Abstract
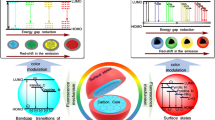
Engineering of the luminescent properties for graphene quantum dots (GQDs) presents two enormous challenges: 1) The bandgap of GQDs is mainly determined by structural defects (size, shape, and the fraction of sp2 and sp3 domains), which results in non-stoichiometric nature; 2) the preparation methods limit the achievement of an accurate chemical structure of GQDs, leading to many controversial explanations over the relationship between the structural defects and bandgaps. Here, single-layered GQDs with an exact structure are obtained by in-situ reaction of intercalated precursors in the confined nanospace of layered double hydroxides (LDHs). Subsequently, the structure-property relationship is uncovered, demonstrating the enhanced fluorescence and activated room temperature phosphorescence of the as-prepared GQDs-LDHs, which originate from synergistic effects: 1) strong confinement provided by the nanospace of LDHs; 2) rich O-containing functional groups on the surface of GQDs resulting from LDH catalysis. Moreover, the colorless nature and dual-emission characteristics of GQDs-LDHs satisfy the preconditions as anti-counterfeiting markers for protecting valuable documents (bank notes, commercial invoices, etc.). Particularly, owing to the low toxicity of GQDs and the edible property of LDHs, the GQDs-LDHs/gelatin capsules could be the new generation of potential green anti-counterfeiting material in the field of food and drugs.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Resch-Genger, U.; Grabolle, M.; Cavaliere-Jaricot, S.; Nit-schke, R.; Nann, T. Quantum dots versus organic dyes as fluorescent labels. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 763–775.
Baker, M. Nanotechnology imaging probes: Smaller and more stable. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 957–962.
He, X.; Gao, J.; Gambhir, S. S.; Cheng, Z. Near-infrared fluorescent nanoprobes for cancer molecular imaging: Sta-tus and challenges. Trends Mol. Med. 2010, 16, 574–583.
Zheng, X. T.; Ananthanarayanan, A.; Luo, K. Q.; Chen, P. Glowing graphene quantum dots and carbon dots: Prop-erties, syntheses, and biological applications. Small 2015, 11, 1620–1636.
Loh, K. P.; Bao, Q. L.; Eda, G.; Chhowalla, M. Graphene oxide as a chemically tunable platform for optical applications. Nat. Chem. 2010, 2, 1015–1024.
Cao, L.; Meziani, M. J.; Sahu, S.; Sun, Y. P. Photolu-minescence properties of graphene versus other carbon nanomaterials. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 171–180.
Yan, J. A.; Xian, L. D.; Chou, M. Y. Structural and electronic properties of oxidized graphene. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 103, 086802.
Li, X. L.; Wang, X. R.; Zhang, L.; Lee, S.; Dai, H. J. Chemically derived, ultrasmooth graphene nanoribbon semiconductors. Science 2008, 319, 1229–1232.
Ponomarenko, L. A.; Schedin, F.; Katsnelson, M. I.; Yang, R.; Hill, E. W.; Novoselov, K. S.; Geim, A. K. Chaotic dirac billiard in graphene quantum dots. Science 2008, 320, 356–358.
Kosynkin, D. V.; Higginbotham, A. L.; Sinitskii, A.; Lomeda, J. R.; Dimiev, A.; Price, B. K.; Tour, J. M. Longitudinal unzipping of carbon nanotubes to form graphene nanoribbons. Nature 2009, 458, 872–876.
Tetsuka, H.; Asahi, R.; Nagoya, A.; Okamoto, K.; Tajima, I.; Ohta, R.; Okamoto, A. Optically tunable amino-functio-nalized graphene quantum dots. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 5333–5338.
Wang, Q.; O’ Hare, D. Recent advances in the synthesis and application of layered double hydroxide (LDH) nanosheets. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 4124–4155.
Shi, W. Y.; He, S.; Wei, M.; Evans, D. G.; Duan, X. Opti-cal pH sensor with rapid response based on a fluorescein- intercalated layered double hydroxide. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 3856–3863.
Shi, W. Y.; Fu, Y.; Li, Z. X.; Wei, M. Multiple and configurable optical logic systems based on layered double hydroxides and chromophore assemblies. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 711–731.
OECD. The Economic Impact of Counterfeiting and Piracy; OECD Publishing: Paris, 2008.
Hu, H. B.; Chen, Q.-W.; Tang, J.; Hu, X.-Y.; Zhou, X.-H. Photonic anti-counterfeiting using structural colors derived from magnetic-responsive photonic crystals with double photonic bandgap heterostructures. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 11048–11053.
Hu, H. B.; Zhong, H.; Chen, C. L.; Chen, Q. W. Mag-netically responsive photonic watermarks on banknotes. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 3695–3702.
Cui, Y.; Hegde, R. S.; Phang, I. Y.; Lee, H. K.; Ling, X. Y. Encoding molecular information in plasmonic nano-structures for anti-counterfeiting applications. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 282–288.
Andres, J.; Hersch, R. D.; Moser, J.-E.; Chauvin, A.-S. A new anti-counterfeiting feature relying on invisible lumi-nescent full color images printed with lanthanide-based inks. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 5029–5036.
Sangeetha, N. M.; Moutet, P.; Lagarde, D.; Sallen, G.; Urbaszek, B.; Marie, X.; Viau, G.; Ressier, L. 3D assembly of upconverting NaYF4 nanocrystals by afm nanoxerography: Creation of anti-counterfeiting microtags. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 9587–9592.
Meruga, J. M.; Baride, A.; Cross, W.; Kellar, J. J.; May, P. S. Red-green-blue printing using luminescence-upconve-rsion inks. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 2221–2227.
You, M. L.; Zhong, J. J.; Hong, Y.; Duan, Z. F.; Lin, M.; Xu, F. Inkjet printing of upconversion nanoparticles for anti- counterfeit applications. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 4423–4431.
Huang, C. B.; Lucas, B.; Vervaet, C.; Braeckmans, K.; Van Calenbergh, S.; Karalic, I.; Vandewoestyne, M.; Deforce, D.; Demeester, J.; De Smedt, S. C. Unbreakable codes in electrospun fibers: Digitally encoded polymers to stop medicine counterfeiting. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 2657–2662.
BfR Home Page. http://www.bfr.bund.de/de/start.html (acc-essed Dec 30, 2016).
Vatier, J.; Ramdani, A.; Vitré, M. T.; Mignon, M. Antacid activity of calcium carbonate and hydrotalcite tablets. Com-parison between in vitro evaluation using the “artificial stomach-duodenum” model and in vivo pH-metry in hea-lthy volunteers. Arzneimittel-Forschung 1994, 44, 514–518.
Carlino, S.; Hudson, M. J. Thermal intercalation of layered double hydroxides: capric acid into an Mg–Al LDH. J. Mater. Chem. 1995, 5, 1433–1442.
Qu, S. N.; Wang, X. Y.; Lu, Q. P.; Liu, X. Y.; Wang, L. J. A Biocompatible fluorescent ink based on water-soluble luminescent carbon nanodots. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 12215–12218.
Deng, Y. H.; Zhao, D. X.; Chen, X.; Wang, F.; Song, H.; Shen, D. Z. Long lifetime pure organic phosphorescence based on water soluble carbon dots. Chem. Commun 2013, 49, 5751–5753.
Sun, J.; Liu, H. M.; Chen, X.; Evans, D. G.; Yang, W. S.; Duan, X. Carbon nanorings and their enhanced lithium storage properties. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 1125–1130.
Campos, L. C.; Manfrinato, V. R.; Sanchez-Yamagishi, J. D.; Kong, J.; Jarillo-Herrero, P. Anisotropic etching and nanoribbon formation in single-layer graphene. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 2600–2604.
Mattevi, C.; Eda, G.; Agnoli, S.; Miller, S.; Mkhoyan, K. A.; Celik, O.; Mastrogiovanni, D.; Granozzi, G.; Garfunkel, E.; Chhowalla, M. Evolution of electrical, chemical, and structural properties of transparent and conducting chem-ically derived graphene thin films. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 2577–2583.
Kudin, K. N.; Ozbas, B.; Schniepp, H. C.; Prud’homme, R. K.; Aksay, I. A.; Car, R. Raman spectra of graphite oxide and functionalized graphene sheets. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 36–41.
Qu, S. N.; Liu, X. Y.; Guo, X. Y.; Chu, M. H.; Zhang, L. G.; Shen, D. Z. Amplified spontaneous green emission and lasing emission from carbon nanoparticles. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 2689–2695.
Lin, L. P.; Rong, M. C.; Lu, S. S.; Song, X. H.; Zhong, Y. X.; Yan, J. W.; Wang, Y. R.; Chen, X. A facile synthesis of highly luminescent nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots for the detection of 2, 4, 6-trinitrophenol in aqueous solution. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 1872–1878.
Zhu, S. J.; Meng, Q. N.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J. H.; Song, Y. B.; Jin, H.; Zhang, K.; Sun, H. C.; Wang, H. Y.; Yang, B. Highly photoluminescent carbon dots for multicolor patterning, sensors, and bioimaging. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 3953–3957.
Deng, Y. H.; Chen, X.; Wang, F.; Zhang, X. A.; Zhao, D. X.; Shen, D. Z. Environment-dependent photon emission from solid state carbon dots and its mechanism. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 10388–10393.
Chen, X. X.; Jin, Q. Q.; Wu, L. Z.; Tung, C.; Tang, X. J. Synthesis and unique photoluminescence properties of nitrogen-rich quantum dots and their applications. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 12542–12547.
Kumar, P.; Dwivedi, J.; Gupta, B. K. Highly luminescent dual mode rare-earth nanorod assisted multi-stage excitable security ink for anti-counterfeiting applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 10468–10475.
Song, L. Q.; Shi, J. J.; Lu, J.; Lu, C. Structure observation of graphene quantum dots by single-layered formation in layered confinement space. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 4846–4850.
Hu, S. L.; Trinchi, A.; Atkin, P.; Cole, I. Tunable photo-luminescence across the entire visible spectrum from car-bon dots excited by white light. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 2970–2974.
Chien, C. T.; Li, S. S.; Lai, W. J.; Yeh, Y. C.; Chen, H. A.; Chen, I. S.; Chen, L. C.; Chen, K. H.; Nemoto, T.; Isoda, S. et al. Tunable photoluminescence from graphene oxide. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 6662–6666.
Frisch, M. J.; Trucks, G. W.; Schlegel, H. B.; Scuseria, G. E.; Robb, M. A.; Cheeseman, J. R.; Montgomery, J. A., Jr.; Vreven, T.; Kudin, K. N.; Burant, J. C. et al. Gaussian 03: Revision B.04; Gaussian, Inc.: Pittsburgh, PA, 2003.
Talma, A. G.; Bovenkamp-Bouwman, A. G. Dehydration of itaconic acid. WO 1995006026, March 2, 1995.
Ai, M.; Ohdan, K. Formation of citraconic anhydride by vapor-phase decarboxy-condensation of pyruvic acid. Stud. Surface Sci. Catal. 1996, 101, 201–209.
Galanty, M. G.; Galanti, A. V. Kinetic study of the isom-erization of itaconic anhydride to citraconic anhydride. J. Org. Chem. 1982, 47, 1572–1574.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2014CB932103), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21571014, 21575010, and 21656001), Beijing Municipal Natural Science Foundation (No. 2172044), and the Open Research Fund Program of Beijing Key Lab of Plant Resource Research and Development, Beijing Technology and Business University (No. PRRD-2016-YB5).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
12274_2017_1820_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Dual-mode emission of single-layered graphene quantum dots in confined nanospace: Anti-counterfeiting and sensor applications
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, L., Xue, N., Zhao, Y. et al. Dual-mode emission of single-layered graphene quantum dots in confined nanospace: Anti-counterfeiting and sensor applications. Nano Res. 11, 2034–2045 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-017-1820-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-017-1820-z