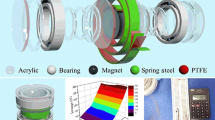
Abstract
Integrated multilayered triboelectric nanogenerators (TENGs) are an efficient approach to solve the insufficient energy problem caused by a single-layered TENG for achieving high output power density. However, most integrated multilayered TENGs have a relatively large volume. Here, a double-induced-mode integrated triboelectric nanogenerator (DI-TENG) based on spring steel plates is presented as a cost-effective, simple, and high-performance device for ambient vibration energy harvesting. The unique stackable rhombus structure, in which spring steel plates act both as skeletons and as electrodes, can enhance the output performance and maximize space utilization. The DI-TENG with five repeated units in a volume of 12 cm × 5 cm × 0.4 cm can generate a short-circuit current of 51 μA and can transfer charges of 1.25 μC in a half period. The contrast experiment is conducted systematically and the results have proved that the DI-TENG has a great advantage over the single-induced-mode TENG (SI-TENG) with only one side of a friction layer on its electrode. Besides, the DI-TENG can easily power a commercial calculator and can be used as a door switch sensor.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Evan, D. The internet of things: How the next evolution of the internet is changing everything. http://www.cisco.com/c/dam/ en_us/about/ac79/docs/innov/IoT_IBSG_0411FINAL.pdf (accessed Jun 13, 2016).
Wang, Z. L.; Song, J. H. Piezoelectric nanogenerators based on zinc oxide nanowire arrays. Science 2006, 312, 242–246.
Qin, Y.; Wang, X. D.; Wang, Z. L. Microfibre-nanowire hybrid structure for energy scavenging. Nature 2008, 451, 809–813.
Wu, N.; Cheng, X. F.; Zhong, Q. Z.; Zhong, J. W.; Li, W. B.; Wang, B.; Hu, B.; Zhou, J. Cellular polypropylene piezoelectret for human body energy harvesting and health monitoring. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 4788–4794.
Beeby, S. P.; Tudor, M. J.; White, N. M. Energy harvesting vibration sources for microsystems applications. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2006, 17, R175–R195.
Li, W. B.; Wu, N.; Zhong, J. W.; Zhong, Q. Z.; Zhao, S.; Wang, B.; Cheng, X. F.; Li, S. L.; Liu, K.; Hu, B. et al. Theoretical study of cellular piezoelectret generators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 1964–1974.
Wang, L.; Yuan, F. G. Vibration energy harvesting by magnetostrictive material. Smart Mater. Struct. 2008, 17, 045009.
Lu, S. N.; Liao, Q. L.; Qi, J. J.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y. C.; Liang, Q. J.; Zhang, G. J.; Zhang, Y. The enhanced performance of piezoelectric nanogenerator via suppressing screening effect with Au particles/ZnO nanoarrays Schottky junction. Nano Res. 2016, 9, 372–379.
Fan, F. R.; Tian, Z. Q.; Wang, Z. L. Flexible triboelectric generator! Nano Energy 2012, 1, 328–334.
Wang, Z. L.; Chen, J.; Lin, L. Progress in triboelectric nanogenerators as a new energy technology and self-powered sensors. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 2250–2282.
Liu, Y.; Niu, S. M.; Wang, Z. L. Theory of tribotronics. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2015, 1, 1500124.
Cui, N. Y.; Liu, J. M.; Gu, L.; Bai, S.; Chen, X. B.; Qin, Y. Wearable triboelectric generator for powering the portable electronic devices. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 18225–18230.
Guo, H. Y.; He, X. M.; Zhong, J. W.; Zhong, Q. Z.; Leng, Q.; Hu, C. G.; Chen, J.; Tian, L.; Xi, Y.; Zhou, J. A nanogenerator for harvesting airflow energy and light energy. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 2079–2087.
Xie, Y. N.; Wang, S. H.; Niu, S. M.; Lin, L.; Jing, Q. S.; Yang, J.; Wu, Z. Y.; Wang, Z. L. Grating-structured freestanding triboelectric-layer nanogenerator for harvesting mechanical energy at 85% total conversion efficiency. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 6599–6607.
Tang, W.; Jiang, T.; Fan, F. R.; Yu, A. F.; Zhang, C.; Cao, X.; Wang, Z. L. Liquid-metal electrode for high-performance triboelectric nanogenerator at an instantaneous energy conversion efficiency of 70.6%. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 3718–3725.
Zhu, G.; Zhou, Y. S.; Bai, P.; Meng, X. S.; Jing, Q. S.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z. L. A shape-adaptive thin-film-based approach for 50% high-efficiency energy generation through micro-grating sliding electrification. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 3788–3796.
Weiss, P. S. A conversation with prof. Zhong Lin Wang, energy harvester. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 2221–2226.
Zhu, G.; Pan, C. F.; Guo, W. X.; Chen, C.-Y.; Zhou, Y. S.; Yu, R. M.; Wang, Z. L. Triboelectric-generator-driven pulse electrodeposition for micropatterning. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 4960–4965.
Zhong, Q. Z.; Zhong, J. W.; Cheng, X. F.; Yao, X.; Wang, B.; Li, W. B.; Wu, N.; Liu, K.; Hu, B.; Zhou, J. Paper-based active tactile sensor array. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 7130–7136.
Chen, J.; Guo, H. Y.; He, X. M.; Liu, G. L.; Xi, Y.; Shi, H. F.; Hu, C. G. Enhancing performance of triboelectric nanogenerator by filling high dielectric nanoparticles into sponge PDMS film. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 736–744.
Zhong, J. W.; Zhu, H. L.; Zhong, Q. Z.; Dai, J. Q.; Li, W. B.; Jang, S.-H.; Yao, Y. G.; Henderson, D.; Hu, Q. Y.; Hu, L. B. et al. Self-powered Human-interactive transparent nanopaper systems. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 7399–7406.
Zhong, J. W.; Zhong, Q. Z.; Hu, Q. Y.; Wu, N.; Li, W. B.; Wang, B.; Hu, B.; Zhou, J. Stretchable self-powered fiberbased strain sensor. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 1798–1803.
Liu, G. L.; Xu, W. N.; Xia, X. N.; Shi, H. F.; Hu, C. G. Newton’s cradle motion-like triboelectric nanogenerator to enhance energy recycle efficiency by utilizing elastic deformation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 21133–21139.
Zhu, G.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Bai, P.; Zhou, Y. S.; Jing, Q. S.; Pan, C. F.; Wang, Z. L. Linear-grating triboelectric generator based on sliding electrification. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 2282–2289.
Wang, S. H.; Lin, L.; Xie, Y. N.; Jing, Q. S.; Niu, S. M.; Wang, Z. L. Sliding-triboelectric nanogenerators based on in-plane charge-separation mechanism. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 2226–2233.
Zhang, C.; Zhou, T.; Tang, W.; Han, C. B.; Zhang, L. M.; Wang, Z. L. Rotating-disk-based direct-current triboelectric nanogenerator. Adv. Energy Mater. 2014, 4, 1301798.
Yang, Y.; Zhang, H. L.; Chen, J.; Jing, Q. S.; Zhou, Y. S.; Wen, X. N.; Wang, Z. L. Single-electrode-based sliding triboelectric nanogenerator for self-powered displacement vector sensor system. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 7342–7351.
Niu, S. M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S. H.; Lin, L.; Zhou, Y. S.; Hu, Y. F.; Wang, Z. L. Theoretical investigation and structural optimization of single-electrode triboelectric nanogenerators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 3332–3340.
Meng, B.; Tang, W.; Zhang, X. S.; Han, M. D.; Liu, W.; Zhang, H. X. Self-powered flexible printed circuit board with integrated triboelectric generator. Nano Energy 2013, 2, 1101–1106.
Wang, S. H.; Xie, Y. N.; Niu, S. M.; Lin, L.; Wang, Z. L. Freestanding triboelectric-layer-based nanogenerators for harvesting energy from a moving object or human motion in contact and non-contact modes. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 2818–2824.
Guo, H. Y.; Leng, Q.; He, X. M.; Wang, M. J.; Chen, J.; Hu, C. G.; Xi, Y. A triboelectric generator based on checker-like interdigital electrodes with a sandwiched pet thin film for harvesting sliding energy in all directions. Adv. Energy Mater. 2015, 5, 1400790.
Han, C. B.; Zhang, C.; Tang, W.; Li, X. H.; Wang, Z. L. High power triboelectric nanogenerator based on printed circuit board (PCB) technology. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 722–730.
Zhu, G.; Bai, P.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z. L. Power-generating shoe insole based on triboelectric nanogenerators for self-powered consumer electronics. Nano Energy 2013, 2, 688–692.
Hou, T.-C.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H. L.; Chen, J.; Chen, L.-J.; Wang, Z. L. Triboelectric nanogenerator built inside shoe insole for harvesting walking energy. Nano Energy 2013, 2, 856–862.
Huang, T.; Wang, C.; Yu, H.; Wang, H. Z.; Zhang, Q. H.; Zhu, M. F. Human walking-driven wearable all-fiber triboelectric nanogenerator containing electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride piezoelectric nanofibers. Nano Energy 2015, 14, 226–235.
Zheng, Q.; Shi, B. J.; Fan, F. R.; Wang, X. X.; Yan, L.; Yuan, W. W.; Wang, S. H.; Liu, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z. L. In vivo powering of pacemaker by breathing-driven implanted triboelectric nanogenerator. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 5851–5856.
Lin, L.; Wang, S. H.; Xie, Y. N.; Jing, Q. S.; Niu, S. M.; Hu, Y. F.; Wang, Z. L. Segmentally structured disk triboelectric nanogenerator for harvesting rotational mechanical energy. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 2916–2923.
Zhu, G.; Chen, J.; Zhang, T. J.; Jing, Q. S.; Wang, Z. L. Radial-arrayed rotary electrification for high performance triboelectric generator. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3426.
Liu, G. L.; Liu, R. P.; Guo, H. Y.; Xi, Y.; Wei, D. P.; Hu, C. G. A novel triboelectric generator based on the combination of a waterwheel-like electrode with a spring steel plate for efficient harvesting of low-velocity rotational motion energy. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2016, 2, 1500448.
Chen, J.; Yang, J.; Li, Z. L.; Fan, X.; Zi, Y. L.; Jing, Q. S.; Guo, H. Y.; Wen, Z.; Pradel, K. C.; Niu, S. M. et al. Networks of triboelectric nanogenerators for harvesting water wave energy: A potential approach toward blue energy. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 3324–3331.
Choi, D.; Lee, S.; Park, S. M.; Cho, H.; Hwang, W.; Kim, D. S. Energy harvesting model of moving water inside a tubular system and its application of a stick-type compact triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 2481–2491.
Bai, P.; Zhu, G.; Lin, Z.-H.; Jing, Q. S.; Chen, J.; Zhang, G.; Ma, J. S.; Wang, Z. L. Integrated multilayered triboelectric nanogenerator for harvesting biomechanical energy from human motions. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 3713–3719.
Yang, W. Q.; Chen, J.; Jing, Q. S.; Yang, J.; Wen, X. N.; Su, Y. J.; Zhu, G.; Bai, P.; Wang, Z. L. 3D stack integrated triboelectric nanogenerator for harvesting vibration energy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 4090–4096.
Li, X. H.; Han, C. B.; Zhang, L. M.; Wang, Z. L. Cylindrical spiral triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 3197–3204.
Yang, P.-K.; Lin, Z.-H.; Pradel, K. C.; Lin, L.; Li, X. H.; Wen, X. N.; He, J.-H.; Wang, Z. L. Paper-based origami triboelectric nanogenerators and self-powered pressure sensors. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 901–907.
Wang, J.; Wen, Z.; Zi, Y. L.; Zhou, P. F.; Lin, J.; Guo, H. Y.; Xu, Y. L.; Wang, Z. L. All-plastic-materials based self-charging power system composed of triboelectric nanogenerators and supercapacitors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 1070–1076.
Zhang, L. M.; Xue, F.; Du, W. M.; Han, C. B.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z. L. Transparent paper-based triboelectric nanogenerator as a page mark and anti-theft sensor. Nano Res. 2014, 7, 1215–1223.
Xie, Y. N.; Wang, S. H.; Niu, S. M.; Lin, L.; Jing, Q. S.; Su, Y. J.; Wu, Z. Y.; Wang, Z. L. Multi-layered disk triboelectric nanogenerator for harvesting hydropower. Nano Energy 2014, 6, 129–136.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, G., Guo, H., Chen, L. et al. Double-induced-mode integrated triboelectric nanogenerator based on spring steel to maximize space utilization. Nano Res. 9, 3355–3363 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-016-1213-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-016-1213-8