Abstract
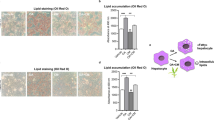
Deoxynivalenol (DON) is a type B trichothecenes that is widely contaminating human and animal foods, leading to several toxicological implications if ingested. Induction of oxidative stress and production of lipid peroxides were suggested to be the reasons for DON-induced cytotoxicity. However, detailed and comprehensive profiling of DON-related lipid hydroperoxides was not identified. Furthermore, the mechanisms behind DON-induced cytotoxicity and oxidative stress have received less attention. Zinc (Zn) is an essential element that has antioxidant activities; however, the protective effects of Zn against DON-induced adverse effects were not examined. Therefore, this study was undertaken to investigate DON-induced cytotoxicity and oxidative damage to human HepG2 cell lines. Furthermore, a quantitative estimation for the formed lipid hydroperoxides was conducted using LC-MS/MS. In addition, DON-induced transcriptomic changes on the inflammatory markers and antioxidant enzymes were quantitatively examined using qPCR. The protective effects of Zn against DON-induced cytotoxicity and oxidative stress, the formation of lipid hydroperoxides (LPOOH), and antioxidant status in HepG2 cells were investigated. Finally, the effects of DON and Zn on the Nrf2-Keap1 pathway were further explored. The achieved results indicated that DON caused significant cytotoxicity in HepG2 cells accompanied by significant oxidative damage and induction of the inflammatory markers. Identification of DON-related LPOOH revealed the formation of 22 LPOOH species including 14 phosphatidylcholine hydroperoxides, 5 triacylglycerol hydroperoxides, and 3 cholesteryl ester hydroperoxides. DON caused significant downregulation of Nrf2-regulated antioxidant enzymes. Zn administration led to significant protection of HepG2 cells against DON-induced adverse effects, probably via activation of the Nrf2-Keap1 pathway.





Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
20 August 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12550-021-00440-0
23 April 2020
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12550-020-00394-9
Abbreviations
- DON:
-
Deoxynivalenol
- Zn:
-
Zinc
- HepG2:
-
Human liver hepatoma cell lines
- PCOOH:
-
Phosphatidylcholine hydroperoxides
- TGOOH:
-
Triacylglycerol hydroperoxides
- CEOOH:
-
Cholesteryl ester hydroperoxides
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium
- DCF-DA:
-
2′,7′-Dichlorofluorescein diacetate
- qPCR:
-
Quantitative real-time PCR
- GST:
-
Glutathione-S-transferases
- NQO1:
-
NAD(P)H dehydrogenase [quinone] 1
- HO 1:
-
Heme oxygenase 1
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- Nrf2:
-
Erythroid 2–related factor 2
- Keap1:
-
Kelch-like ECH-associated protein-1
References
Adesso S, Autore G, Quaroni A, Popolo A, Severino L, Marzocco S (2017) The food contaminants nivalenol and deoxynivalenol induce inflammation in intestinal epithelial cells by regulating reactive oxygen species release. Nutrients 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9121343
Andreini C, Banci L, Bertini I, Rosato A (2006) Counting the zinc proteins encoded in the human genome. J Proteome Res 5:196–201. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr050361j
Bennett JW, Klich M (2003) Mycotoxins. Clin Microbiol Rev 16:497–516
Birkner S, Weber S, Dohle A, Schmahl G, Bolt H, Follmann W (2003) Activities of drug metabolizing enzymes in bovine colon epithelial cell cultures. Arch Toxicol 77:621–629. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-003-0490-7
Bonaventura P, Benedetti G, Albare’de F, Miossec P (2015) Zinc and its role in immunity and inflammation. Autoimmun Rev 14:277–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2014.11.008
Burger HM, Abel S, Gelderblom WCA (2018) Modulation of key lipid raft constituents in primary rat hepatocytes by fumonisin B1 - implications for cancer promotion in the liver. Food Chem Toxicol 115:34–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2018.03.004
Carballo D, Moltó JC, Berrada H, Ferrer E (2018) Presence of mycotoxins in ready-to-eat food and subsequent risk assessment. Food Chem Toxicol 121:558–565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2018.09.054
Chasapis CT, Loutsidou AC, Spiliopoulou CA, Stefanidou ME (2012) Zinc and human health: an update. Arch Toxicol 86:521–534. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-011-0775-1
Chen Z, Zang L, Wu Y, Nakayama H, Shimada Y, Shrestha R, Zhao Y, Miura Y, Chiba H, Hui SP, Nishimura N (2018) Lipidomic profiling on oxidized phospholipids in type 2 diabetes mellitus model zebrafish. Anal Sci 34:1201–1208. https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.18P281
Choi AM, Alam J (1996) Heme oxygenase-1: function, regulation, and implication of a novel stress-inducible protein in oxidant-induced lung injury. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 15:9–19
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N (1987) Single-step method of isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162:156–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(87)90021-2
Darwish WS, Ikenaka Y, Nakayama SMM, Mizukawa H, Ishizuka M (2016) Constitutive effects of lead on aryl hydrocarbon receptor gene battery and protection by β-carotene and ascorbic acid in human HepG2 cells. J Food Sci 81:T275–T281. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.13162
Darwish WS, Ikenaka Y, Nakayama S, Mizukawa H, Thompson LA, Ishizuka M (2018) β-carotene and retinol reduce benzo[a]pyrene-induced mutagenicity and oxidative stress via transcriptional modulation of xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes in human HepG2 cell line. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25:6320–6328. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0977-z
Darwish WS, Chiba H, El-Ghareeb WR, Elhelaly AE, Hui SP (2019a) Determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon content in heat-treated meat retailed in Egypt: health risk assessment, benzo[a]pyrene induced mutagenicity and oxidative stress in human colon (CaCo-2) cells and protection using rosmarinic and ascorbic acids. Food Chem 290:114–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.03.127
Darwish WS, Chiba H, Elhelaly AE, Hui SP (2019b) Estimation of cadmium content in Egyptian foodstuffs: health risk assessment, biological responses of human HepG2 cells to food-relevant concentrations of cadmium, and protection trials using rosmarinic and ascorbic acids. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 26:15443–15457. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04852-5
Feng C, Li D, Jiang L, Liu X, Li Q, Geng C, Sun X, Yang G, Yao X, Chen M (2017) Citreoviridin induces triglyceride accumulation in hepatocytes through inhibiting PPAR-α in vivo and in vitro. Chem Biol Interact 273:212–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2017.06.021
Ferrer E, Juan-García A, Font G, Ruiz MJ (2009) Reactive oxygen species induced by beauvericin, patulin and zearalenone in CHO-K1 cells. Toxicol in Vitro 23:1504–1509
Folch J, Lees M, Stanley GHS (1957) A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J Biol Chem 226:497–509
Furse S, de Kroon AI (2015) Phosphatidylcholine’s functions beyond that of a membrane brick. Mol Membr Biol 32:117–119
Habig WH, Pabst MJ, Jakoby WB (1974) Glutathione S-transferases. The first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem 249:7130–7139
Habrowska-Górczyńska DE, Kowalska K, Urbanek KA, Domińska K, Sakowicz A, Piastowska-Ciesielska AW (2019) Deoxynivalenol modulates the viability, ROS production and apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. Toxins (Basel) 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11050265
Ho LH, Ruffin RE, Murgia C, Li L, Krilis SA, Zalewski PD (2004) Labile zinc and zinc transporter ZnT4 in mast cell granules: role in regulation of caspase activation and NF-jB translocation. J Immunol 172:7750–7760. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.172.12.7750
Huang TC, Chang WT, Hu YC, Hsieh BS, Cheng HL, Yen JH, Chiu PR, Chang KL (2018) Zinc protects articular chondrocytes through changes in Nrf2-mediated antioxidants, cytokines and matrix metalloproteinases. Nutrients 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10040471
Hui SP, Chiba H, Jin S, Nagasaka H, Kurosawa T (2010) Analyses for phosphatidylcholine hydroperoxides by LC/MS. J Chromatogr B 878:1677–1682. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2010.04.011
Hui SP, Sakurai T, Ohkawa F, Furumaki H, Jin S, Fuda H, Takeda S, Kurosawa T, Chiba H (2012) Detection and characterization of cholesteryl ester hydroperoxides in oxidized LDL and oxidized HDL by use of an Orbitrap mass spectrometer. Anal Bioanal Chem 404:101–112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-012-6118-0
Hui SP, Sakurai T, Takeda S, Jin S, Fuda H, Kurosawa T, Chiba H (2013) Analysis of triacylglycerol hydroperoxides in human lipoproteins by Orbitrap mass spectrometer. Anal Bioanal Chem 405:4981–4987. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-013-6903-4
Iwase T, Tajima A, Sugimoto S, Okuda K, Hironaka I, Kamata Y, Takada K, Mizunoe Y (2013) A simple assay for measuring catalase activity: a visual approach. Sci Rep 3:3081. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep03081
Jarosz M, Olbert M, Wyszogrodzka G, Młyniec K, Librowski T (2017) Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of zinc. Zinc-dependent NF-κB signaling. Inflammopharmacology 25:11–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-017-0309-4
Joko S, Watanabe M, Fuda H, Takeda S, Furukawa T, Hui SP, Shrestha R, Chiba H (2017) Comparison of chemical structures and cytoprotection abilities between direct and indirect antioxidants. J Funct Foods 35:245–255
Juan-García A, Juan C, Tolosa J, Ruiz MJ (2019) Effects of deoxynivalenol, 3-acetyl-deoxynivalenol and 15-acetyl deoxynivalenol on parameters associated with oxidative stress in HepG2 cells. Mycotoxin Res 35:197–205. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12550-019-00344-0
Kang R, Li R, Dai P, Li Z, Li Y, Li C (2019) Deoxynivalenol induced apoptosis and inflammation of IPEC-J2 cells by promoting ROS production. Environ Pollut 251:689–698. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.05.026
Katika MR, Hendriksen PJ, van Loveren H, Peijnenburg ACM (2015) Characterization of the modes of action of deoxynivalenol (DON) in the human Jurkat T-cell line. J Immunotoxicol 12:206–216. https://doi.org/10.3109/1547691X.2014.925995
Kind T, Liu KH, Lee DY, DeFelice B, Meissen JK, Fiehn O (2013) LipidBlast in silico tandem mass spectrometry database for lipid identification. Nat Methods 10:755–758. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2551
Kouadio JH, Mobio TA, Baudrimont I, Moukha S, Dano SD, Creppy EE (2005) Comparative study of cytotoxicity and oxidative stress induced by deoxynivalenol, zearalenone or fumonisin B1 in human intestinal cell line Caco-2. Toxicology 213:56–65
Krishnaswamy R, Devaraj SN, Padma VV (2010) Lutein protects HT-29 cells against deoxynivalenol-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis: prevention of NF-κB nuclear localization and down regulation of NF-κB and cyclo-oxygenase – 2 expressions. Free Radic Biol Med 49:50–60
Lansdown ABG, Mirastschijski U, Stubbs N et al (2007) Zinc in wound healing: theoretical, experimental, and clinical aspects. Wound Repair Regen 15:2–16. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1524-475X.2006.00179.x
Leal M, Shimada A, Ruíz F, González E, Mejía D (2009) Effect of lycopene on lipid peroxidation and glutathione-dependent enzymes induced by T-2 toxin in vivo. Toxicol Lett 109:1–10
Li S, Tan HY, Wang N, Zhang ZJ, Lao L, Wong CW, Feng Y (2015) The role of oxidative stress and antioxidants in liver diseases. Int J Mol Sci 16:26087–26124. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161125942
Li H, Malyar RM, Zhai N, Wang H, Liu K, Liu D, Pan C, Gan F, Huang K, Miao J, Chen X (2019) Zinc supplementation alleviates OTA-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in MDCK cells by up-regulating metallothioneins. Life Sci 234:116735. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116735
Ma Q (2013) Role of nrf2 in oxidative stress and toxicity. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 53:401–426. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-011112-140320
Malhotra A, Dhawan DK (2014) Current view of zinc as a hepatoprotective agent in conditions of chlorpyrifos induced toxicity. Pestic Biochem Physiol 112:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2014.04.007
Ooi TC, Chan KM, Sharif R (2017) Zinc L-carnosine suppresses inflammatory responses in lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW 264.7 murine macrophages cell line via activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 39:259–267. https://doi.org/10.1080/08923973.2017.1344987
Pestka JJ (2007) Deoxynivalenol: toxicity, mechanisms and animal health risks. Anim Feed Sci Technol 137:283–298
Ren ZH, Deng HD, Wang YC, Deng JL, Zuo ZC, Wang Y, Peng X, Cui HM, Fang J, Yu SM, Shen LH, Hu YC (2016) The Fusarium toxin zearalenone and deoxynivalenol affect murine splenic antioxidant functions, interferon levels, and T-cell subsets. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 41:195–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2015.12.007
Schwarz M, Lossow K, Kopp JF, Schwerdtle T, Kipp AP (2019) Crosstalk of Nrf2 with the trace elements selenium, iron, zinc, and copper. Nutrients 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11092112
Shaw P, Chattopadhyay A (2019) Nrf2-ARE signaling in cellular protection: mechanism of action and the regulatory mechanisms. J Cell Physiol. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.29219
Sinha K, Das J, Pal PB, Sil PC (2013) Oxidative stress: the mitochondria-dependent and mitochondria-independent pathways of apoptosis. Arch Toxicol 87:1157–1180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-013-1034-4
Szabó A, Fébel H, Ali O, Kovács M (2019) Fumonisin B1 induced compositional modifications of the renal and hepatic membrane lipids in rats - dose and exposure time dependence. Food Addit Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess 22:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1080/19440049.2019.1652772
Wang X, Zuo Z, Zhao C, Zhang Z, Peng G, Cao S, Hu Y, Yu S, Zhong Z, Deng J, Ren Z (2016) Protective role of selenium in the activities of antioxidant enzymes in piglet splenic lymphocytes exposed to deoxynivalenol. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 47:53–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2016.09.003
Wang X, Tang J, Geng F, Zhu L, Chu X, Zhang Y, Ur Rahman S, Chen X, Jiang Y, Zhu D, Feng S, Li Y, Wu J (2018) Effects of deoxynivalenol exposure on cerebral lipid peroxidation, neurotransmitter and calcium homeostasis of chicks in vivo. Toxicon 150:60–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2018.05.010
Wang J, Jin Y, Wu S, Yu H, Zhao Y, Fang H, Shen J, Zhou C, Fu Y, Li R, Wang R, Wang J, Zheng K, Fan Q, Chen B, Zhang J (2019) Deoxynivalenol induces oxidative stress, inflammatory response and apoptosis in bovine mammary epithelial cells. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl). https://doi.org/10.1111/jpn.13180
Wu QH, Wang X, Yang W, Nüssler AK, Xiong LY, Kuča K, Dohnal V, Zhang XJ, Yuan ZH (2014) Oxidative stress-mediated cytotoxicity and metabolism of T-2 toxin and deoxynivalenol in animals and humans: an update. Arch Toxicol 88:1309–1326. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-014-1280-0
Wu Q, Wang X, Nepovimova E, Wang Y, Yang H, Li L, Zhang X, Kuca K (2017) Antioxidant agents against trichothecenes: new hints for oxidative stress treatment. Oncotarget 28:110708–110726. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.22800
Yan M, Song Y, Wong CP et al (2008) Zinc deficiency alters DNA damage response genes in normal human prostate epithelial cells. J Nutr 138:667–673
Yang W, Yu M, Fu J, Bao W, Wang D, Hao L, Yao P, Nüssler AK, Yan H, Liu L (2014) Deoxynivalenol induced oxidative stress and genotoxicity in human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Food Chem Toxicol 64:383–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2013.12.012
Yang X, Lv Y, Huang K, Luo Y, Xu W (2016) Zinc inhibits aflatoxin B1-induced cytotoxicity and genotoxicity in human hepatocytes (HepG2 cells). Food Chem Toxicol 92:17–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2016.03.012
Yang X, Wang H, Huang C, He X, Xu W, Luo Y, Huang K (2017) Zinc enhances the cellular energy supply to improve cell motility and restore impaired energetic metabolism in a toxic environment induced by OTA. Sci Rep 7(1):14669. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-14868-x
Yang J, Zhu C, Ye J, Lv Y, Wang L, Chen Z, Jiang Z (2019a) Protection of porcine intestinal-epithelial cells from deoxynivalenol-induced damage by resveratrol via the Nrf2 signaling pathway. J Agric Food Chem 67:1726–1735. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.8b03662
Yang JH, Wang JH, Guo WB, Ling AR, Luo AQ, Liu D, Yang XL, Zhao ZH (2019b) Toxic effects and possible mechanisms of deoxynivalenol exposure on sperm and testicular damage in BALB/c mice. J Agric Food Chem 67:2289–2295. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.8b04783
Yu M, Wei ZY, Xu ZH, Pan JQ, Chen JH (2018) Oxidative damage and Nrf2 translocation induced by toxicities of deoxynivalenol on the placental and embryo on gestation day 12.5 d and 18.5 d. Toxins (Basel) 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10090370
Yu M, Peng Z, Liao Y, Wang L, Li D, Qin C, Hu J, Wang Z, Cai M, Cai Q, Zhou F, Shi S, Yang W (2019) Deoxynivalenol-induced oxidative stress and Nrf2 translocation in maternal liver on gestation day 12.5 d and 18.5 d. Toxicon 161:17–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2019.02.018
Zhang X, Jiang L, Geng C, Cao J, Zhong L (2009) The role of oxidative stress in deoxynivalenol-induced DNA damage in HepG2 cells. Toxicon 54:513–518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2009.05.021
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original version of this article was revised: The original version of this paper was published with error. The presentation of author name "Tan Hui" should be "Hui Tan".
This article has been retracted. Please see the retraction notice for more detail: https://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12550-021-00440-0
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 24 kb)
About this article
Cite this article
Darwish, W.S., Chen, Z., Li, Y. et al. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Deoxynivalenol-induced alterations in the redox status of HepG2 cells: identification of lipid hydroperoxides, the role of Nrf2-Keap1 signaling, and protective effects of zinc. Mycotoxin Res 36, 287–299 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12550-020-00392-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12550-020-00392-x