Abstract
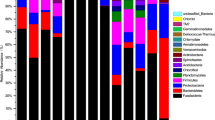
We investigated the influence of host species on intestinal microbiota by comparing the gut bacterial community structure of four cohabitating freshwater fish larvae, silver carp, grass carp, bighead carp, and blunt snout bream, using denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) of the amplified 16S and 18S rRNA genes. Similarity clustering indicated that the intestinal microbiota derived from these four fish species could be divided into four groups based on 16S rRNA gene similarity, whereas the eukaryotic 18S rRNA genes showed no distinct groups. The water sample from the shared environment contained microbiota of an independent group as indicated by both 16S and 18S rRNA genes segments. The bacterial community structures were visualized using rank-abundance plots fitted with linear regression models. Results showed that the intestinal bacterial evenness was significantly different between species (P<0.05) and between species and the water sample (P<0.01). Thirty-five relatively dominant bands in DGGE patterns were sequenced and grouped into five major taxa: Proteobacteria (26), Actinobacteria (5), Bacteroidetes (1), Firmicutes (2), and Cyanobacterial (1). Six eukaryotes were detected by sequencing 18S rRNA genes segments. The present study suggests that the intestines of the four fish larvae, although reared in the same environment, contained distinct bacterial populations, while intestinal eukaryotic microorganisms were almost identical.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ager, D., Evans, S., Li, H., Lilley, A.K., and van der Gast, C.J. 2010. Anthropogenic disturbance affects the structure of bacterial communities. Environ. Microbiol. 12, 670–678.
Austin, B. 2006. The bacterial microflora of fish, revised. The Scientific World J. 6, 931–945.
Bäckhed, F., Ding, H., Wang, T., Hooper, L.V., Koh, G.Y., Nagy, A., Semenkovich, C.F., and Gordon, J.I. 2004. The gut microbiota as an environmental factor that regulates fat storage. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 15718–15723.
Bates, J.M., Mittge, E., Kuhlman, J., Baden, K.N., Cheesman, S.E., and Guillemin, K. 2006. Distinct signals from the microbiota promote different aspects of zebrafish gut differentiation. Develop. Biol. 297, 374–386.
Brunvold, L., Sandaa, R.-A., Mikkelsen, H., Welde, E., Bleie, H., and Bergh, Ø. 2007. Characterisation of bacterial communities associated with early stages of intensively reared cod (Gadus morhua) using Denaturing Gradient Gel Electrophoresis (DGGE). Aquaculture 272, 319–327.
Cahill, M.M. 1990. Bacterial flora of fishes: A review. Microb. Ecol. 19, 21–41.
Camp, J.G., Kanther, M., Semova, I., and Rawls, J.F. 2009. Patterns and scales in gastrointestinal microbial ecology. Gastroenterology 136, 1989–2002.
Cole, J.R., Chai, B., Farris, R.J., Wang, Q., Kulam, S.A., McGarrell, D.M., Garrity, G.M., and Tiedje, J.M. 2005. The ribosomal database project (RDP-II): sequences and tools for high-throughput rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 33, D294–296.
Dabrowski, K. 1984. The feeding of fish larvae: present <state of the art> and perspectives. Reprod. Nutr. Develop. 24, 807–833.
de La Cochetière, M.-F., Durand, T., Lalande, V., Petit, J.-C., Potel, G., and Beaugerie, L. 2008. Effect of antibiotic therapy on human fecal microbiota and the relation to the development of Clostridium difficile. Microb. Ecol. 56, 395–402.
Eichner, C.A., Erb, R.W., Timmis, K.N., and Wagner-Dobler, I. 1999. Thermal gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of bioprotection from pollutant shocks in the activated sludge microbial community. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 65, 102–109.
Gordon, J.I. 2005. A genomic view of our symbiosis with members of the gut microbiota. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 40, S28.
Hansen, G.H. and Olafsen, J.A. 1999. Bacterial interactions in early life stages of marine cold water fish. Microb. Ecol. 38, 1–26.
Holben, W.E., Williams, P., Saarinen, M., Särkilahti, L.K., and Apajalahti, J.H.A. 2002. Phylogenetic cnalysis of intestinal microflora indicates a novel mycoplasma phylotype in farmed and wild salmon. Microb. Ecol. 44, 175–185.
Hovda, M.B., Lunestad, B.T., Fontanillas, R., and Rosnes, J.T. 2007. Molecular characterisation of the intestinal microbiota of farmed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Aquaculture 272, 581–588.
Hubert, N., Hanner, R., Holm, E., Mandrak, N.E., Taylor, E., Burridge, M., Watkinson, D., Dumont, P., Curry, A., Bentzen, P., and et al. 2008. Identifying canadian freshwater fishes through DNA barcodes. PLoS One 3, e2490.
Jensen, S., Øvreås, L., Bergh, Ø., and Torsvik, V. 2004. Phylogenetic analysis of bacterial communities associated with larvae of the atlantic halibut propose succession from a uniform normal flora. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 27, 728–736.
Kim, D.-H., Brunt, J., and Austin, B. 2007. Microbial diversity of intestinal contents and mucus in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). J. Appl. Microbiol. 102, 1654–1664.
Kovacs, A., Ben-Jacob, N., Tayem, H., Halperin, E., Iraqi, F., and Gophna, U. 2011. Genotype is a stronger determinant than sex of the mouse gut microbiota. Microb. Ecol. 61, 423–428.
Ley, R.E., Hamady, M., Lozupone, C., Turnbaugh, P.J., Ramey, R.R., Bircher, J.S., Schlegel, M.L., Tucker, T.A., Schrenzel, M.D., Knight, R., and et al. 2008. Evolution of mammals and their gut microbes. Science 320, 1647–1651.
Ley, R.E., Peterson, D.A., and Gordon, J.I. 2006. Ecological and evolutionary forces shaping microbial diversity in the human intestine. Cell 124, 837–848.
Li, X.M., Yu, Y.H., Feng, W.S., Yan, Q.Y., Wu, L., and Zhang, X. 2009. Relationship between DNA polymorphism and species composition of plankton community in an artificial Lake. J. Lake Sci. 21, 378–384.
Lilley, A.K., Fry, J.C., Bailey, M.J., and Day, M.J. 1996. Comparison of aerobic heterotrophic taxa isolated from four root domains of mature sugar beet (Beta vulgaris). FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 21, 231–242.
Loisel, P., Harmand, J., Zemb, O., Latrille, E., Lobry, C., Delgenes, J.-P., and Godon, J.-J. 2006. Denaturing gradient electrophoresis (DGE) and single-strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP) molecular fingerprintings revisited by simulation and used as a tool to measure microbial diversity. Environ. Microbiol. 8, 720–731.
Magne, F., Abély, M., Boyer, F., Morville, P., Pochart, P., and Suau, A. 2006. Low species diversity and high interindividual variability in faeces of preterm infants as revealed by sequences of 16S rRNA genes and PCR-temporal temperature gradient gel electrophoresis profiles. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 57, 128–138.
Moreno, C., Romero, J., and Espejo, R.T. 2002. Polymorphism in repeated 16S rRNA genes is a common property of type strains and environmental isolates of the genus Vibrio. Microbiology 148, 1233–1239.
Muyzer, G., de Waal, E.C., and Uitterlinden, A.G. 1993. Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 59, 695–700.
Navarrete, P., Espejo, R., and Romero, J. 2009. Molecular analysis of microbiota along the digestive tract of juvenile Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.). Microb. Ecol. 57, 550–561.
Navarrete, P., Magne, F., Mardones, P., Riveros, M., Opazo, R., Suau, A., Pochart, P., and Romero, J. 2010. Molecular analysis of intestinal microbiota of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 71, 148–156.
Nieto, T.P., Toranzo, A.E., and Barja, J.L. 1984. Comparison between the bacterial flora associated with fingerling rainbow trout cultured in two different hatcheries in the North-West of Spain. Aquaculture 42, 193–206.
Olafsen, J.A. 2001. Interactions between fish larvae and bacteria in marine aquaculture. Aquaculture 200, 223–237.
Rawls, J.F., Mahowald, M.A., Goodman, A.L., Trent, C.M., and Gordon, J.I. 2007. In vivo imaging and genetic analysis link bacterial motility and symbiosis in the zebrafish gut. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 7622–7627.
Rawls, J.F., Samuel, B.S., and Gordon, J.I. 2004. Gnotobiotic zebrafish reveal evolutionarily conserved responses to the gut microbiota. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 4509–4601.
Romero, J. and Navarrete, P. 2006. 16S rDNA-based analysis of dominant bacterial populations associated with early life stages of coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch). Microb. Ecol. 51, 422–430.
Sakata, T., Okabayashi, J., and Kakimoto, D. 1980. Variations in the intestinal flora of tilapia reared in fresh- and seawater. Bull. Japan. Soc. Sci. Fish 46, 967–975.
Savas, S., Kubilay, A., and Basmaz, N. 2005. Effect of bacterial load in feeds on intestinal microflora of seabream (Sparus aurata) larvae and juveniles. The Israeli Journal of Aquaculture-Bamidgeh 57, 3–9.
Spanggaard, B., Huber, I., Nielsen, J., Nielsen, T., Appel, K.F., and Gram, L. 2000. The microflora of rainbow trout intestine: a comparison of traditional and molecular identification. Aquaculture 182, 1–15.
Sugita, H., Nakamura, T., Tanaka, K., and Deguchi, Y. 1994. Identification of aeromonas species isolated from freshwater fish with the microplate hybridization method. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 60, 3036–3038.
Tamura, K., Dudley, J., Nei, M., and Kumar, S. 2007. MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 24, 1596–1599.
Tanaka, R., Ootsubo, M., Sawabe, T., Ezura, Y., and Tajima, K. 2004. Biodiversity and in situ abundance of gut microflora of abalone (Haliotis discus hannai) determined by culture-independent techniques. Aquaculture 241, 453–463.
Tannock, G.W. 2001. Molecular assessment of intestinal microflora. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 73, 410S–414S.
Thomas, A., Ricardo, V.-J., and Lena, G. 1998. Yeasts isolated from the intestine of rainbow trout adhere to and grow in intestinal mucus. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 7, 115–126.
van der Gast, C.J., Allen, I., Laskin, S.S., and Geoffrey, M.G. 2008. Chapter 6: islands shaping thought in microbial ecology. Advan. Appl. Microbiol. 64, 167–182.
van der Gast, C.J., Jefferson, B., Reid, E., Robinson, T., Bailey, M.J., Judd, S.J., and Thompson, I.P. 2006. Bacterial diversity is determined by volume in membrane bioreactors Environ. Microbiol. 8, 1048–1055.
van Hannen, E., van Agterveld, M., Gons, H., and Laanbroek, H. 1998. Revealing genetic diversity of eukaryotic microorganisms in aquatic environments by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. J. Phycol. 34, 206–213.
Ward, N., Steven, B., Penn, K., Methé, B., and Detrich, W. 2009. Characterization of the intestinal microbiota of two Antarctic notothenioid fish species. Extremophiles 13, 679–685.
Ward, R.D., Zemlak, T.S., Innes, B.H., Last, P.R., and Hebert, P.D.N. 2005. DNA barcoding Australia’s fish species. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond., Ser. B: Biol. Sci. 360, 1847–1857.
Whitman, W.B., Coleman, D.C., and Wiebe, W.J. 1998. Prokaryotes: The unseen majority. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 6578–6583.
Wielen, P.W.J.J., Keuzenkamp, D.A., Lipman, L.J.A., Knapen, F., and Biesterveld, S. 2002. Spatial and temporal variation of the intestinal bacterial community in commercially raised broiler chickens during growth. Microb. Ecol. 44, 286–293.
Woodcock, S., Gast, C.J.v.d., Bell, T., Lunn, M., Curtis, T.P., Head, I.M., and Sloan, W.T. 2007. Neutral assembly of bacterial communities. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 62, 171–180.
Yu, Y.H., Yan, Q.Y., and Feng, W.S. 2008. Spatiotemporal heterogeneity of plankton communities in Lake Donghu, China, as revealed by PCR-denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and its relation to biotic and abiotic factors. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 63, 328–337.
Zhou, Z.G., Liu, Y.C., Shi, P.J., He, S.X., Yao, B., and Ring, E. 2009. Molecular characterization of the autochthonous microbiota in the gastrointestinal tract of adult yellow grouper (Epinephelus awoara) cultured in cages. Aquaculture 286, 184–189.
Zoetendal, E.G., Akkermans, A.D.L., Akkermans-van Vliet, W.M., de Visser, J.A.G.M., and de Vos, W.M. 2001. The host genotype affects the bacterial community in the human gastronintestinal tract. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 13, 129–134.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Yu, Y., Feng, W. et al. Host species as a strong determinant of the intestinal microbiota of fish larvae. J Microbiol. 50, 29–37 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-012-1340-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-012-1340-1