Abstract
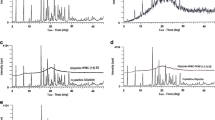
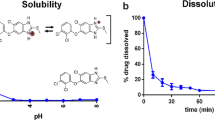
Solid dispersions of saquinavir mesylate containing either Gelucire® 44/14 or poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) 4000, or mixtures of each carrier with Tween 80 or polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP) K30 were prepared in order to enhance the drug dissolution rate. These systems were prepared by the melting method and characterized by X-ray powder diffraction, microscopical techniques, and Raman spectroscopy aiming to establish a relationship between physicochemical and dissolution properties under different cooling conditions. Modifications in degree of crystalline order/disorder over time were observed in preparations with both carriers. Overall, formulations cooled and stored at −20 °C showed less variation in dissolution rates than those at 25 °C. Although Tween 80 has enhanced the known self-emulsifying properties of Gelucire® 44/14, its combination with PEG 4000 displayed miscibility problems. The addition of PVP K30 was not the most effective approach in enhancing the dissolution in early steps; however, the drug dissolution was stable after 7 days of storage at 25 °C. The combination of PEG 4000 and PVP K30 maintained the dissolution properties for 60 and 90 days at 25 °C/95 % relative humidity and 40 °C/75 % (f 2 values >50), respectively.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albano, A.A., M.H. Infeld, W. Phuapradit, N.H. Shah, and L. Zhang. 2009. Saquinavir mesylate oral dosage form. 20090054481 (Patent). http://www.faqs.org/patents/app/20090054481. Accessed 10 July 2010.
Aso, Y., and S. Yoshioka. 2005. Molecular mobility of nifedipine–PVP and phenobarbital–PVP solid dispersions as measured by 13C-NMR spin-lattice relaxation time. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 95: 318–325.
Bates, S., G. Zografi, D. Engers, K. Morris, K. Crowley, and A. Newman. 2006. Analysis of amorphous and nanocrystalline solids from their X-ray diffraction patterns. Pharmaceutical Research 23: 2333–2348.
Buchanan, C.M., N.L. Buchanan, K.J. Edgar, J.L. Little, M.G. Ramsey, K.M. Ruble, V.J. Wacher, and M.F. Wempe. 2008. Pharmacokinetics of saquinavir after intravenous and oral dosing of saquinavir: Hydroxybutenyl-beta-cyclodextrin formulations. Biomacromolecules 9: 305–313.
Chambin, O., and V. Jannin. 2005. Interest of multifunctional lipid excipients: Case of Gelucire 44/14. Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy 31: 527–534.
Damian, F., N. Blaton, L. Naesens, J. Balzarini, R. Kinget, P. Augustijns, and G. Van den Mooter. 2000. Physicochemical characterization of solid dispersions of the antiviral agent UC-781 with polyethylene glycol 6000 and Gelucire 44/14. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 10: 311–322.
Dhirendra, K., S. Lewis, N. Udupa, and K. Atin. 2009. Solid dispersions: a review. Pakistan Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 22: 234–246.
Food and Drug Administration. 1997. Guidance for industry: Dissolution testing of immediate release solid oral dosage forms. Rockville, MD: US Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research.
Gorajana, A., A. Rajendran, and N.K. Rao. 2010. Preparation and in vitro evaluation of solid dispersions of nimodipine using PEG 4000 and PVP K30. Journal of Pharmaceutical Research and Health Care 2: 163–169.
Heo, M.Y., Z.Z. Piao, T.W. Kim, Q.R. Cao, A. Kim, and B.J. Lee. 2005. Effect of solubilizing and microemulsifying excipients in polyethylene glycol 6000 solid dispersion on enhanced dissolution and bioavailability of ketoconazole. Archives of Pharmacal Research 5: 604–611.
Knechten, H., T. Lutz, P. Pulik, T. Martin, A. Tappe, and H. Jaeger. 2010. Safety and efficacy in HIV-1-infected patients treated with ritonavir-boosted saquinavir mesylate. Archives of Drug Information 3: 26–36.
Kumar, P., S. Kumar, A. Kumar, and M. Cander. 2010. Physicochemical characterization of solid dispersions of cefdinir with PVP K-30 and PEG 4000. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Science and Technology 3: 948–956.
Labuschagne, P.W., S.G. Kazarianb, and R.E. Sadikua. 2001. Supercritical CO2-assisted preparation of ibuprofen-loaded PEG–PVP complexes. Journal of Supercritical Fluids 57: 190–197.
Lindenberg, M., S. Kopp, and J.B. Dressman. 2004. Classification of orally administered drugs on the World Health Organization Model List of Essential Medicines according to the biopharmaceutics classification system. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics 58: 265–278.
Liu, R., Z. Liu, C. Zhang, and B. Zhang. 2011. Gelucire 44/14 as a novel absorption enhancer for drugs with different hydrophilicities: In vitro and in vivo improvement on transcorneal permeation. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 100: 3186–3195.
Meaney, C.M., and C.M. O’Driscoll. 2000. A comparison of the permeation enhancement potential of simple bile salt and mixed bile salt: Fatty acid micellar systems using the CaCo-2 cell culture model. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 207: 21–30.
Mirza, S., J. Heinamaki, I. Miroshnyk, J. Rantanen, L. Christiansen, M. Karjalainen, and J. Yliruusi. 2006. Understanding processing-induced phase transformations in erythromycin–PEG 6000 solid dispersions. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 95: 1723–1732.
Mohsin, K., M.A. Long, and C.W. Pouton. 2009. Design of lipid-based formulations for oral administration of poorly water-soluble drugs: Precipitation of drug after dispersion of formulations in aqueous solution. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 98: 3582–3595.
Moore, J.W., and H.H. Flanner. 1996. Mathematical comparison of dissolution profiles. Pharmaceutical Technology 20: 64–74.
Morris, K.R., G.T. Knipp, and A.T. Serajuddin. 1992. Structural properties of polyethylene glycol–polysorbate 80 mixture, a solid dispersion vehicle. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 81: 1185–1188.
Onyeji, C.O., Adebayob, A.S., and Babalola, C.P. 1999. Effects of absorption enhancers in chloroquine suppository formulations: I: In vitro release characteristics. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 9: 131–136.
Pathak, S.M., P. Musmade, S. Dengle, A. Karthik, K. Bhat, and N. Udupa. 2010. Enhanced oral absorption of saquinavir with methyl-beta-cyclodextrin-preparation and in vitro and in vivo evaluation. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 41: 440–451.
Potluri, R.H.K., S. Bandari, R. Jukanti, and P.R. Veeraredy. 2011. Solubility enhancement and physicochemical characterization of carvedilol solid dispersion with Gelucire 50/13. Archives of Pharmacal Research 34: 51–57.
Serajuddin, A.T.M. 1999. Solid dispersion of poorly water-soluble drugs: Early promises, subsequent problems, and recent breakthroughs. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 88: 1058–1066.
Suhagia, B.N., H.M. Patel, S.A. Shah, I. Rathod, and V.K. Parmar. 2006. Preparation and characterization of etoricoxib–polyethylene glycol 4000 plus polyvinylpyrrolidone K30 solid dispersions. Acta Pharmaceutica 56: 285–298.
Sutananta, W., D.Q.M. Craig, and J.M. Newton. 1996. The use of dielectric analysis as a means of characterising the effects of moisture uptake by pharmaceutical glyceride bases. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 132: 1–8.
Svensson, A., C. Neves, and B. Cabane. 2004. Hydration of an amphiphilic excipient, Gelucire® 44/14. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 281: 107–118.
Thybo, P., J. Kristensen, and L. Hovgaard. 2007. Characterization and physical stability of tolfenamic acid–PVP K30 solid dispersions. Pharmaceutical Development and Technology 12: 43–53.
Tuntikulwattana, S., A. Mitrevej, T. Kerdcharoen, D.B. Williams, and N. Sinchaipanid. 2010. Development and optimization of micro/nanoporous osmotic pump tablets. AAPS PharmSciTech 11: 924–935.
Unga, J., P. Matsson, and D. Mahlin. 2010. Understanding polymer—lipid solid dispersions—the properties of incorporated lipids govern the crystallisation behaviour of PEG. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 386: 61–70.
United States Pharmacopeial Convention Inc., C.o.E. 2006. <941> X-ray diffraction. The United States Pharmacopeia USP 29; The National Formulary NF 24 through First Supplement. Rockville, MD: U.S.P.C. Inc., Board of Trustees, 29.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge FAPESC/CNPq/MS/SES-SC (Grant Number 15.949/2009-2) for financial support. We also thank CAPES/MEC (Nanobiotechnology Network, Grant Number 759/2009) and CNPq/MCT for the authors fellowships. All the XRPD and SEM measurements were performed in multiuser facilities provided by the Federal University of Santa Catarina: Central Laboratory of Electron Microscopy (LCME) and X-ray Diffraction Laboratory (LDRX), respectively. Silvia L. Cuffini thanks to CAPES/PVE program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Caon, T., Konig, R.A., da Cruz, A.C.C. et al. Development and physicochemical characterization of saquinavir mesylate solid dispersions using Gelucire 44/14 or PEG 4000 as carrier. Arch. Pharm. Res. 36, 1113–1125 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-013-0142-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-013-0142-2