Abstract
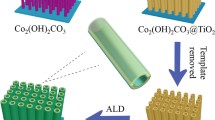
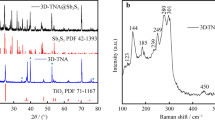
This paper reports a simple yet efficient method for the synthesis of hierarchical TiO2-B nanowire@α-Fe2O3 nanothorn core-branch arrays based on a stepwise hydrothermal approach. The as-fabricated hybrid arrays show impressive performance as a high-capacity anode for lithium-ion batteries. The key design in this study is a core-branch hybrid architecture, which not only provides large surface active sites for lithium ion insertion/extraction, but also enables fast charge transport owing to the reduced diffusion paths for both electrons and lithium ions. The peculiar combination of attributes of TiO2 (good structural stability) and Fe2O3 (large specific capacity) provides the hybrid array electrodes with several desirable electrochemical features: large reversible capacity (∼800 mA·h·g−1 for specific mass capacity and ∼750 μA·h·cm−2 for specific areal capacity), good cycling stability, and high rate capability. The impressive electrochemical performance, together with the facile synthesis procedure, may provide an efficient platform to integrate the TiO2 nanowire@Fe2O3 nanothorn core-branch arrays as a three-dimensional thin film electrode for lithium-ion microbatteries.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dunn, B.; Long, J. W.; Rolison, D. R. Rethinking multifunction in three dimensions for miniaturizing electrical energy storage. Electrochem. Soc. Inter. 2008, 17, 49–53.
Zhou, Y. N.; Xue, M. Z.; Fu, Z. W. Nanostructured thin film electrodes for lithium storage and all-solid-state thin-film lithium batteries. J. Power Sources 2013, 234, 310–332.
Kitaura, H.; Hayashi, A.; Ohtomo, T.; Hama, S.; Tatsumisago, M. Fabrication of electrode-electrolyte interfaces in all-solid-state rechargeable lithium batteries by using a supercooled liquid state of the glassy electrolytes. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 118–124.
Zhu, J.; Feng, J.; Lu, L.; Zeng, K. In situ study of topography, phase and volume changes of titanium dioxide anode in all-solid-state thin film lithium-ion battery by biased scanning probe microscopy. J. Power Sources 2012, 197, 224–230.
Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, K.; Hosono, E.; Zhou, H. Design and synthesis of a novel nanothorn VO2(B) hollow microsphere and their application in lithium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 2835–2840.
Pan, J. H.; Han, G.; Zhou, R.; Zhao, X. S. Hierarchical n-doped TiO2 hollow microspheres consisting of nanothorns with exposed anatase {101} facets. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 6942–6944.
Xu, W.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, N.; Niu, B.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, H. Nanoporous anatase TiO2/single-wall carbon nanohorns composite as superior anode for lithium ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2013, 232, 193–198.
Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; Ding, Y.; Guan, L. Single-walled carbon nanohorns coated with Fe2O3 as a superior anode material for lithium ion batteries. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 7416–7418.
Oudenhoven, J. F. M.; Baggetto, L.; Notten, P. H. L. All-solid-state lithium-ion microbatteries: A review of various three-dimensional concepts. Adv. Energy Mater. 2011, 1, 10–33.
Notten, P. H. L.; Roozeboom, F.; Niessen, R. A. H.; Baggetto, L. 3-D integrated all-solid-state rechargeable batteries. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 4564–4567.
Etacheri, V.; Marom, R.; Elazari, R.; Salitra, G.; Aurbach, D. Challenges in the development of advanced Li-ion batteries: A review. Energy Environ Sci. 2011, 4, 3243–3262.
Lin, Y. M.; Nagarale, R. K.; Klavetter, K. C.; Heller, A.; Mullins, C. B. SnO2 and TiO2 supported SnO2 lithium battery anodes with improved electrochemical performance. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 11134–11139.
Ortiz, G. F.; Hanzu, I.; Lavela, P.; Tirado, J. L.; Knauth, P.; Djenizian, T. A novel architectured negative electrode based on titania nanotube and iron oxide nanowire composites for li-ion microbatteries. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 4041–4046.
Ji, L.; Lin, Z.; Alcoutlabi, M.; Zhang, X. Recent developments in nanostructured anode materials for rechargeable lithiumion batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 2682–2699.
Cheng, F.; Liang, J.; Tao, Z.; Chen, J. Functional materials for rechargeable batteries. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 1695–1715.
Luo, W.; Hu, X.; Sun, Y.; Huang, Y. Surface modification of electrospun TiO2 nanofibers via layer-by-layer self-assembly for high-performance lithium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 4910–4915.
Ni, J.; Yang, L.; Wang, H.; Gao, L. A high-performance hybrid supercapacitor with Li4Ti5O12-C nanocomposite prepared by in situ and ex situ carbon modification. J. Solid State Electrchem. 2012, 16, 2791–2796.
Tang, Y.; Tan, X.; Hou, G.; Cao, H.; Zheng, G. Synthesis of dense nanocavities inside TiO2 nanowire array and its electrochemical properties as a three-dimensional anode material for Li-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 78, 154–159.
Guo, J.; Liu, J. Topotactic conversion-derived Li4Ti5O12-rutile TiO2 hybrid nanowire array for high-performance lithium ion full cells. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 12950–12957.
Lv, M.; Zheng, D.; Ye, M.; Xiao, J.; Guo, W.; Lai, Y.; Sun, L.; Lin, C.; Zuo, J. Optimized porous rutile TiO2 nanorod arrays for enhancing the efficiency of dye-sensitized solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 1615–1622.
Wei, W.; Oltean, G.; Tai, C.-W.; Edström, K.; Björefors, F.; Nyholm, L. High energy and power density TiO2 nanotube electrodes for 3D lithium ion microbatteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 8160–8169.
Wang, H.; Ma, D.; Huang, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, X. General and controllable synthesis strategy of metal oxide/TiO2 hierarchical heterostructures with improved lithium-ion battery performance. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 701.
Wang, Z.; Lou, X. W. TiO2 nanocages: Fast synthesis, interior functionalization and improved lithium storage properties. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 4124–4129.
Zhang, X.; Chen, H.; Xie, Y.; Guo, J. Ultralong life lithiumion battery anode with superior high-rate capability and excellent cyclic stability from mesoporous Fe2O3@ TiO2 core-shell nanorods. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 3912–3918.
Zhu, G. N.; Wang, Y. G.; Xia, Y. Y. Ti-based compounds as anode materials for lithium ion batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 6652–6667.
Yang, M. C.; Lee, Y. Y.; Xu, B.; Powers, K.; Meng, Y. S. TiO2 flakes as anode materials for lithium ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2012, 207, 166–172.
Gu, X.; Chen, L.; Liu, S.; Xu, H.; Yang, J.; Qian, Y. Hierarchical core-shell α-Fe2O3@C nanotubes as a high-rate and long-life anode for advanced lithium ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 3439–3444.
Lou, X. W.; Archer, L. A.; Yang, Z. Hollow micro-/nanostructures: Synthesis and applications. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 3987–4019.
Xu, L. Q. D. J.; Li, P.; Qian, Y. T. In situ synthesis, magnetic property, and formation mechanism of Fe3O4 particles encapsulated in 1D bamboo-shaped carbon microtubes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 3871–3875.
Wang, Z.; Luan, D.; Madhavi, S.; Hu, Y.; Lou, X. W. Assembling carbon-coated α-Fe2O3 hollow nanohorns on the CNT backbone for superior lithium storage capability. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 5252–5256.
Liu, N.; Shen, J.; Liu, D. A Fe2O3 nanoparticle/carbon aerogel composite for use as an anode material for lithium ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 97, 271–277.
Luo, Y.; Luo, J.; Jiang, J.; Zhou, W.; Yang, H.; Qi, X.; Zhang, H.; Fan, H. J.; Yu, D. Y. W.; Li, C. M.; et al. Seed-assisted synthesis of highly ordered TiO2@α-Fe2O3 core/shell arrays on carbon textiles for lithium-ion battery applications. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 6559–6566.
Yu, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wu, H. B.; Lou, X. W. TiO2 nanotube arrays grafted with Fe2O3 hollow nanorods as integrated electrodes for lithium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 122–127.
Luo, J.; Xia, X.; Luo, Y.; Guan, C.; Liu, J.; Qi, X.; Ng, C. F.; Yu, T.; Zhang, H.; Fan, H. J. Rationally designed hierarchical TiO2@Fe2O3 hollow nanostructures for improved lithium ion storage. Adv. Energy Mater. 2013, 3, 737–743.
Dylla, A. G. H.; Henkelman, G.; Stevenson, K. J. Lithium insertion in nanostructured TiO2 (B) architectures. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 1104–1112.
Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Yu, C.; Wu, H. B.; Wang, G.; Dong, Q.; Qiu, J.; Eychmuller, A.; David Lou, X. W. A flexible TiO2 (B)-based battery electrode with superior power rate and ultralong cycle life. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 3462–3467.
Ren, Y.; Liu, Z.; Pourpoint, F.; Armstrong, A. R.; Grey, C. P.; Bruce, P. G. Nanoparticulate TiO2(B): An anode for lithium-ion batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 2164–2167.
Saito, M.; Nakano, Y.; Takagi, M.; Honda, N.; Tasaka, A.; Inaba, M. Improvement of tap density of TiO2(B) powder as high potential negative electrode for lithium ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2013, 244, 50–55.
Zhuang, W.; Lu, L.; Wu, X.; Jin, W.; Meng, M.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, X. TiO2-B nanofibers with high thermal stability as improved anodes for lithium ion batteries. Electrochem. Commun. 2013, 27, 124–127.
Li, J.; Wan, W.; Zhou, H.; Li, J.; Xu, D. Hydrothermal synthesis of TiO2(B) nanowires with ultrahigh surface area and their fast charging and discharging properties in Li-ion batteries. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 3439–3441.
Aravindan, V.; Shubha, N.; Cheah, Y. L.; Prasanth, R.; Chuiling, W.; Prabhakar, R. R.; Madhavi, S. Extraordinary long-term cycleability of TiO2-B nanorods as anodes in full-cell assembly with electrospun membranes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 308–316.
Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, Y.; Yang, J.; Sun, P.; Liu, Y. Hydrothermal growth of layered titanate nanosheet arrays on titanium foil and their topotactic transformation to heterostructured TiO2 photocatalysts. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 22276–22285.
Xiong, W.; Wang, Y. D.; Xia, H. TiO2 nanowire arrays with mixed phases directly grown on Ti foil and their electrochemical properties as anode material for lithium ion batteries. Mater. Technol. 2013, 28, 260–264.
Liao, J. Y.; Xiao, X.; Higgins, D.; Lui, G.; Chen, Z. Self-supported single crystalline H2Ti8O17 nanoarrays as integrated three-dimensional anodes for lithium-ion microbatteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 568–574.
Tang, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Feng, H.; Lu, J.; Li, J. Preparation, structure, and electrochemical properties of reduced graphene sheet films. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 2782–2789.
Yamashita, T.; Hayes, P. Analysis of XPS spectra of Fe2+ and Fe3+ ions in oxide materials. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 254, 2441–2449.
Pradhan, G. K.; Parida, K. M. Fabrication, growth mechanism, and characterization of α-Fe2O3 nanorods. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 317–323.
Lin, F.; Song, H.; Tian, S.; Chen, X.; Zhou, J.; Wang, F. Fe1.5Ti0.5O3 nanoparticles as an anode material for lithiumion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 83, 305–310.
Grosvenor, A. P.; Kobe, B. A.; Biesinger, M. C.; McIntyre, N. S. Investigation of multiplet splitting of Fe 2p XPS spectra and bonding in iron compounds. Surf. Interface Anal. 2004, 36, 1564–1574.
Armstrong, A. R.; Armstrong, G.; Canales, J.; García, R.; Bruce, P. G. Lithium-ion intercalation into TiO2-B nanowires. Adv. Mater. 2005, 17, 862–865.
Reddy, M. V.; Yu, T.; Sow, C. H.; Shen, Z. X.; Lim, C. T.; Subba Rao, G. V.; Chowdari, B. V. R. α-Fe2O3 nanoflakes as an anode material for lithium ion batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2007, 17, 2792–2799.
Li, R.; Xie, Z.; Lu, H.; Zhang, D. W.; Yu, A. Fabrication of ZnO@TiO2 core-shell nanotube arrays as three-dimensional anode material for lithium ion batteries. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2013, 8, 11118–11124.
Guan, D.; Li, J.; Gao, X.; Yuan, C. Controllable synthesis of MoO3-deposited TiO2 nanotubes with enhanced lithiumion intercalation performance. J. Power Sources 2014, 246, 305–312.
Luo, Y.; Luo, J.; Zhou, W.; Qi, X.; Zhang, H.; Yu, D. Y. W.; Li, C. M.; Fan, H. J.; Yu, T. Controlled synthesis of hierarchical graphene-wrapped TiO2@Co3O4 coaxial nanobelt arrays for high-performance lithium storage. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 273–281.
Liao, J. Y.; Higgins, D.; Lui, G.; Chabot, V.; Xiao, X.; Chen, Z. Multifunctional TiO2-C/MnO2 core-double-shell nanowire arrays as high-performance 3D electrodes for lithium ion batteries. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 5467–5473.
Xu, X.; Fan, Z.; Ding, S.; Yu, D.; Du, Y. Fabrication of MoS2 nanosheet@TiO2 nanotube hybrid nanostructures for lithium storage. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 5245–5250.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, H., Xiong, W., Lim, C.K. et al. Hierarchical TiO2-B nanowire@α-Fe2O3 nanothorn core-branch arrays as superior electrodes for lithium-ion microbatteries. Nano Res. 7, 1797–1808 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-014-0539-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-014-0539-3