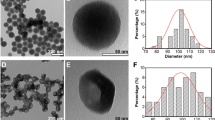
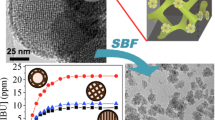
Abstract
Precise control over the morphology, nanostructure, composition, and particle size of molecularly organic–inorganic hybrid mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles (MONs) still remains a major challenge, which severely restricts their broad applications. In this work, an efficient bridged organic group-determined growth strategy has been proposed for the facile synthesis of highly dispersed and uniform MONs with multifarious Janus morphologies, nanostructures, organic–inorganic hybrid compositions, and particle sizes, which can be easily controlled simply by varying the bridged organic groups and the concentration of bis-silylated organosilica precursors used in the synthesis. In addition, the formation mechanism of Janus MONs determined by the bridged organic group has been discussed. Based on the specific structures, compositions, and asymmetric morphologies, all the synthesized Janus MONs with hollow structures (JHMONs) demonstrate excellent performances in nanomedicine as desirable drug carriers with high drug-loading efficiencies/capacities, pH-responsive drug releasing, and enhanced therapeutic efficiencies, as attractive contrast-enhanced contrast agents for ultrasound imaging, and as excellent bilirubin adsorbents with noticeably high adsorption capacities and high blood compatibilities. The developed versatile synthetic strategy and the obtained JHMONs are extremely important in the development and applications of MONs, particularly in the areas of nanoscience and nanotechnology.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lai, N. C.; Lin, C.; Ku, P.; Chang, L. L.; Liao, K. W.; Lin, W. T.; Yang, C. M. Hollow mesoporous Ia3d silica nanospheres with singleunit-cell-thick shell: Spontaneous formation and drug delivery application. Nano Res. 2014, 7, 1439–1448.
Chen, D. Y.; Mei, X.; Ji, G.; Lu, M. H.; Xie, J. P.; Lu, J. M.; Lee, J. Y. Reversible lithium-ion storage in silver-treated nanoscale hollow porous silicon particles. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 2409–2413.
Gao, F.; Botella, P.; Corma, A.; Blesa, J.; Dong, L. Monodispersed mesoporous silica nanoparticles with very large pores for enhanced adsorption and release of DNA. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 1796–1804.
Chen, J. C.; Zhang, R. Y.; Han, L.; Tu, B.; Zhao, D. Y. One-pot synthesis of thermally stable gold@mesoporous silica core–shell nanospheres with catalytic activity. Nano Res. 2013, 6, 871–879.
Pan, L. M.; He, Q. J.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Ma, M.; Zhang, L. L.; Shi, J. L. Nuclear-targeted drug delivery of TAT peptideconjugated monodisperse mesoporous silica nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 5722–5725.
Kim, T.; Momin, E.; Choi, J.; Yuan, K.; Zaidi, H.; Kim, J.; Park, M.; Lee, N.; McMahon, M. T.; Quinones-Hinojosa, A. et al. Mesoporous silica-coated hollow manganese oxide nanoparticles as positive T 1 contrast agents for labeling and MRI tracking of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 2955–2961.
Wang, X.; Chen, H. R.; Chen, Y.; Ma, M.; Zhang, K.; Li, F. Q.; Zheng, Y. Y.; Zeng, D. P.; Wang, Q.; Shi, J. L. Perfluorohexane-encapsulated mesoporous silica nanocapsules as enhancement agents for highly efficient high intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU). Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 785–791.
Luo, G. F.; Chen, W. H.; Jia, H. Z.; Sun, Y. X.; Cheng, H.; Zhuo, R. X.; Zhang, X. Z. An indicator-guided photo-controlled drug delivery system based on mesoporous silica/gold nanocomposites. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 1893–1905.
Chen, Y.; Chu, C.; Zhou, Y. C.; Ru, Y. F.; Chen, H. R.; Chen, F.; He, Q. J.; Zhang, Y. L.; Zhang, L. L.; Shi, J. L. Reversible pore-structure evolution in hollow silica nanocapsules: Large pores for siRNA delivery and nanoparticle collecting. Small 2011, 7, 2935–2944.
Fan, W. P.; Shen, B.; Bu, W. B.; Chen, F.; Zhao, K. L.; Zhang, S. J.; Zhou, L. P.; Peng, W. J.; Xiao, Q. F.; Xing, H. Y. et al. Rattle-structured multifunctional nanotheranostics for synergetic chemo-/radiotherapy and simultaneous magnetic/ luminescent dual-mode imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 6494–6503.
Yang, Y. N.; Yu, M. H.; Song, H.; Wang, Y.; Yu, C. Z. Preparation of fluorescent mesoporous hollow silica-fullerene nanoparticles via selective etching for combined chemotherapy and photodynamic therapy. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 11894–11898.
Terentyuk, G.; Panfilova, E.; Khanadeev, V.; Chumakov, D.; Genina, E.; Bashkatov, A.; Tuchin, V.; Bucharskaya, A.; Maslyakova, G.; Khlebtsov, N. et al. Gold nanorods with a hematoporphyrin-loaded silica shell for dual-modality photodynamic and photothermal treatment of tumors in vivo. Nano Res. 2014, 7, 325–337.
Zhang, K.; Chen, H. R.; Zhou, X. X.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, G. B.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Shi, J. L. Unconventional Pd nanoparticles' growth induced by a competitive effect between temperaturedependent coordination and reduction of grafted amino ligands for Heck reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 1515–1523.
Chen, Y.; Chen, H. R.; Shi, J. L. In vivo bio-safety evaluations and diagnostic/therapeutic applications of chemically designed mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 3144–3176.
Lin, Y.-S.; Haynes, C. L. Impacts of mesoporous silica nanoparticle size, pore ordering, and pore integrity on hemolytic activity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 4834–4842.
Rosenholm, J. M.; Mamaeva, V.; Sahlgren, C.; Lindén, M. Nanoparticles in targeted cancer therapy: Mesoporous silica nanoparticles entering preclinical development stage. Nanomedicine 2012, 7, 111–120.
Zhang, L. X.; Zhu, M.; Guo, L. M.; Li, L.; Shi, J. L. Bilirubin adsorption property of mesoporous silica and amine-grafted mesoporous silica. Nano-Micro Lett. 2009, 1, 14–18.
Zhang, L. X.; Zhang, W. H.; Shi, J. L.; Hua, Z. L.; Li, Y. S.; Yan, J. A New Thioether functionalized organic-inorganic mesoporous composite as a highly selective and capacious Hg2+ adsorbent. Chem. Commun. 2003, 210–211.
Mikhaylov, G.; Mikac, U.; Magaeva, A. A.; Itin, V. I.; Naiden, E. P.; Psakhye, I.; Babes, L.; Reinheckel, T.; Peters, C.; Zeiser, R. et al. Ferri-liposomes as an MRI-visible drug-delivery system for targeting tumours and their microenvironment. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 594–602.
Cabral, H.; Matsumoto, Y.; Mizuno, K.; Chen, Q.; Murakami, M.; Kimura, M.; Terada, Y.; Kano, M. R.; Miyazono, K.; Uesaka, M. et al. Accumulation of sub-100 nm polymeric micelles in poorly permeable tumours depends on size. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 815–823.
Du, X.; Li, X. Y.; Xiong, L.; Zhang, X. J.; Kleitz, F.; Qiao, S. Z. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles with organo-bridged silsesquioxane framework as innovative platforms for bioimaging and therapeutic agent delivery. Biomaterials 2016, 91, 90–127.
Wang, W. D.; Lofgreen, J. E.; Ozin, G. A. Why PMO? Towards functionality and utility of periodic mesoporous organosilicas. Small 2010, 6, 2634–2642.
Modak, A.; Mondal, J.; Bhaumik, A. Pd-grafted periodic mesoporous organosilica: An efficient heterogeneous catalyst for hiyama and sonogashira couplings, and cyanation reactions. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 2840–2855.
Yang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, A. M.; Sun, H.; Li, X. S.; Liu, S. Y.; Zhang, P. F.; Zhang, X. A single Au nanoparticle anchored inside the porous shell of periodic mesoporous organosilica hollow spheres. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 3404–3411.
Rekha, P.; Sharma, V.; Mohanty, P. Synthesis of cyclophosphazene bridged mesoporous organosilicas for CO2 capture and Cr (VI) removal. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2016, 219, 93–102.
Rekha, P.; Muhammad, R.; Mohanty, P. Sonochemical synthesis of cyclophosphazene bridged mesoporous organosilicas and their application in methyl orange, congo red and Cr(VI) removal. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 67690–67699.
Kim, D. J.; Chung, J. S.; Ahn, W. S.; Kang, G. W.; Cheong, W. J. Morphology control of organic–inorganic hybrid mesoporous silica by microwave heating. Chem. Lett. 2004, 33, 422–423.
Rebbin, V.; Schmidt, R.; Fröba, M. Spherical particles of phenylene-bridged periodic mesoporous organosilica for high-performance liquid chromatography. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 5210–5214.
Wu, M. Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L. X.; Li, X. Y.; Cai, X. J.; Du, Y. Y.; Zhang, L. L.; Shi, J. L. A salt-assisted acid etching strategy for hollow mesoporous silica/organosilica for pH-responsive drug and gene co-delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 766–775.
Zhou, Z.; Taylor, R. N. K.; Kullmann, S.; Bao, H. X.; Hartmann, M. Mesoporous organosilicas with large cage-like pores for high efficiency immobilization of enzymes. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 2627–2632.
Chen, Y.; Shi, J. L. Chemistry of mesoporous organosilica in nanotechnology: Molecularly organic–inorganic hybridization into frameworks. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 3235–3272.
Chen, Y.; Xu, P. F.; Chen, H. R.; Li, Y. S.; Bu, W. B.; Shu, Z.; Li, Y. P.; Zhang, J. M.; Zhang, L. X.; Pan, L. M. et al. Colloidal HPMO nanoparticles: Silica-etching chemistry tailoring, topological transformation, and nano-biomedical applications. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 3100–3105.
Li, X. M.; Zhou, L.; Wei, Y.; El-Toni, A. M.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, D. Y. Anisotropic growth-induced synthesis of dualcompartment Janus mesoporous silica nanoparticles for bimodal triggered drugs delivery. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 15086–15092.
Li, X. M.; Zhou, L.; Wei, Y.; El-Toni, A. M.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, D. Y. Anisotropic encapsulation-induced synthesis of asymmetric single-hole mesoporous nanocages. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 5903–5906.
Fang, X. L.; Chen, C.; Liu, Z. H.; Liu, P. X.; Zheng, N. F. A cationic surfactant assisted selective etching strategy to hollow mesoporous silica spheres. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 1632–1639.
Zou, H. B.; Wang, R. W.; Li, X. X.; Wang, X.; Zeng, S. J.; Ding, S.; Li, L.; Zhang, Z. T.; Qiu, S. L. An organosilanedirected growth-induced etching strategy for preparing hollow/yolk–shell mesoporous organosilica nanospheres with perpendicular mesochannels and amphiphilic frameworks. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 12403–12412.
Li, J.; Wei, Y.; Li, W.; Deng, Y. H.; Zhao, D. Y. Magnetic spherical cores partly coated with periodic mesoporous organosilica single crystals. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 1647–1651.
Suteewong, T.; Sai, H.; Hovden, R.; Muller, D.; Bradbury, M. S.; Gruner, S. M.; Wiesner, U. Multicompartment mesoporous silica nanoparticles with branched shapes: An epitaxial growth mechanism. Science 2013, 340, 337–341.
Croissant, J.; Cattoën, X.; Wong Chi Man, M.; Dieudonné, P.; Charnay, C.; Raehm, L.; Durand, J.-O. One-pot construction of multipodal hybrid periodic mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles with crystal-like architectures. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 145–149.
Bao, X. Y.; Li, X.; Zhao, X. S. Synthesis of large-pore methylene-bridged periodic mesoporous organosilicas and its implications. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 2656–2661.
Brinker, C. J. Hydrolysis and condensation of silicates: Effects on structure. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1988, 100, 31–50.
Brinker, C. J.; Scherer, G. W. Sol-Gel Science: The Physics and Chemistry of Sol-Gel Processing; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1990.
Ujiie, H.; Shimojima, A.; Kuroda, K. Synthesis of colloidal Janus nanoparticles by asymmetric capping of mesoporous silica with phenylsilsesquioxane. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 3211–3214.
Chen, Y.; Meng, Q. S.; Wu, M. Y.; Wang, S. G.; Xu, P. F.; Chen, H. R.; Li, Y. P.; Zhang, L. X.; Wang, L. Z.; Shi, J. L. Hollow mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles: A generic intelligent framework-hybridization approach for biomedicine. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 16326–16334.
Tao, G. J.; Zhang, L. X.; Hua, Z. L.; Chen, Y.; Guo, L. M.; Zhang, J. M.; Shu, Z.; Gao, J. H.; Chen, H. R.; Wu, W. et al. Highly efficient adsorbents based on hierarchically macro/mesoporous carbon monoliths with strong hydrophobicity. Carbon 2014, 66, 547–559.
Gerweck, L. E.; Seetharaman, K. Cellular pH gradient in tumor versus normal tissue: Potential exploitation for the treatment of cancer. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 1194–1198.
Wei, H. L.; Xu, L.; Ren, J.; Jia, L. Y. Adsorption of bilirubin to magnetic multi-walled carbon nanotubes as a potential application in bound solute dialysis. Colloid. Surf. A 2012, 405, 38–44.
Asano, T.; Tsuru, K.; Hayakawa, S.; Osaka, A. Bilirubin adsorption property of sol–gel-derived titania particles for blood purification therapy. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 1067–1072.
Guo, L. M.; Zhang, L. X.; Zhang, J. M.; Zhou, J.; He, Q. J.; Zeng, S. Z.; Cui, X. Z.; Shi, J. L. Hollow mesoporous carbon spheres-an excellent bilirubin adsorbent. Chem. Commun. 2009, 6071–6073.
Chen, Y.; Yin, Q.; Ji, X. F.; Zhang, S. J.; Chen, H. R.; Zheng, Y. Y.; Sun, Y.; Qu, H. Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y. P. et al. Manganese oxide-based multifunctionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles for pH-responsive MRI, ultrasonography and circumvention of MDR in cancer cells. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 7126–7137.
Chen, Y.; Gao, Y.; Chen, H. R.; Zeng, D. P.; Li, Y. P.; Zheng, Y. Y.; Li, F. Q.; Ji, X. F.; Wang, X.; Chen, F. et al. Engineering inorganic nanoemulsions/nanoliposomes by fluoride-silica chemistry for efficient delivery/co-delivery of hydrophobic agents. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 1586–1597.
Ma, Z. F.; Bai, J.; Wang, Y. C.; Jiang, X. E. Impact of shape and pore size of mesoporous silica nanoparticles on serum protein adsorption and RBCs hemolysis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 2431–2438.
Teng, Z. G.; Wang, S. J.; Su, X. D.; Chen, G. T.; Liu, Y.; Luo, Z. M.; Luo, W.; Tang, Y. X.; Ju, H. X.; Zhao, D. Y. et al. Facile synthesis of yolk–shell structured inorganic–organic hybrid spheres with ordered radial mesochannels. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 3741–3747.
Acknowledgements
We greatly acknowledge financial support from the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2016YFA0203700), Shanghai Natural Science Foundation (No. 16ZR1440300), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 61275208, 51302293, and 51672303), Shanghai Rising-Star Program (No. 14QA1404100), Youth Innovation Promotion Association of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. 2013169) and Development Fund for Shanghai Talents (2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
12274_2017_1592_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Generic synthesis and versatile applications of molecularly organic–inorganic hybrid mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles with asymmetric Janus topologies and structures
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tao, G., Bai, Z., Chen, Y. et al. Generic synthesis and versatile applications of molecularly organic–inorganic hybrid mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles with asymmetric Janus topologies and structures. Nano Res. 10, 3790–3810 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-017-1592-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-017-1592-5