Abstract
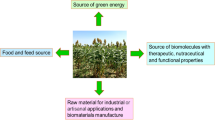
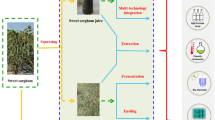
Fossil energy resources, the primary source of transport fuel in the world is depleting dramatically to meet the ever-increasing energy demands globally. Crop plants are one of the best sources of renewable energy which can be used as feedstock for biofuel production. Sweet sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench], a C4 Graminaceous crop which has sugar-rich stalks and which is a water-use efficient crop has a very good potential as an alternative feed stock for ethanol production. It is the only crop that provides grain and stem that can be used for sugar, alcohol, syrup, jaggery, fodder, fuel, bedding, roofing, fencing, paper and chewing. Sweet sorghum juices usually contain approximately 16–18% fermentable sugar, which can be directly fermented into ethanol by yeast. Technical challenges of using sweet sorghum for biofuels are a short harvest period for highest sugar content and fast sugar degradation during storage. Various review works based on the problems of sweet sorghum were described in this review. Some studies are on the genetic potential of sweet sorghum for higher green cane yield and juice extractability where as some studies are purely on the shelf life of the juice how to preserve the juice with low cost against bacterial contamination. Studies also involve testing the potential of genotypes for superior yields of cane during post rainy and summer seasons also to make the cane available for maximum period in a year. Studies on fermentation and hydrolysis of lignocellulose are also addressed in this review.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almodares, A., and M.R. Hadi. 2009. Production of bioethanol from sweet sorghum: A review. African Journal of Agricultural Research 4(9): 772–780.
Areesirisuk, Atsadawut, Lakkana Laopaiboon, Naulchan Khongsay, and Pattana Laopaiboon. 2010. Improvement of gas chromatographic analysis for organic acids and solvents in acetone-butanolethanol fermentation from sweet sorghum juice. African Journal of Biotechnology 9(38): 6422–6429.
Ban, Jingyang, Yu Jianliang, Xu Zhang, and Tianwei Tan. 2008. Ethanol production from sweet sorghum residual. Frontiers of Chemical Science and Engineering 2(4): 452–455.
Bala Ravi, S., P.R. Biswas, and C.V. Ratnavathi. 1997. Genetic variability and stability for the major traits of sweet sorghum. In: Proceedings of the first international sweet sorghum conference, September 14–19, 298–303.
Bayrock, D.P., and W.M. Ingledew. 2001. Application of multistage continuous fermentation for production of fuel alcohol by very-high-gravity fermentation technology. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology 27: 87–93.
Bulawayo, B., J.M. Bvochora, M.I. Muzondo, and R. Zvauya. 1996. Ethanol production by fermentation of sweet-stem sorghum juice using various yeast strains. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology 12: 357–360.
Chohnan, Shigeru, Megumi Nakane, M. Habibur Rahman, Youji Youji, Takanori Takanori, Hiroyuki Ohta, and Yasurou Kurusu. 2011. Fuel ethanol production from sweet sorghum using repeated-batch fermentation. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering 111(4): 433–436.
Gyalai-Korpos, M., J. Feczak, and K. Reczey. 2008. Sweet sorghum juice and bagasse as a possible feedstock for bioethanol production. Hungarian Journal of Industrial Chemistry 36(1–2): 43–48.
Hunsigi, Gururaj, N.R. Yekkeli, and B.Y. Kongawad. 2010. Sweet stalk sorghum: An alternative sugar crop for ethanol production. Sugar Technology 12(1): 79–80.
Jacques, K., T.P. Lyons, and D.R Kelsall. (1999). The alcohol textbook. 3rd ed, 388. Nottingham: Nottingham University Press.
Jianliang, Yu., Xu Zhang, and Tianwei Tan. 2009. Optimization of media conditions for the production of ethanol from sweet sorghum juice by immobilized Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biomass and Bioenergy 33: 521–526.
Jianliang, Yu., Jing Zhong, Xu Zhang, and Tianwei Tan. 2010. Ethanol production from H2SO3-steam-pretreated fresh sweet sorghum stem by simultaneous saccharification and fermentation. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology 160: 401–409.
Khongsay, Naulchan, Lakkana Laopaiboon, and Pattana Laopaiboon. 2010. Growth and batch ethanol fermentation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae on sweet sorghum stem juice under normal and very high gravity conditions. Biotechnology 9(1): 9–16.
Kundiyana, D.K., D.D. Bellmer, R.L. Huhnke, M.R. Wilkins, and P.L. Claypool. 2010. Influence of temperature, pH and yeast on in-field production of ethanol from unsterilized sweet sorghum juice. Biomass and Bioenergy 3(4): 1481–1486.
Laopaiboon, Lakkana, Pornthap Thanonkeo, Prasit Jaisil, and Pattana Laopaiboon. 2007. Ethanol production from sweet sorghum juice in batch and fed-batch fermentations by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology 23(2007): 1497–1501.
Laopaiboon, Lakkana, Sunan Nuanpeng, Penjit Srinophakun, Preekamol Klanrit, and Pattana Laopaiboon. 2009. Ethanol production from sweet sorghum juice using very high gravity technology: Effects of carbon and nitrogen supplementations. Bioresource Technology 100: 4176–4182.
Li, Bing-Zhi, Venkatesh Balan, Ying-Jin Yuan, and Bruce E. Dale. 2010. Process optimization to convert forage and sweet sorghum bagasse to ethanol based on ammonia fiber expansion (AFEX) pretreatment. Bioresource Technology 101: 1285–1292.
Liu, Ronghou, Jinxia Li, and Fei Shen. 2008. Refining bioethanol from stalk juice of sweet sorghum by immobilized yeast fermentation. Renewable Energy 33(5): 1130–1135.
Quintero, J.A., M.I. Montoya, O.J. Sanchez, O.H. Giraldo, and C.A. Cardona. 2008. Fuel ethanol production from sugarcane and corn: Comparative analysis for a Colombian case. Energy 33: 385–399.
Ratnavathi, C.V., B. Dayakar Rao, P.G. Padmaja, S. Ravikumar, S. Reddy, B. S. Vijaykumar, M. Pallav, V.V. Komala, D. Gopalakrishna, and N. Seetharama. 2005. Sweet sorghum the wonder crop for biofuel production, NATP Technical Report No. 27, April 2005.
Ratnavathi, C.V., K. Suresh, B.S. Vijay Kumar, M. Pallavi, V.V. Komala, and N. Seetharama. 2010. Study on genotypic variation for ethanol production from sweet sorghum juice. Biomass and Bioenergy 34: 947–952.
Ronghou, Liu, and Fei Shen. 2008. Impacts of main factors on bioethanol fermentation from stalk juice of sweet sorghum by immobilized Saccharomyces cerevisiae (CICC 1308). Bioresource Technology 99: 847–854.
Rubin, E. M. 2008. Genomics of cellulosic biofuels. Nature 454: 841–845.
Sipos, Bálint, Jutka Réczey, Zsolt Somorai, Zsófia Kádár, Dóra Dienes, and Kati Réczey. 2009. Sweet sorghum as feedstock for ethanol production: Enzymatic hydrolysis of steam-pretreated bagasse. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology 153: 151–162.
Sun, Y., and J. Cheng. 2002. Hydrolysis of lignocellulosic materials for ethanol production: A review. Bioresource Technology 83(1): 1–11.
Wu, Xiaorong, Scott Staggenborg, Johathan L. Propheter, William L. Rooney, Jianming Yu, and Donghai Wang. 2010. Features of sweet sorghum juice and their performance in ethanol fermentation. Industrial Crops and Products 31: 164–170.
Yu, Qiang, Xinshu Zhuang, Zhenhong Yuan, Wen Wang, Wei Qi, Qiong Wang, and Xuesong Tan. 2011. Step-change flow rate liquid hot water pretreatment of sweet sorghum bagasse for enhancement of total sugars recovery. Applied Energy 88(7): 2472–2479.
Zhang, M., C. Eddy, K. Deanda, M. Finkelstein, and S. Picataggio. 1995. Metabolic engineering of a pentose metabolism pathway in ethanologenic Zymomonas mobilis. Science 267: 240–243.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely acknowledge the financial support from National Agricultural Technology Project (ICAR) through the project NATP RNPS-24 (2000–2005) and NFBSFARA (ICAR) (2011–2015) on sweet sorghum.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ratnavathi, C.V., Chakravarthy, S.K., Komala, V.V. et al. Sweet Sorghum as Feedstock for Biofuel Production: A Review. Sugar Tech 13, 399–407 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-011-0112-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-011-0112-2