Abstract
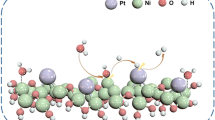
Downsizing noble metal nanoparticles, such as Pt, is an essential goal for many catalytic reactions. A non-noble metal sacrificial approach was used to immobilize monodispersed Pt nanoparticles (NPs) with a mean size of 1.2 nm on reduced graphene oxide (RGO). ZnO co-precipitated with Pt NPs and subsequently sacrificed by acid etching impedes the diffusion of Pt atoms onto the primary Pt particles and also their aggregation during the reduction of precursors. The resulting ultrafine Pt nanoparticles exhibit high activity (a turnover frequency of 284 min−1 at 298 K) in the hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane. The non-noble metal sacrificial approach is demonstrated as a general approach to synthesize well-dispersed noble metal NPs for catalysis.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wu, B. R.; Zheng, N. F. Surface and interface control of noble metal nanocrystals for catalytic and electrocatalytic applications. Nano Today 2013, 8, 168–197.
Jung, N.; Chung, D. Y.; Ryu, J.; Yoo, S. J.; Sung, Y. E. Pt-based nanoarchitecture and catalyst design for fuel cell applications. Nano Today 2014, 9, 433–456.
Tiwari, J. N.; Nath, K.; Kumar, S.; Tiwari, R. N.; Kemp, K. C.; Le, N. H.; Youn, D. H.; Lee, J. S.; Kim, K. S. Stable platinum nanoclusters on genomic DNA–graphene oxide with a high oxygen reduction reaction activity. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2221.
Qiao, B. T.; Wang, A. Q.; Yang, X. F.; Allard, L. F.; Jiang, Z.; Cui, Y. T.; Liu, J. Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, T. Singleatom catalysis of CO oxidation using Pt1/FeO x . Nat. Chem. 2011, 3, 634–641.
Zhang, M.; Zhao, Y. H.; Yan, L.; Peltier, R.; Hui, W. L.; Yao, X.; Cui, Y. L.; Chen, X. F.; Sun, H. Y.; Wang, Z. K. Interfacial engineering of bimetallic Ag/Pt nanoparticles on reduced graphene oxide matrix for enhanced antimicrobial activity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 8834–8840.
Goia, D. V.; Matijevic, E. Preparation of monodispersed metal particles. New J. Chem. 1998, 22, 1203–1215.
Thanh, N. T. K.; Maclean, N.; Mahiddine, S. Mechanisms of nucleation and growth of nanoparticles in solution. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 7610–7630.
Zhang, P. F.; Zhu, H. Y.; Dai, S. Porous carbon supports: Recent advances with various morphologies and compositions. ChemCatChem 2015, 7, 2788–2805.
Meek, S. T.; Greathouse, J. A.; Allendorf, M. D. Metalorganic frameworks: A rapidly growing class of versatile nanoporous materials. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 249–267.
Chen, Y.; Zhu, Q.-L.; Tsumori, N.; Xu, Q. Immobilizing highly catalytically active noble metal nanoparticles on reduced graphene oxide: A non-noble metal sacrificial approach. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 106–109.
Tan, C. L.; Huang, X.; Zhang, H. Synthesis and applications of graphene-based noble metal nanostructures. Mater. Today 2013, 16, 29–36.
Liu, M. M.; Zhang, R. Z.; Chen, W. Graphene-supported nanoelectrocatalysts for fuel cells: Synthesis, properties, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 5117–5160.
Chen, Y.; Yan, C. L.; Schmidt, O. G. Strain-driven formation of multilayer graphene/GeO2 tubular nanostructures as highcapacity and very long-life anodes for lithium-ion batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2013, 3, 1269–1274.
Liu, P. X.; Zhao, Y.; Qin, R. X.; Mo, S. G.; Chen, G. X.; Gu, L.; Chevrier, D. M.; Zhang, P.; Guo, Q.; Zang, D. D. et al. Photochemical route for synthesizing atomically dispersed palladium catalysts. Science 2016, 352, 797–800.
Wu, S. L.; Liu, J.; Liang, D. W.; Sun, H. M.; Ye, Y. X.; Tian, Z. F.; Liang, C. H. Photo-excited in situ loading of Pt clusters onto rGO immobilized SnO2 with excellent catalytic performance toward methanol oxidation. Nano Energy 2016, 26, 699–707.
Wu, S. L.; Liu, J.; Tian, Z. F.; Cai, Y. Y.; Ye, Y. X.; Yuan, Q. L.; Liang, C. H. Highly dispersed ultrafine Pt nanoparticles on reduced graphene oxide nanosheets: In situ sacrificial template synthesis and superior electrocatalytic performance for methanol oxidation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 22935–22940.
Jiang, H.-L.; Xu, Q. Catalytic hydrolysis of ammonia borane for chemical hydrogen storage. Catal. Today 2011, 170, 56–63.
Yadav, M.; Xu, Q. Liquid-phase chemical hydrogen storage materials. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 9698–9725.
Li, J.; Zhu, Q.-L.; Xu, Q. Highly active AuCo alloy nanoparticles encapsulated in the pores of metal-organic frameworks for hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 5899–5901.
Aranishi, K.; Jiang, H.-L.; Akita, T.; Haruta, M.; Xu, Q. One-step synthesis of magnetically recyclable Au/Co/Fe triple-layered core–shell nanoparticles as highly efficient catalysts for the hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane. Nano Res. 2011, 4, 1233–1241.
Metin, Ö.; Özkar, S.; Sun, S. H. Monodisperse nickel nanoparticles supported on SiO2 as an effective catalyst for the hydrolysis of ammonia-borane. Nano Res. 2010, 3, 676–684.
Zhou, L. M.; Zhang, T. R.; Tao, Z. L.; Chen, J. Ni nanoparticles supported on carbon as efficient catalysts for the hydrolysis of ammonia borane. Nano Res. 2014, 7, 774–781.
Hummers, W. S.; Offeman, R. E. Preparation of graphitic oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1958, 80, 1339.
Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yu, P.; Ma, Y. W. Stable dispersions of graphene and highly conducting graphene films: A new approach to creating colloids of graphene monolayers. Chem. Commun. 2009, 4527–4529.
Hong, Y.; Wang, J.; Yuan, B.; Liu, Y.; Bian, L.; Jia, M.; Jiang, F. Template free synthesis of ZnO spindles and flowers via hydrothermal route. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 2014, 113, 178–183.
Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, D. C.; Yu, P.; Ma, Y. W. High performance supercapacitors based on reduced graphene oxide in aqueous and ionic liquid electrolytes. Carbon 2011, 49, 573–580.
Tsai, C.-H.; Hung, C.-I.; Yang, C.-F.; Houng, M.-P. Hydrogen peroxide treatment on ZnO substrates to investigate the characteristics of Pt and Pt oxide Schottky contacts. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 257, 610–615.
Aijaz, A.; Karkamkar, A.; Choi, Y. J.; Tsumori, N.; Rö nnebro, E.; Autrey, T.; Shioyama, H.; Xu, Q. Immobilizing highly catalytically active Pt nanoparticles inside the pores of metal–organic framework: A double solvents approach. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 13926–13929.
Chandra, M.; Xu, Q. Room temperature hydrogen generation from aqueous ammonia-borane using noble metal nanoclusters as highly active catalysts. J. Power Sources 2007, 168, 135–142.
Wang, X.; Liu, D. P.; Song, S. Y.; Zhang, H. J. Synthesis of highly active Pt-CeO2 hybrids with tunable secondary nanostructures for the catalytic hydrolysis of ammonia borane. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 10207–10209.
Khalily, M. A.; Eren, H.; Akbayrak, S.; Susapto, H. H.; Biyikli, N.; Özkar, S.; Guler, M. O. Facile synthesis of threedimensional Pt-TiO2 nano-networks: A highly active catalyst for the hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia–borane. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 12257–12261.
Zhu, Q.-L.; Li, J.; Xu, Q. Immobilizing metal nanoparticles to metal–organic frameworks with size and location control for optimizing catalytic performance. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 10210–10213.
Chandra, M.; Xu, Q. A high-performance hydrogen generation system: Transition metal-catalyzed dissociation and hydrolysis of ammonia–borane. J. Power Sources 2006, 156, 190–194.
Yang, X. J.; Cheng, F. Y.; Liang, J.; Tao Z. L.; Chen J. Carbon-supported Ni1–x @Ptx (x = 0.32, 0.43, 0.60, 0.67, and 0.80) core–shell nanoparticles as catalysts for hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of ammonia borane. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 1984–1990.
Chen, W. Y.; Ji, J.; Feng, X.; Duan, X. Z.; Qian, G.; Li, P.; Zhou, X. G.; Chen, D.; Yuan, W. K. Mechanistic insight into size-dependent activity and durability in Pt/CNT catalyzed hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 16736–16739.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Ms. Jun Li for XPS and Dr. Takeyuki Uchida for TEM measurements and AIST and METI for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
12274_2017_1593_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Monodispersed Pt nanoparticles on reduced graphene oxide by a non-noble metal sacrificial approach for hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Yang, X., Kitta, M. et al. Monodispersed Pt nanoparticles on reduced graphene oxide by a non-noble metal sacrificial approach for hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane. Nano Res. 10, 3811–3816 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-017-1593-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-017-1593-4