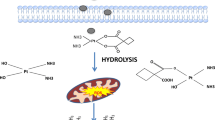
Abstract
Docetaxel, an inhibitor of microtubule depolymerization, has been used for many malignancies. Due to its toxicity and the non-selective distribution of its commercial formulation, Taxotere®, new formulations with less toxicity and tumor targeting need to be explored. For its safety and ease of factory scale production, nanoemulsion, was selected to encapsulate docetaxel. The particle size of docetaxel loaded nanoemulsion (DNE) was 72.3 nm, the average zeta potential was −6.38 mV, the encapsulation efficiency was 93.1% and the drug loading capacity was 2.87%. Although DNE presented similar antiproliferation effects on both U87 cells and bEnd.3 cells, its in vivo toxicity was significantly lower than Taxotere®. In vivo fluorescent imaging suggested nanoemulsions loaded with a fluorescent probe could distribute to the brain and accumulate at the glioma site. The pharmacological experiments also confirmed that the DNE could target glioma sites and prolong the median survival time of mice with gliomas. In conclusion, DNE is a new, less toxic, drug formulation that is effective for brain glioma therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alyautdin, R. N., Petrov, V. E., Langer, K., Berthold, A., Kharkevich, D. A., and Kreuter, J., Delivery of loperamide across the blood-brain barrier with polysorbate 80-coated polybutylcyanoacrylate nanoparticles. Pharm. Res., 14, 325–328 (1997).
Azmin, M. N., Stuart, J. F., and Florence, A. T., The distribution and elimination of methotrexate in mouse blood and brain after concurrent administration of polysorbate 80. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol., 14, 238–242 (1985).
Bissery, M. C., Preclinical pharmacology of docetaxel. Eur. J. Cancer, 31ASuppl 4, S1–S6 (1995).
Calvo, P., Gouritin, B., Chacun, H., Desmaele, D., D’Angelo, J., Noel, J. P., Georgin, D., Fattal, E., Andreux, J. P., and Couvreur, P., Long-circulating PEGylated polycyanoacrylate nanoparticles as new drug carrier for brain delivery. Pharm. Res., 18, 1157–1166 (2001).
Cascinu, S., Graziano, F., Barni, S., Labianca, R., Comella, G., Casaretti, R., Frontini, L., Catalano, V., Baldelli, A. M., and Catalano, G., A phase II study of sequential chemo therapy with docetaxel after the weekly PELF regimen in advanced gastric cancer. A report from the Italian group for the study of digestive tract cancer. Br. J. Cancer, 84, 470–474 (2001).
Cortes, J. E. and Pazdur, R., Docetaxel. J. Clin. Oncol., 13, 2643–2655 (1995).
Eisenhauer, E. A. and Trudeau, M., An overview of phase II studies of docetaxel in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Eur. J. Cancer, 31ASuppl 4, S11–S13 (1995).
Fang, J., Sawa, T., and Maeda, H., Factors and mechanism of “EPR” effect and the enhanced antitumor effects of macromolecular drugs including SMANCS. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol., 519, 29–49 (2003).
Gao, X., Tao, W., Lu, W., Zhang, Q., Zhang, Y., Jiang, X., and Fu, S., Lectin-conjugated PEG-PLA nanoparticles: preparation and brain delivery after intranasal administration. Biomaterials, 27, 3482–3490 (2006).
Gueritte-Voegelein, F., Guenard, D., Lavelle, F., Le Goff, M. T., Mangatal, L., and Potier, P., Relationships between the structure of taxol analogues and their antimitotic activity. J. Med. Chem., 34, 992–998 (1991).
Gulyaev, A. E., Gelperina, S. E., Skidan, I. N., Antropov, A. S., Kivman, G. Y., and Kreuter, J., Significant transport of doxorubicin into the brain with polysorbate 80-coated nanoparticles. Pharm. Res., 16, 1564–1569 (1999).
Hobbs, S. K., Monsky, W. L., Yuan, F., Roberts, W. G., Griffith, L., Torchilin, V. P., and Jain, R. K., Regulation of transport pathways in tumor vessels: role of tumor type and microenvironment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 95, 4607–4612 (1998).
Hu, K., Li, J., Shen, Y., Lu, W., Gao, X., Zhang, Q., and Jiang, X., Lactoferrin-conjugated PEG-PLA nanoparticles with improved brain delivery: in vitro and in vivo evaluations. J. Control. Release, 134, 55–61 (2009).
Jones-Bolin, S., Zhao, H., Hunter, K., Klein-Szanto, A., and Ruggeri, B., The effects of the oral, pan-VEGF-R kinase inhibitor CEP-7055 and chemotherapy in orthotopic models of glioblastoma and colon carcinoma in mice. Mol. Cancer Ther., 5, 1744–1753 (2006).
Kreuter, J., Alyautdin, R. N., Kharkevich, D. A., and Ivanov, A. A., Passage of peptides through the blood-brain barrier with colloidal polymer particles (nanoparticles). Brain Res., 674, 171–174 (1995).
Kreuter, J., Ramge, P., Petrov, V., Hamm, S., Gelperina, S. E., Engelhardt, B., Alyautdin, R., von Briesen, H., and Begley, D. J., Direct evidence that polysorbate-80-coated poly(butylcyanoacrylate) nanoparticles deliver drugs to the CNS via specific mechanisms requiring prior binding of drug to the nanoparticles. Pharm. Res., 20, 409–416 (2003).
Liu, B., Yang, M., Li, R., Ding, Y., Qian, X., Yu, L., and Jiang, X., The antitumor effect of novel docetaxel-loaded thermosensitive micelles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm., 69, 527–534 (2008).
Lu, W., Zhang, Y., Tan, Y. Z., Hu, K. L., Jiang, X. G., and Fu, S. K., Cationic albumin-conjugated pegylated nanoparticles as novel drug carrier for brain delivery. J. Control. Release, 107, 428–448 (2005).
Maeda, H., SMANCS and polymer-conjugated macromolecular drugs: advantages in cancer chemotherapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev., 46, 169–185 (2001).
Mao, C., Wan, J., Chen, H., Xu, H., and Yang, X., Emulsifiers’ composition modulates venous irritation of the nanoemulsions as a lipophilic and venous irritant drug delivery system. AAPS PharmSciTech, 10, 1058–1064 (2009).
Matsumura, Y. and Maeda, H., A new concept for macromolecular therapeutics in cancer chemotherapy: mechanism of tumoritropic accumulation of proteins and the antitumor agent smancs. Cancer Res., 46, 6387–6392 (1986).
Nagane, M., Pan, G., Weddle, J. J., Dixit, V. M., Cavenee, W. K., and Huang, H. J., Increased death receptor 5 expression by chemotherapeutic agents in human gliomas causes synergistic cytotoxicity with tumor necrosis factorrelated apoptosis-inducing ligand in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res., 60, 847–853 (2000).
Olivier, J. C., Drug transport to brain with targeted nanoparticles. NeuroRx, 2, 108–119 (2005).
Pang, Z., Feng, L., Hua, R., Chen, J., Gao, H., Pan, S., Jiang, X., and Zhang, P., Lactoferrin-Conjugated Biodegradable Polymersome Holding Doxorubicin and Tetrandrine for Chemotherapy of Glioma Rats. Mol. Pharm., 7, 1995–2005 (2010).
Pardridge, W. M., Drug targeting to the brain. Pharm. Res., 24, 1733–1744 (2007).
Ryan, D. P., Kulke, M. H., Fuchs, C. S., Grossbard, M. L., Grossman, S. R., Morgan, J. A., Earle, C. C., Shivdasani, R., Kim, H., Mayer, R. J., and Clark, J. W., A Phase II study of gemcitabine and docetaxel in patients with metastatic pancreatic carcinoma. Cancer, 94, 97–103 (2002).
Sampath, P., Rhines, L. D., DiMeco, F., Tyler, B. M., Park, M. C., and Brem, H., Interstitial docetaxel (taxotere), carmustine and combined interstitial therapy: a novel treatment for experimental malignant glioma. J. Neurooncol., 80, 9–17 (2006).
Tankanow, R. M., Docetaxel: a taxoid for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm., 55, 1777–1791 (1998).
Ten, T. A., Verweij, J., and Loos, W. J., Sparreboom, A., Pharmacological effects of formulation vehicles: implications for cancer chemotherapy. Clin. Pharmacokinet., 42, 665–685 (2003).
Torchilin, V. P., Passive and active drug targeting: drug delivery to tumors as an example. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol., 3–53 (2010).
Trudeau, M. E., Docetaxel: a review of its pharmacology and clinical activity. Can. J. Oncol., 6, 443–457 (1996).
Upadhyay, K. K., Bhatt, A. N., Castro, E., Mishra, A. K., Chuttani, K., Dwarakanath, B. S., Schatz, C., Le Meins, J. F., and Misra, A., Lecommandoux, S., In vitro and in vivo evaluation of docetaxel loaded biodegradable polymersomes. Macromol. Biosci., 10, 503–512 (2010).
Xu, Z., Chen, L., Gu, W., Gao, Y., Lin, L., Zhang, Z., Xi, Y., and Li, Y., The performance of docetaxel-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles targeted to hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomaterials, 30, 226–232 (2009).
Zhan, C., Gu, B., Xie, C., Li, J., Liu, Y., and Lu, W., Cyclic RGD conjugated poly(ethylene glycol)-co-poly(lactic acid) micelle enhances paclitaxel anti-glioblastoma effect. J. Control. Release, 143, 136–142 (2010).
Zhao, M., Su, M., Lin, X., Luo, Y., He, H., Cai, C., and Tang, X., Evaluation of docetaxel-loaded intravenous lipid emulsion: pharmacokinetics, tissue distribution, antitumor activity, safety and toxicity. Pharm. Res., 27, 1687–1702 (2010).
Zhou, H., Yue, Y., Liu, G., Li, Y., Zhang, J., Gong, Q., Yan, Z., and Duan, M., Preparation and characterization of a lecithin nanoemulsion as a topical delivery system. Nanoscale Res. Lett., 5, 224–230 (2009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gaoe, H., Pang, Z., Pan, S. et al. Anti-glioma effect and safety of docetaxel-loaded nanoemulsion. Arch. Pharm. Res. 35, 333–341 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-012-0214-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-012-0214-8