Abstract
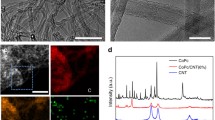
Metal phthalocyanines (MePcs) have been considered as promising catalysts for CO2 reduction electrocatalysis due to high turnover frequency and structural tunability. However, their performance is often limited by low current density and the performance of some systems is controversial. Here, we report a carbon nanotube (CNT) hybridization approach to study the electrocatalytic performance of MePcs (Me = Co, Fe and Mn). MePc molecules are anchored on CNTs to form the hybrid materials without noticeable molecular aggregations. The MePc/CNT hybrids show higher activities and better stabilities than their molecular counterparts. FePc/CNT is slightly less active than CoPc/CNT, but it could deliver higher Faradaic efficiencies for CO production at low overpotentials. In contrast, the catalytic performance of MePc molecules directly loaded on substrate is hindered by molecular aggregation, especially for FePc and MnPc. Our results suggest that carbon nanotube hybridization is an efficient approach to construct advanced MePc electrocatalysts and to understand their catalytic performance.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sakakura, T.; Choi, J. C.; Yasuda, H. Transformation of carbon dioxide. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2365–2387.
Qiao, J. L.; Liu, Y. Y.; Hong, F.; Zhang, J. J. A review of catalysts for the electroreduction of carbon dioxide to produce low-carbon fuels. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 631–675.
Nielsen, D. U.; Hu, X. M.; Daasbjerg, K.; Skrydstrup, T. Chemically and electrochemically catalysed conversion of CO2 to CO with follow-up utilization to value-added chemicals. Nat. Catal. 2018, 1, 244–254.
Seh, Z. W.; Kibsgaard, J.; Dickens, C. F.; Chorkendorff, I.; Nørskov, J. K.; Jaramillo, T. F. Combining theory and experiment in electrocatalysis: Insights into materials design. Science 2017, 355, eaad4998.
Weekes, D. M.; Salvatore, D. A.; Reyes, A.; Huang, A.; Berlinguette, C. P. Electrolytic CO2 reduction in a flow cell. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 910–918.
Varela, A. S.; Ju, W.; Strasser, P. Molecular nitrogen-carbon catalysts, solid metal organic framework catalysts, and solid metal/nitrogen-doped carbon (MNC) catalysts for the electrochemical CO2 reduction. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1703614.
Diercks, C. S.; Liu, Y. Z.; Cordova, K. E.; Yaghi, O. M. The role of reticular chemistry in the design of CO2 reduction catalysts. Nat. Mater. 2018, 17, 301–307.
Lin, S.; Diercks, C. S.; Zhang, Y. B.; Kornienko, N.; Nichols, E. M.; Zhao, Y. B.; Paris, A. R.; Kim, D.; Yang, P. D.; Yaghi, O. M. et al. Covalent organic frameworks comprising cobalt porphyrins for catalytic CO2 reduction in water. Science 2015, 349, 1208–1213.
Lu, Q.; Jiao, F. Electrochemical CO2 reduction: Electrocatalyst, reaction mechanism, and process engineering. Nano Energy 2016, 29, 439–456.
Kumar, B.; Brian, J. P.; Atla, V.; Kumari, S.; Bertram, K. A.; White, R. T.; Spurgeon, J. M. New trends in the development of heterogeneous catalysts for electrochemical CO2 reduction. Catal. Today 2016, 270, 19–30.
Meshitsuka, S.; Ichikawa, M.; Tamaru, K. Electrocatalysis by metal phthalocyanines in the reduction of carbon dioxide. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1974, 158–159.
Lieber, C. M.; Lewis, N. S. Catalytic reduction of carbon dioxide at carbon electrodes modified with cobalt phthalocyanine. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1984, 106, 5033–5034.
Manbeck, G. F.; Fujita, E. A review of iron and cobalt porphyrins, phthalocyanines and related complexes for electrochemical and photochemical reduction of carbon dioxide. J. Porphyr. Phthalocya. 2015, 19, 45–64.
Han, N.; Wang, Y.; Ma, L.; Wen, J. G.; Li, J.; Zheng, H. C.; Nie, K. Q.; Wang, X. X.; Zhao, F. P.; Li, Y. F. et al. Supported cobalt polyphthalocyanine for high-performance electrocatalytic CO2 reduction. Chem 2017, 3, 652–664.
Furuya, N.; Koide, S. Electroreduction of carbon dioxide by metal phthalocyanines. Electrochim. Acta 1991, 36, 1309–1313.
Abe, T.; Yoshida, T.; Tokita, S.; Taguchi, F.; Imaya, H.; Kaneko, M. Factors affecting selective electrocatalytic CO2 reduction with cobalt phthalocyanine incorporated in a polyvinylpyridine membrane coated on a graphite electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1996, 412, 125–132.
Kramer, W. W.; McCrory, C. C. L. Polymer coordination promotes selective CO2 reduction by cobalt phthalocyanine. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 2506–2515.
Zhu, M. H.; Ye, R. Q.; Jin, K.; Lazouski, N.; Manthiram, K. Elucidating the reactivity and mechanism of CO2 electroreduction at highly dispersed cobalt phthalocyanine. ACS Energy Lett. 2018, 3, 1381–1386.
Morlanés, N.; Takanabe, K.; Rodionov, V. Simultaneous reduction of CO2 and splitting of H2O by a single immobilized cobalt phthalocyanine electrocatalyst. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 3092–3095.
Pan, Y.; Lin, R.; Chen, Y. J.; Liu, S. J.; Zhu, W.; Cao, X.; Chen, W. X.; Wu, K. L.; Cheong, W. C.; Wang, Y. et al. Design of single-atom Co-N5 catalytic site: A robust electrocatalyst for CO2 reduction with nearly 100% CO selectivity and remarkable stability. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 4218–4221.
Yang, H. B.; Hung, S. F.; Liu, S.; Yuan, K. D.; Miao, S.; Zhang, L. P.; Huang, X.; Wang, H. Y.; Cai, W. Z.; Chen, R. et al. Atomically dispersed Ni(I) as the active site for electrochemical CO2 reduction. Nat. Energy 2018, 3, 140–147.
Abe, T.; Imaya, H.; Yoshida, T.; Tokita, S.; Schlettwein, D.; Wöhrle, D.; Kaneko, M. Electrochemical CO2 reduction catalysed by cobalt octacyanophthalocyanine and its mechanism. J. Porphyr. Phthalocya. 1997, 1, 315–321.
Weng, Z.; Wu, Y. S.; Wang, M. Y.; Jiang, J. B.; Yang, K.; Huo, S. J.; Wang, X. F.; Ma, Q.; Brudvig, G. W.; Batista, V. S. et al. Active sites of copper-complex catalytic materials for electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 415.
Dinh, C. T.; Burdyny, T.; Kibria, G.; Seifitokaldani, A.; Gabardo, C. M.; de Arquer, F. P. G.; Kiani, A.; Edwards, J. P.; De Luna, P.; Bushuyev, O. S. et al. CO2 electroreduction to ethylene via hydroxide-mediated copper catalysis at an abrupt interface. Science 2018, 360, 783–787.
De Luna, P.; Quintero-Bermudez, R.; Dinh, C. T.; Ross, M. B.; Bushuyev, O. S.; Todorović, P.; Regier, T.; Kelley, S. O.; Yang, P. D.; Sargent, E. H. Catalyst electro-redeposition controls morphology and oxidation state for selective carbon dioxide reduction. Nat. Catal. 2018, 1, 103–110.
Zhuang, T. T.; Liang, Z. Q.; Seifitokaldani, A.; Li, Y.; De Luna, P.; Burdyny, T.; Che, F. L.; Meng, F.; Min, Y. M.; Quintero-Bermudez, R. et al. Steering post-C-C coupling selectivity enables high efficiency electroreduction of carbon dioxide to multi-carbon alcohols. Nat. Catal. 2018, 1, 421–428.
Zhang, Z.; Xiao, J. P.; Chen, X. J.; Yu, S.; Yu, L.; Si, R.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S. H.; Meng, X. G.; Wang, Y. et al. Reaction mechanisms of well-defined metal-N4 sites in electrocatalytic CO2 reduction. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 16339–16342.
Furuya, N.; Matsui, K. Electroreduction of carbon dioxide on gas-diffusion electrodes modified by metal phthalocyanines. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 1989, 271, 181–191.
Zagal, J. H.; Griveau, S.; Silva, J. F.; Nyokong, T.; Bedioui, F. Metallophthalocyanine-based molecular materials as catalysts for electrochemical reactions. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2010, 254, 2755–2791.
Sorokin, A. B. Phthalocyanine metal complexes in catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 8152–8191.
Zhang, X.; Wu, Z. S.; Zhang, X.; Li, L. W.; Li, Y. Y.; Xu, H. M.; Li, X. X.; Yu, X. L.; Zhang, Z. S.; Liang, Y. Y. et al. Highly selective and active CO2 reduction electrocatalysts based on cobalt phthalocyanine/carbon nanotube hybrid structures. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14675.
Yoshida, T.; Kamato, K.; Tsukamoto, M.; Iida, T.; Schlettwein, D.; Wöhrle, D.; Kaneko, M. Selective electroacatalysis for CO2 reduction in the aqueous phase using cobalt phthalocyanine/poly-4-vinylpyridine modified electrodes. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1995, 385, 209–225.
Ju, W.; Bagger, A.; Hao, G. P.; Varela, A. S.; Sinev, I.; Bon, V.; Roldan Cuenya, B.; Kaskel, S.; Rossmeisl, J.; Strasser, P. Understanding activity and selectivity of metal-nitrogen-doped carbon catalysts for electrochemical reduction of CO2. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 944.
Acknowledgements
Y. Y. L. acknowledges financial supports from Shenzhen fundamental research funding (No. JCYJ20160608140827794).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
12274_2019_2455_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Revealing the hidden performance of metal phthalocyanines for CO2 reduction electrocatalysis by hybridization with carbon nanotubes
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Z., Wang, Y., Zhang, X. et al. Revealing the hidden performance of metal phthalocyanines for CO2 reduction electrocatalysis by hybridization with carbon nanotubes. Nano Res. 12, 2330–2334 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-019-2455-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-019-2455-z