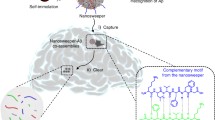
Abstract
Proteolytic degradation of amyloid-β (Aβ) aggregates and clearance of Aβ-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) have received significant attention for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). However, it is difficult, and often unfeasible, to directly upregulate or transport intracellular native enzymes. More importantly, penetration of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) has presented a major impediment. Herein, we report on the rational design of a polyoxometalatebased nanozyme with both protease-like activity for depleting Aβ aggregates, and superoxide dismutase (SOD)-like activity for scavenging Aβ-mediated ROS. Furthermore, this nanozyme acts as a metal chelator to remove Cu from Cu-induced Aβ oligomers. More intriguingly, the nanozyme can cross the BBB and exhibits low toxicity. This work provides new insights into the design and synthesis of inorganic nanozymes as multifunctional therapeutic agents in the treatment of AD.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haass, C.; Selkoe, D. J. Soluble protein oligomers in neurodegeneration: Lessons from the Alzheimer’s amyloid β-peptide. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 101–112.
Götz, J.; Ittner, L. M. Animal models of Alzheimer’s disease and frontotemporal dementia. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 9, 532–544.
Zhang, M.; Mao, X. B.; Yu, Y.; Wang, C. X.; Yang, Y. L.; Wang. C. Nanomaterials for reducing amyloid cytotoxicity. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 3780–3801.
Qing, G. Y.; Zhao, S. L.; Xiong, Y. T.; Lv, Z. Y.; Jiang, F. L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, M. X.; Sun. T. L. Chiral effect at protein/graphene interface: A bioinspired perspective to understand amyloid formation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 10736–10742.
Edrey, Y. H.; Oddo, S.; Cornelius, C.; Caccamo, A.; Calabrese, V.; Buffenstein, R. Oxidative damage and amyloid-β metabolism in brain regions of the longest-lived rodents. J. Neurosci. Res. 2014, 92, 195–205.
Choi, J. S.; Braymer, J. J.; Nang, R. P. R.; Ramamoorthy, A.; Lim, M. H. Design of small molecules that target metal-Aβ species and regulate metal-induced Aβ aggregation and neurotoxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 21990–21995.
Geng, J.; Li, M.; Ren, J. S.; Wang, E. B.; Qu, X. G. Polyoxometalates as inhibitors of the aggregation of amyloid β peptides associated with Alzheimer's disease. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 4184–4188.
Huang, F.; Wang, J. Z.; Qu, A. T.; Shen, L. L.; Liu, J. J.; Liu, J. F.; Zhang, Z. K.; An, Y. L.; Shi, L. Q. Maintenance of amyloid β peptide homeostasis by artificial chaperones based on mixed-shell polymeric micelles. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 8985–8990.
Lee, T. Y.; Suh, J. Target-selective peptide-cleaving catalysts as a new paradigm in drug design. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1949–1957.
Grasso, G.; Giuffrid, M. L.; Rizzarelli, E. Metallostasis and amyloid β-degrading enzymes. Metallomics 2012, 4, 937–949.
Geng, J.; Li, M.; Wu, L.; Ren, J. S.; Qu, X. G. Liberation of copper from amyloid plaques: Making a risk factor useful for Alzheimer’s disease treatment. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 9146–9155.
Wei, H.; Wang, E. K. Nanomaterials with enzyme-like characteristics (nanozymes): Next-generation artificial enzymes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6060–6093.
Faller, P.; Hureau, C.; La Penna, G. Metal ions and intrinsically disordered proteins and peptides: From Cu/Zn amyloid-β to general principles. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 2252–2259.
Cabaleiro-Lago, C.; Quinlan-Pluck, F.; Lynch, I.; Lindman, S.; Minogue, A. M.; Thulin, E.; Walsh, D. M.; Dawson, K. A.; Linse, S. Inhibition of amyloid β protein fibrillation by polymeric nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 15437–15443.
Yoo, S.; Yang, M.; Brender, J. R.; Subramanian, V.; Sun, K.; Joo, N. E.; Jeong, S. H.; Ramamoorthy, A.; Kotov, N. A. Inhibition of amyloid peptide fibrillation by inorganic nanoparticles: Functional similarities with proteins. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 5110–5115.
Hedstrom, L. Serine protease mechanism and specificity. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 4501–4523.
Gao, N.; Sun, H. J.; Dong, K.; Ren, J. S.; Duan, T. C.; Xu, C.; Qu, X. G. Transition-metal-substituted polyoxometalate derivatives as functional anti-amyloid agents for Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3422.
Timári, S.; Cerea, R.; Várnagy, K. Characterization of CuZnSOD model complexes from a redox point of view: Redox properties of copper(II) complexes of imidazole containing ligands. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2011, 105, 1009–1017.
Macdonell, A.; Johnson, N. A. B.; Surman, A. J.; Cronin, L. Configurable nanosized metal oxide oligomers via precise “click” coupling control of hybrid polyoxometalates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 5662–5665.
Xing, X. L.; Liu, R. J.; Yu, X. L.; Zhang, G. J.; Cao, H. B.; Yao, J. N.; Ren, B. Z.; Jiang, Z. X.; Zhao, H. Self-assembly of CdS quantum dots with polyoxometalate encapsulated gold nanoparticles: Enhanced photocatalytic activities. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 1488–1494.
Wang, Y. F.; Neyman, A.; Arkhangelsky, E.; Gitis, V.; Meshi, L.; Weinstock, I. A. Self-Assembly and structure of directly imaged inorganic-anion monolayers on a gold nanoparticle. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 17412–17422.
Hinterwirth, H.; Kappe, S.; Waitz, T.; Prohaska, T.; Lindner, W.; Lämmerhofer, M. Quantifying thiol ligand density of self-assembled monolayers on gold nanoparticles by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 1129–1136.
Ojea-Jiménez, I.; García-Fernández, L.; Lorenzo, J.; Puntes, V. F. Facile preparation of cationic gold nanoparticlebioconjugates for cell penetration and nuclear targeting. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 7692–7702.
Keita, B.; Biboum, R. N.; Mbomekallé, I. M.; Floquet, S.; Simonnet-Jégat, C.; Cadot, E.; Miserque, F.; Berthet, P.; Nadjo, L. One-step synthesis and stabilization of gold nanoparticles in water with the simple oxothiometalate Na2[Mo3(µ3-S)(µ-S)3(Hnta)3]. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 3196–3199.
Gao, L. Z.; Zhuang, J.; Nie, L.; Zhang, J. B.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, N.; Wang, T. H.; Feng, J.; Yang, D. L.; Perrett, S. et al. Intrinsic peroxidase-like activity of ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 577–583.
Gao, N.; Sun, H. J.; Dong, K.; Ren, J. S.; Qu, X. G. Goldnanoparticle- based multifunctional amyloid-β inhibitor against Alzheimer’s disease. Chem.—Eur. J. 2015, 21, 829–835.
Symes, M. D.; Cronin, L. Decoupling hydrogen and oxygen evolution during electrolytic water splitting using an electroncoupled- proton buffer. Nat. Chem. 2013, 5, 403–409.
Perera, V. S.; Liu, H. J.; Wang, Z. Q.; Huang, S. D. Cellpermeable Au@ZnMoS4 core–shell nanoparticles: Toward a novel cellular copper detoxifying drug for Wilson’s disease. Chem. Mater. 2013, 25, 4703–4709.
Chen, Z. W.; Li, Z. H.; Wang, J. S.; Ju, E. G.; Zhou, L.; Ren, J. S.; Qu, X. G. A multi-synergistic platform for sequential irradiation-activated high-performance apoptotic cancer therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 522–529.
Lin, Z. M.; Monteiro-Riviere, N. A.; Riviere, J. E. Pharmacokinetics of metallic nanoparticles. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 7, 189–217.
Ye, D.; Raghnaill, M. N.; Bramini, M.; Mahon, E.; Åberg, C.; Salvati, A.; Dawson, K. A. Nanoparticle accumulation and transcytosis in brain endothelial cell layers. Nanoscale, 2013, 5, 11153–11165.
Soto, C.; Sigurdsson, E. M.; Morelli, L.; Kumar, R. A.; Castano, E. M.; Frangione, B. β-sheet breaker peptides inhibit fibrillogenesis in a rat brain model of amyloidosis: Implications for Alzheimer’s therapy. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 822–826.
Xiong, L. Q.; Yang, T. S.; Yang, Y.; Xu, C. J.; Li, F. Y. Long-term in vivo biodistribution imaging and toxicity of polyacrylic acid-coated upconversion nanophosphors. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 7078–7085.
Yu, H. J.; Ren, J. S.; Qu, X. G. Time-dependent DNA condensation induced by amyloid β-peptide. Biophys. J. 2007, 92, 185–191.
Geng, J.; Zhao, C.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Alzheimer’s disease amyloid beta converting left-handed Z-DNA back to righthanded B-form. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 7187–7189.
Geng, J.; Qu, K. G.; Ren, J. S.; Qu, X. G. Rapid and efficient screening of Alzheimer’s disease β-amyloid inhibitors using label-free gold nanoparticles. Mol. BioSyst. 2010, 6, 2389–2391.
Zhang, G. J.; Keita, B.; Biboum, R. N.; Miserque, F.; Berthet, P.; Dolbecq, A.; Mialane, P.; Catalae, L.; Nadjo, L. Synthesis of various crystalline gold nanostructures in water: The polyoxometalate β-[H4PMo12O40]3– as the reducing and stabilizing agent. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 8639–8644.
Yiu, H. H. P.; Wright, P. A.; Botting, N. P. Enzyme immobilisation using SBA-15 mesoporous molecular sieves with functionalised surfaces. J. Mol. Catal. B: Enzym. 2001, 15, 81–92.
Adachi, T.; Marklund, S. L. Interactions between human extracellular superoxide dismutase C and sulfated polysaccharides. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 8537–8541.
Frisch, M. J.; Trucks, G. W.; Schlegel, H. B.; Scuseria, G. E.; Robb, M. A.; Cheeseman, J. R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G. A. et al. Gaussian 09, Revision B. 01; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, 2009.
Runge, E.; Gross, E. K. U. Density-functional theory for time-dependent systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1984, 52, 997–1000.
Becker, A. D. A new mixing of hartree-fock and local densityfunctional theories. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 1372–1377.
Lee, C.; Yang, W. T.; Parr, R. G. Development of the Colle- Salvetti correlation-energy formula into a functional of the electron density. Phys. Rev. B 1988, 37, 785–789.
Hay, P. J.; Wadt, W. R. Ab initio effective core potentials for molecular calculations. Potentials for the transition metal atoms Sc to Hg. J. Chem. Phys. 1985, 82, 270–283.
Cossi, M.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Tomasi, J. Ab initio study of ionic solutions by a polarizable continuum dielectric model. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1998, 286, 253–260.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, N., Dong, K., Zhao, A. et al. Polyoxometalate-based nanozyme: Design of a multifunctional enzyme for multi-faceted treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Nano Res. 9, 1079–1090 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-016-1000-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-016-1000-6