Abstract
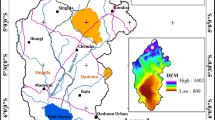
Land use/land cover changes (LULCC) are one of the foremost aspects of environmental changes caused by human-induced activities mainly in rapidly developing areas. This study endeavors to evaluate and compare three hybrid models: stochastic Markov chain (ST-MC), cellular automata-Markov chain (CA-MC), and multi-layer perceptron-Markov chain (MLP-MC) to predict future land use/land cover (LULC) scenario in Varanasi district. LULC information extracted for years 1988 and 2001 was first employed to predict LULC scenario for 2015 using three hybrid models. The predicted results were compared with the observed LULC information for the year 2015 to appraise the validity of models through kappa index statistics. The MLP-MC model yielded reliable and best results. Finally, based on this consequence, the prediction of future LULC scenarios for years 2030 and 2050 was performed. The findings of this study exhibited the constant but overall increase of built up area and a considerable reduction in agricultural land. The results also demonstrate the potentiality of MLP-MC hybrid model for better understanding of spatio-temporal dynamics and predicting future landsacpe scenario in Varanasi district of Uttar Pradesh, India.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adhikari S, Southworth J (2012) Simulating forest cover changes of Bannerghatta National Park based on a CA-Markov model: a remote sensing approach. Remote Sens 4:3215–3243
Ahmed B, Ahmed R (2012) Modeling urban land cover growth dynamics using multi-temporal satellite images: a case study of Dhaka, Bangladesh. ISPRS Int J Geo-Inf 1:3–31
Al-sharif AA, Pradhan B (2014a) Urban sprawl analysis of Tripoli metropolitan city (Libya) using remote sensing data and multivariate logistic regression model. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 42(1):149–163
Al-sharif AA, Pradhan B (2014b) Monitoring and predicting land use change in Tripoli metropolitan city using an integrated Markov chain and cellular automata models in GIS. Arab J Geosci 7:4291–4301
Araya YH, Cabral P (2010) Analysis and modeling of urban land cover change in Setúbal and Sesimbra, Portugal. Remote Sens 2(6):1549–1563
Arsanjani JJ, Kainz W, Mousivand AJ (2011) Tracking dynamic land-use change using spatially explicit Markov chain based on cellular automata: the case of Tehran. Int J Image Data Fusion 2:329–345
Arsanjani JJ, Helbich M, Kainz W, Boloorani AD (2013) Integration of logistic regression, Markov chain and cellular automata models to simulate urban expansion. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 21:265–275
Atkinson PM, Tatnall ARL (1997) Introduction neural networks in remote sensing. Int J Remote Sens 18(4):699–709
Barredo JI, Kasanko M, McCormick N, Lavalle C (2003) Modelling dynamic spatial processes: simulation of urban future scenarios through cellular automata. Landsc Urban Plan 64:145–160
Basharin GP, Langville AN, Naumov VA (2004) The life and work of A.A. Markov. Linear Algebra Appl 386:3–26
Bhatta B (2010) Analysis of urban growth and sprawl from remote sensing data. Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg
Bonan GB (2008) Ecological climatology—concepts and applications, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Bozkaya AG, Balcik FB, Goksel C, Esbah H (2015) Forecasting land-cover growth using remotely sensed data: a case study of the Igneada protection area in Turkey. Environ Monit Assess 187:59
Brown DG, Pijanowski BC, Duh JD (2000) Modelling the relationships between land use and land cover on private lands in the Upper Midwest, USA. J Environ Manag 59:247–263
Carlson TN, Azofeifa SGA (1999) Satellite remote sensing of land use changes in and around San José, Costa Rica. Remote Sens Environ 70:247–256
Clarke KC, Hoppen S (1997) A self-modifying cellular automaton model of historical urbanization in the San Francisco Bay area. Environ Plann B Plann Des 24:247–261
Congalton RG, Green K (1999) Assessing the accuracy of remotely sensed data: principles and practices. CRC/Lewis, Boca Raton
Dadhich PN, Hanaoka S (2011) Spatio-temporal urban growth modeling of Jaipur, India. J Urban Technol 18:45–65
Dickinson RE (1995) Land processes in climate models. Remote Sens Environ 51:27–38
Dwivedi RS, Sreenivas K, Ramana KV (2005) Land-use/land-cover change analysis in part of Ethiopia using Landsat Thematic Mapper data. Int J Remote Sens 26(7):1285–1287
Eastman JR (2006) IDRISI Andes tutorial. Clark Labs, Worcester
Eastman JR (2009) IDRISI Taiga guide to GIS and image processing; manual version 16.02. Clark Labs, Worcester
Eastman JR (2012) IDRISI Selva Tutorial. Clark University, Worcester
Eastman JR, Jiang H, Toledano J (1998) Multi-criteria and multi-objective decision making for land allocation using GIS. In: Beinat E, Nijkamp P (eds) Multicriteria analysis for land use management. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 227–251
Fathizad H, Rostami N, Faramarzi M (2015) Detection and prediction of land cover changes using Markov chain model in semi-arid rangeland in western Iran. Environ Monit Assess 187:629
Fortin MJ, Boots B, Csillag F, Remmel TK (2003) On the role of spatial stochastic models in understanding landscape indices in ecology. Oikos 102:203–212
Giriraj A, Irfan-Ullah M, Murthy MSR, Beierkuhnlein C (2008) Modelling spatial and temporal forest cover change patterns (1973-2020): a case study from South Western Ghats (India). Sensors 8:6132–6153
Guan D, Li H, Inohae T, Su W, Nagaie T, Hokao K (2011) Modeling urban land use change by the integration of cellular automaton and Markov model. Ecol Model 222:3761–3772
Hu X, Weng Q (2009) Estimating impervious surfaces from medium spatial resolution imagery using the self-organizing map and multi-layer perceptron neural networks. Remote Sens Environ 113:2089–2102
Hua L, Tang L, Cui S, Yin K (2014) Simulating urban growth using the SLEUTH model in a coastal peri-urban district in China. Sustainability 6:3899–3914
Jantz CA, Goetz SJ, Shelley MK (2003) Using the SLEUTH urban growth model to simulate the impacts of future policy scenarios on urban land use in the Baltimore–Washington metropolitan area. Environ Plann B Plann Des 30:251–271
Ji CY (2000) Land-use classification of remotely sensed data using Kohonen self organizing feature map neural networks. Photogramm Eng Remote Sens 66:1451–1460
Kamusoko C, Aniya M, Adi B, Manjoro M (2009) Rural sustainability under threat in Zimbabwe-simulation of future land use/cover changes in the Bindura district based on the Markov-cellular automata model. Appl Geogr 29:435–447
Kilic S (2006) Environmental monitoring of land use and land cover changes in a Mediterranean region of Turkey. Environ Monit Assess 114(1–3):157–168
Kumar R, Nandy S, Agarwal R, Kushwaha SPS (2014) Forest cover dynamics analysis and prediction modeling using logistic regression model. Ecol Indic 45:444–455
Lambin EF, Turner BL, Geist HJ, Agbola SB, Angelsen A, Bruce JW, Coomes OT, Dirzo R, Fischer G, Folke C (2001) The causes of land-use and land-cover change: moving beyond the myths. Glob Environ Chang 11(4):261–269
Maithani S (2015) Neural networks-based simulation of land cover scenarios in Doon Valley, India. Geocarto Int 30:163–185
Mas JF, Flores JJ (2008) The application of artificial neural networks to the analysis of remotely sensed data. Int J Remote Sens 29:617–663
Mas JF, Kolb M, Paegelow M, Olmedo MTC, Houet T (2014) Inductive pattern-based land use/cover change models: a comparison of four software packages. Environ Model Softw 51:94–111
Mas JF, Velazquez A, Gallegos JRD, Saucedo RM, Alcantare C, Bocco G, Castro R, Fernandez T, Vega AP (2004) Assessing land use/cover changes: a nationwide multi date spatial database for Mexico. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 5:249–261
Miller AB, Bryant ES, Birnie RW (1998) An analysis of land cover changes in the northern forest of New England using multi-temporal LANDSAT MSS data. Int J Remote Sens 19(2):245–265
Mishra VN, Prasad R, Kumar P, Gupta DK, Srivastava PK (2017) Dual-polarimetric C-band SAR data for land use/land cover classification by incorporating textural information. Environ Earth Sci 76(1):26
Mishra VN, Rai PK (2016) A remote sensing aided multi-layer perceptron-Markov chain analysis for land use and land cover change prediction in Patna district (Bihar), India. Arab J Geosci 9(4):1–18
Mishra VN, Rai PK, Mohan K (2014) Prediction of land use changes based on land change modeler (LCM) using remote sensing: a case study of Muzaffarpur (Bihar), India. J Geogr Inst Jovan Cvijic 64:111–127
Mitsova D, Shuster W, Wang X (2011) A cellular automata model of land cover change to integrate urban growth with open space conservation. Landsc Urban Plan 99(2):141–153
Moghadam HS, Helbich M (2013) Spatiotemporal urbanization processes in the megacity of Mumbai, India: a Markov chains-cellular automata urban growth model. Appl Geogr 40:140–149
Mozumder C, Tripathi NK (2014) Geospatial scenario based modelling of urban and agricultural intrusions in Ramsar wetland Deepor Beel in Northeast India using a multi-layer perceptron neural network. Int J Appl Earth Observ Geoinf 32:92–104
Mozumder C, Tripathi NK, Losiri C (2016) Comparing three transition potential models: a case study of built-up transitions in North-East India. Comput Environ Urban Syst 59:38–49
Muller R, Middleton J (1994) A Markov model of land-use change dynamics in the Niagara region, Ontario, Canada. Landsc Ecol 9:151–157
Olmedo MTC, Paegelow M, Mas JF (2013) Interest in intermediate soft-classified maps in land change model validation: suitability versus transition potential. Int J Geogr Inf Sci 27:2343–2361
Paudel S, Yuan F (2012) Assessing landscape changes and dynamics using patch analysis and GIS modeling. Int J Appl Earth Observ Geoinf 16:66–76
Pijanowski BC, Pithadia S, Shellito BA, Alexandridis K (2005) Calibrating a neural network based urban change model for two metropolitan areas of the Upper Midwest of the United States. Int J Geogr Inf Sci 19:197–215
Pontius RG (2000) Quantification error versus location error in comparison of categorical maps. Photogramm Eng Remote Sens 66:1011–1016
Prenzel B (2004) Remote sensing-based quantification of land-cover and land-use change for planning. Prog Plan 61:281–299
Seto KC, Woodcock CE, Song C, Huang X, Lu J, Kaufmann RK (2002) Monitoring land use change in the Pearl River Delta using Landsat TM. Int J Remote Sens 23(10):1985–2004
Tang J, Wang L, Yao Z (2007) Spatio-temporal urban landscape change analysis using the Markov chain model and a modified genetic algorithm. Int J Remote Sens 28(15):3255–3271
Thapa RB, Murayama Y (2012) Scenario based urban growth allocation in Kathmandu Valley, Nepal. Landsc Urban Plan 105:140–148
Thies B, Meyer H, Nauss T, Bendix J (2014) Projecting land use and land-cover changes in a tropical mountain forest of Southern Ecuador. J Land Use Sci 9(1):1–33
Triantakonstantis D, Mountrakis G (2012) Urban growth prediction: a review of computational models and human perceptions. J Geogr Inf Syst 4:555–587
Vapnik VN (1999) An overview of statistical learning theory. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 10(5):988–999
Veldkamp A, Fresco LO (1996) CLUE: a conceptual model to study the conversion of land use and its effects. Ecol Model 85:253–270
Verburg PH, de Nijs TCM, RitsemavanEck J, Visser H, de Jong K (2004) Method to analyseneighbourhood characteristics of land use patterns. Comput Environ Urban Syst 28:667–690
Wang SQ, Zheng XQ, Zang XB (2012) Accuracy assessments of land use change simulation based on Markov-cellular automata model. Procedia Environ Sci 13:1238–1245
Weng Q (2002) Land use change analysis in the Zhujiang Delta of China using satellite remote sensing, GIS and stochastic modelling. J Environ Manag 64:273–284
Zhu Z, Liu L, Chen Z, Zhang J, Verburg PH (2010) Land-use change simulation and assessment of driving factors in the loess hilly region—a case study as Pengyang County. Environ Monit Assess 164:133–142
Zhu Z, Woodcock CE (2014) Continuous change detection and classification of land cover using all available Landsat data. Remote Sens Environ 144:152–171
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge the United States Geological Survey (USGS) for the free access to Landsat data used in the present study. The authors are also grateful to the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments which helped in improving the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mishra, V.N., Rai, P.K., Prasad, R. et al. Prediction of spatio-temporal land use/land cover dynamics in rapidly developing Varanasi district of Uttar Pradesh, India, using geospatial approach: a comparison of hybrid models. Appl Geomat 10, 257–276 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12518-018-0223-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12518-018-0223-5