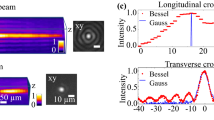
Abstract
Electron beam micro-drilling processes have some advantages, such as high aspect ratio of 3–10, and applicable usages of difficult-to-cut material. The process has always required some lensing system optimization with an electromagnetic system for a high-density electron beam profile. This paper suggests the inlet hole characteristics depending on the focus conditions with a 120 kV electron beam. Normally charged particles during the focusing process could be affected by circular and focusing motions in the magnetic force field. However, it always has space charging forces between each electron particle. Therefore, we could analyze the effect of the inlet hole shape depending on the focus conditions that have different space charging conditions, such as converging and diverging beam envelopes. This study analyzed the effects of the shape and size of the burr of drilled holes with respect to converging and diverging focus conditions. In addition, a Monte Carlo simulation was conducted to verify the effect of the focus condition on the scattering process. The experimental results show that converging electron beams are more effective on the reducing burr at the edge of the inlet hole. The simulation results suggest that the behavior of back scattered electrons can be altered under different focus conditions and that it can affect energy absorption by BSEs.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Marimuthu, S., Antar, M., & Dunleavey, J. (2019). Characteristics of micro-hole formation during fibre laser drilling of aerospace superalloy. Precision Engineering, 55, 339–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precisioneng.2018.10.002
Aamir, M., Giasin, K., Tolouei-Rad, M., & Vafadar, A. (2020). A review: Drilling performance and hole quality of aluminium alloys for aerospace applications. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 9(6), 12484–12500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.09.003
Pan, H., Liu, Z., Qiu, M., Zhang, M., & Deng, C. (2021). Extreme wire electrical discharge machining based on semiconductor characteristics. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 115(7), 2477–2489. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-07019-0
McNally, C. A., Folkes, J., & Pashby, I. R. (2004). Laser drilling of cooling holes in aeroengines: State of the art and future challenges. Materials Science and Technology, 20(7), 805–813. https://doi.org/10.1179/026708304225017391
Li, C., Zhang, B., Li, Y., Tong, H., Ding, S., Wang, Z., & Zhao, L. (2018). Self-adjusting EDM/ECM high speed drilling of film cooling holes. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 262, 95–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2018.06.026
Gautam, G. D., & Pandey, A. K. (2018). Pulsed Nd:YAG laser beam drilling: A review. Optics & Laser Technology, 100, 183–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2017.09.054
Li, C., Xu, X., Li, Y., Tong, H., Ding, S., Kong, Q., Zhao, L., & Ding, J. (2019). Effects of dielectric fluids on surface integrity for the recast layer in high speed EDM drilling of nickel alloy. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 783, 95–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.12.283
Yazman, Ş, Köklü, U., Urtekin, L., Morkavuk, S., & Gemi, L. (2020). Experimental study on the effects of cold chamber die casting parameters on high-speed drilling machinability of casted AZ91 alloy. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 57, 136–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.05.050
Lee, H.-M., Choi, J.-H., & Moon, S.-J. (2020). Machining characteristics of glass substrates containing chemical components in femtosecond laser helical drilling. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology, 8(2), 375–385. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-020-00242-2
Liu, Y., Geng, D., Shao, Z., Zhou, Z., Jiang, X., & Zhang, D. (2021). A study on strengthening and machining integrated ultrasonic peening drilling of Ti-6Al-4V. Materials & Design, 212, 110238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2021.110238
Tao, S., Gao, Z., & Shi, H. (2021). Characterization of printed circuit board micro-holes drilling process by accurate analysis of drilling force signal. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing, 23(2), 131–138. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-021-00603-0
Kim, D., Kim, Y.-S., Song, K. Y., Ahn, S. H., & Chu, C. N. (2022). Kerosene supply effect on performance of aluminum nitride micro-electrical discharge machining. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing, 23(6), 581–591. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-021-00568-0
Nguyen, T.-T., Tran, V.-T., & Le, M.-T. (2022). Comprehensive optimization of the electrical discharge drilling in terms of energy efficiency and hole characteristics. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing, 23(7), 807–824. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-022-00675-6
Masuzawa, T. (2000). State of the art of micromachining. CIRP Annals, 49(2), 473–488. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0007-8506(07)63451-9
Kelly Ferjutz, Joseph R. Davis, und Nikki D. Wheat (1994). Welding, Brazing, and Soldering. ASM Handbook, (Vol. 6, pp. 15–18). https://doi.org/10.31399/asm.hb.v06.9781627081733
Kim, J., Lee, W. J., & Park, H. W. (2016). The state of the art in the electron beam manufacturing processes. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing, 17(11), 1575–1585. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-016-0184-8
Leitz, K.-H., Koch, H., Otto, A., Maaz, A., Löwer, T., & Schmidt, M. (2012). Numerical simulation of drilling with pulsed beams. Physics Procedia, 39, 881–892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phpro.2012.10.113
Jung, S. T., Kang, E. G., Park, J. W., Kim, T. W., & Baek, S. Y. (2020). A study on proposal of e-beam drilling machining criterion by using on vaporized amplification sheets in a high-power density electron beam. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 20(7), 4231–4234. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2020.17548
Kim, H., Jung, S., Lee, J., & Baek, S. (2021). A study on multi-hole machining of high-power density electron beam using a vaporized amplification sheet. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 115(5), 1411–1419. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-07046-x
Huang, B., Chen, X., Pang, S., & Hu, R. (2017). A three-dimensional model of coupling dynamics of keyhole and weld pool during electron beam welding. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 115, 159–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2017.08.010
Zhou, J., Tsai, H.-L., & Wang, P.-C. (2005). Transport phenomena and keyhole dynamics during pulsed laser welding. Journal of Heat Transfer, 128(7), 680–690. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.2194043
Rai, R. R., Palmer, T., Elmer, J., & Debroy, T. (2009). Heat transfer and fluid flow during electron beam welding of 304L stainless steel alloy. Welding Journal (Miami, Fla), 88, 54s–61s.
Elena-Manuela, S., Păvălache, A., Gabriel, D., Dontu, O., Besnea, D., & Vasile, I. (2010). Mechanism of keyhole formation in laser welding. In Romanian Review Precision Mechanics, Optics and Mechatronics, 20, 171–176.
Schwarz, H. (1964). Mechanism of high-power-density electron beam penetration in metal. Journal of Applied Physics, 35(7), 2020–2029. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1702787
Cline, H. E., & Anthony, T. R. (1977). Heat treating and melting material with a scanning laser or electron beam. Journal of Applied Physics, 48(9), 3895–3900. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.324261
Yang, Z., & He, J. (2021). Numerical investigation on fluid transport phenomena in electron beam welding of aluminum alloy: Effect of the focus position and incident beam angle on the molten pool behavior. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 164, 106914. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2021.106914
Haeff, A. V. (1939). Space-charge effects in electron beams. Proceedings of the IRE, 27(9), 586–602. https://doi.org/10.1109/JRPROC.1939.228758
Lawson, J. D. (1954). Electron trajectories in strip beams constrained by a magnetic field. Proceedings of the IRE, 42(7), 1147–1151. https://doi.org/10.1109/JRPROC.1954.274548
Shimizu, R., Kataoka, Y., Ikuta, T., Koshikawa, T., & Hashimoto, H. (1976). A Monte Carlo approach to the direct simulation of electron penetration in solids. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 9(1), 101–113. https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/9/1/017
Shimizu, R., & Ze-Jun, D. (1992). Monte Carlo modelling of electron-solid interactions. Reports on Progress in Physics, 55(4), 487–531. https://doi.org/10.1088/0034-4885/55/4/002
Kanaya, K., & Okayama, S. (1972). Penetration and energy-loss theory of electrons in solid targets. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 5(1), 43–58. https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/5/1/308
Kanaya, K., & Ono, S. (1978). The energy dependence of a diffusion model of an electron probe into solid targets. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 11(11), 1495–1498. https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/11/11/008
Klassen, A., Bauereiß, A., & Körner, C. (2014). Modelling of electron beam absorption in complex geometries. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 47(6), 065307. https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/47/6/065307
Park, H., Kang, J. G., Kim, J. S., Kang, E. G., Choi, S.-K., Kim, J., & Park, H. W. (2022). Predictive modeling of microhole profile drilled using a focused electron beam with backing materials. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 177, 107584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2022.107584
Kim, J., Lee, W. J., & Park, H. W. (2018). Temperature predictive model of the large pulsed electron beam (LPEB) irradiation on engineering alloys. Applied Thermal Engineering, 128, 151–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.08.142
Carriere, P. R., & Yue, S. (2017). Energy absorption during pulsed electron beam spot melting of 304 stainless steel: Monte-Carlo simulations and in-situ temperature measurements. Vacuum, 142, 114–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2017.04.039
Demers, H., Poirier-Demers, N., Couture, A. R., Joly, D., Guilmain, M., de Jonge, N., & Drouin, D. (2011). Three-dimensional electron microscopy simulation with the CASINO Monte Carlo software. SCANNING: The Journal of Scanning Microscopies, 33, 135–146. https://doi.org/10.1002/sca.20262
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy Republic of Korea, Grant No. 20015739.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, JG., Kim, Js., Min, BK. et al. Inlet Hole Shape Analysis Depending on the Focus Conditions for Electron Beam Micro-hole Drilling. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 24, 1307–1317 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-023-00785-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-023-00785-9