoring of three brands. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 68, 1925–1931.
Blanton, L. H., Adams, S. M., Beard, R. S., Wei, G., Bulens, S. N., Widdowson, M., et al. (2006). Molecular and epidemiologic trends of Calicivirus associated with outbreaks of acute gastroenteritis in the United States, 2000–2004. Journal of Infectious Disease, 183, 413–421.
Burkhardt III, W., Calci, K. R., Watkins, W. W., Rippey, S. R., & Chirtel, S. J. (2000). Inactivation of indicator microorganisms in estuarine waters. Water Research, 34, 2207–2214.
Burkhardt III, W., Woods, J. W., Nordstrom, J., & Hartman, G. (2006). A realtime RT-PCR protocol for the simultaneous detection of norovirus and enterovirus. Laboratory information bulletin #4369. Washington, DC: U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2006). Prevention of specific infectious diseases: hepatitis, viral, type A. In Travelers’ health: Yellow book. Health information for international travel, 2005–2006. Available at: http://www2.ncid.cdc.gov/travel/yb/utils/ybGet.asp?section=dis&obj=hav.htm. Accessed March 2008.
Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2007). Norovirus activity—United States, 2006–2007. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, 56, 842–846.
Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2009). Surveillance for foodborne outbreaks—United States. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, 38, 609–615.
Constantini, V., Loisy, F., Jones, L., LeGuyader, F. S., & Saif, L. J. (2006). Human and animal enteric caliciviruses in oysters from different coastal regions of the United States. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 72, 1800–1809.
Costa-Mattioli, M., Di Napoli, A., Ferre, V., Billaudel, S., Perez-Bercoff, R., & Cristina, J. (2003). Genetic variability of hepatitis A virus. Journal of General Virology, 84, 3191–3201.
Depaola, A., Jones, J. L., Woods, J. W., Burkhardt III, W., Calci, K. R., Krantz, J. A., Bowers, J. C., Kastrui, K., Byars, R. H., Jacobs, E., Hill-Williams, D., & Nabe, K. (2010). Bacterial and viral pathogens in live oysters: U.S. markets survey 2007. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. doi:10.1128/AEM.02590-09.
Desenclos, J. C., Klontz, K. C., Wilder, M. H., Nainan, O. V., Margolis, H. S., & Gunn, R. A. (1991). A multistate outbreak of hepatitis A caused by the consumption of raw oysters. American Journal of Public Health, 81, 1268–1272.
Ellender, R. D., Mapp, J. B., Middlebrooks, B. C., Cooks, D. W., & Cake, E. W. (1980). Natural enterovirus and fecal coliform contamination of Gulf coast oysters. Journal of Food Protection, 43, 105–110.
Flannery, J., Keaveney, S., & Dore, W. (2009). Use of FRNA bacteriophage to indicate the risk of contamination in Irish oysters. Journal of Food Protection, 72, 2358–2362.
Frost, H. W. (1925). Report of committee on the sanitary control of the shellfish industry in the United States. Public Health Reports, 53(Suppl), 1–17.
Gardner, S. N., Kuczmarski, T. A., Vitalis, E. A., & Slezar, T. R. (2003). Limitations of Taqman PCR for detecting divergent viral pathogens illustrated by hepatitis A, B, C, and E viruses and human immunodeficiency virus. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 41, 2417–2427.
Goyal, S. M., Gerba, C. P., & Melnick, J. L. (1979). Human enteroviruses in oysters and their overlying waters. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 37, 572–581.
Hall, T. (1999). BioEdit, a user friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acid Symposium Series, 41, 95–98.
Hutin, Y. J. F., Pool, V., Cramer, E. H., Nainan, O. V., Weth, J., Williams, I. T., et al. (1999). A multistate, foodborne outbreak of hepatitis A. New England Journal of Medicine, 340, 595–602.
Jansen, R., Siegl, G., & Lemon, S. M. (1990). Molecular epidemiology of human hepatitis A virus defined by an antigen-capture polymerase chain reaction method. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences United States of America, 87, 2867–2871.
Joshi, M. S., Walimbe, A. M., & Chitambar, S. D. (2008). Evaluation of genomic regions of hepatitis A virus for phylogenetic anlaysis: Suitability of the 2C region for genotyping. Journal of Virological Methods, 153, 36–42.
Kageyama, T., Kojima, S., Shinohara, M., Uchida, K., Fukushi, S., Hoshino, F. B., et al. (2003). Broadly reactive and highly sensitive assay for Norwalk-like viruses based on real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR. Journal Clinical Microbiology, 41, 1548–1557.
Kingsley, D., Mead, G. K., & Richards, G. P. (2002). Detection of both hepatitis A and Norwalk-like virus in imported clams associated with food-borne illnesses. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 68, 3914–3918.
Koopmans, M., & Duizer, E. (2004). Foodborne viruses: An emerging problem. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 90, 23–41.
Kroneman, A., Verhoef, L., Harris, J., Vennema, H., Duizer, E., van Duynhoven, Y., et al. (2008). Analysis of integrated virological and epidemiological reports of norovirus outbreaks collected within the foodborne viruses in Europe network from 1 July 2001 to 30 June 2006. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 46, 2959–2965.
Lees, D. (2000). Viruses and bivalve shellfish. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 59, 81–116.
Lowther, J. A., Avant, J. M., Gizynski, K., Rangdale, R. E., & Lees, D. N. (2010). Comparison between quantitative real-time reverse transcription PCR results for norovirus in oysters and self-reported gastroenteric illness in restaurant customers. Journal of Food Protection, 73, 305–311.
Lynch, M., Painter, J., Woodruff, R., & Braden, C. (2006). Surveillance for foodborne disease outbreaks—United States—1998–2002. MMWR, 55, 1–34.
Mead, P. S., Slutsker, L., Dietz, V., McCaig, L. F., Bresee, J. S., Shapiro, C., et al. (1999). Food-related illness and death in the United States. Emerging Infectious Disease, 5, 607–625.
Mullendore, J. L., Sobsey, M. D., & Shieh, Y. C. (2001). Improved method for the recovery of hepatitis A virus from oysters. Journal of Virological Methods, 94, 25–35.
Nainan, O. V., Armstrong, G. L., Han, X.-H., Williams, I., Bell, B. P., & Margolis, H. S. (2005). Hepatitis a molecular epidemiology in the United States, 1996–1997: Sources of infection and implications of vaccination policy. Journal of Infectious Disease, 191, 957–963.
Nainan, O. V., Xia, G., Vaughan, G., & Margolis, H. S. (2006). Diagnosis of a hepatitis A virus infection: A molecular approach. Clinical Microbiology Reviews, 19, 63–79.
Pan, C., & Schnurr, D. (2008). Viral gastroenteritis (norovirus) outbreaks: 2007–2008. Resource document. Viral and Rickettsial Disease Laboratory, California Department of Public Health. www.cdph.ca.gov/programs/vrdl/Documents/ViralGastroenteritisOutBreaks0708.doc (norovirus activity 2007-2008).
Patel, M. M., Hall, A. J., Vinje, J., & Parashar, U. D. (2009). Noroviruses: A comprehensive review. Journal of Clinical Virology, 44, 1–8.
Richards, G. P., Watson, M. A., Fankhauser, R. L., & Monroe, S. S. (2004). Genogroup I and genogroup II norovirus detection in stool samples by real-time reverse transcription PCR using highly degenerative universal primers. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 70, 7179–7184.
Robertson, B. H., Jansen, R. W., Khanna, B., Totsuka, A., Nainan, O. V., Siegl, G. A., et al. (1992). Genetic relatedness of hepatitis A virus strains recovered from different geographical regions. Journal of General Virology, 73, 1365–1377.
Schwab, K. J., Estes, M. K., Neill, F. H., & Atmar, R. L. (1997). Use of heat release and an internal RNA standard control in reverse transcription-PCR detection of Norwalk virus from stool samples. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 35, 511–514.
Shieh, Y. C., Khudyakov, Y. E., Xia, G., Ganova-Raeva, L. M., Khambaty, F., Woods, J. W., et al. (2007). Molecular confirmation of oysters as the vector for hepatitis A in a 2005 multistate outbreak. Journal Food Protection, 70, 145–150.
Shieh, Y. C., Woods, J. W., & Calci, K. R. (2003). Molecular surveillance of enterovirus and Norwalk-like virus in oysters relocated to a municipal sewage-impacted gulf estuary. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 69, 7130–7136.
Siebenga, J., Kronemen, A., Vennema, H., Duizer, E., & Koopmans, M. (2008). Food-borne viruses in Europe Network Report: The norovirus GII.4 2006b (for U.S. named Minerva-like, for Japan Kobe 034-like, for U.K. V6) variant now dominant in early seasonal surveillance. Eurosurveillance, 13, 1–4.
Tamura, K., Dudley, J., Nei, M., & Kumar, S. (2007). Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 8, 1596–1599.
Terio, V., Martella, P., Moschidou, P., Pinto, P. D., Tantillo, G., & Buonavoglia, C. (2010). Norovirus in retail shellfish. Food Microbiology, 27, 29–32.
Zheng, D., Ando, T., Fankhauser, R. R., Beard, R. S., Glass, R. I., & Monroe, S. S. (2006). Norovirus classification and proposed strain nomenclature. Virology, 346, 312–323.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the GCSL retail study team (Angelo DePaola, Jessica Jones, Kevin Calci, and Jeffrey Krantz); individuals at participating FDA-ORA laboratories (Emily Jacobs and Angela Swinford—FDA SRL, Khamphet Nabe and June Wetherington—FDA PRL-NW, Kuppuswamy Kasturi and Jose Obano—FDA NRL, and Donna Hill-Williams and Nelly Tran—FDA PRL-SW. We thank the ISSC for financial support and FDA personnel and individuals from the collecting states. We would also like to thank Susan McCarthy for review of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Woods, J.W., Burkhardt, W. Occurrence of Norovirus and Hepatitis A Virus in U.S. Oysters. Food Environ Virol 2, 176–182 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12560-010-9040-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12560-010-9040-7