Summary
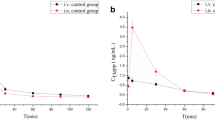
This paper describes further exploration of the effect of polysorbate 80 on the absorption, distribution, and elimination of methotrexate (MTX). This study has confirmed the earlier finding that polysorbate 80 could increase the absorption of MTX from the mouse gastrointestinal tract and enhance the drugs uptake into the brain. The experiments reported here suggest that polysorbate 80 has a direct effect on the blood-brain barrier leading to the increased uptake of MTX, which is evident following IV administration. Measurements of MTX excreted in the urine and faeces confirmed the role of polysorbate 80 in facilitating the excretion of MTX into the bile and urine. Polysorbate 80 administered PO did not cause any reduction of plasma volume, thus excluding the possibility that the higher MTX concentrations measured in mice after concurrent administration of polysorbate PO might result from a reduction in blood volume due to osmotic effects. At the doses given, polysorbate 80 appeared not to have a damaging effect on the gastrointestinal mucosa.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albelson HT, Ensminger W, et al. (1979) High-dose methotrexate-carboxypeptidase. A selective approach to the therapy of central nervous tumours. In: Kisliuk RL, Brown GW (eds) Chemistry and biology of pteridines. Vol 4, North Holland, Amsterdam, pp 629–633
Albelson HT, Kufe DW, Skarin AT, Major P, et al. (1981) The treatment of central nervous system tumours with methotrexate. Cancer Treat Rep [Suppl] 65:137
Attwood D, Florence AT (1983) Surfactant systems. Their chemistry, pharmacy and biology. Chapman and Hall, London
Azmin MN (1983) Polysorbate 80 and the absorption and distribution of methotrexate in the mouse. PhD thesis, University of Strathclyde, Glasgow
Azmin MN, Stuart JFB, Calman KC, Florence AT (1982) Effects of polysorbate 80 on the absorption and distribution of oral methotrexate (MTX) in mice. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 9:161
Bertino JR (1981) Clinical use of methotrexate, with emphasis on use of high-dose. Cancer Treat Rep [Suppl] 65:131
Bryan AJ, Kaur R, Robinson G, Thomas NW, Wilson CG (1980) Histological and physiological studies on intestine of rat exposed to solutions of Myrij 52 and PEG 200. Int J Pharm 7:145
Condit PT, Chanes RE, Joel W (1969) Renal toxicity of methotrexate. Cancer 23:126
Gantt L, Crochman N, Dyniewicz JM (1961) Effect of a detergent on gastro-intestinal absorption of a steroid. Lancet I:486
Harrison SD, Cusic AM, McAfee SM (1981) Tween 80 increase plasma adriamycin concentration in mice by an apparent reduction of plasma volume. Eur J Cancer 17:387
Hasegawa H, Allen JC, Mehta BM, Shapiro WR, Posner JB (1979) Enhancement of CNS penetration of methotrexate by hyperosmolar intracarotid mannitol on carcinomatous meningitis. Neurology 29:1280
Hikal AH (1981) Effect of polysorbate 80 on the apparent partition coefficient of drugs on their intestinal absorption in the rat: II. Phenobarbital. Int J Pharm 7:205
Jacobs SA, Stroller RG, Chabner BA et al. (1976) 7-hydroxymethotrexate as a urinary metabolite in human subjects and rhesus monkeys receiving high-dose methotrexate. J Clin Invest 57:534
Kaneda A, Nishimura K, Muranishi S, Sezaki H (1974) Mechanism of drug absorption from micellar solution: II. Effect of polysorbate 80 on the absorption of micelle-free drug. Chem Pharm Bull 23:523
Katzemi K, Arita T, Muranishi S (1965) Absorption and excretion of drugs: XXVI. Effect of non-ionic surface-active agents on rectal absorption of sulphonamides. Chem Pharm Bull 13:976
Levin VA, Patlack CS, Landahl HD (1980) Heuristic modelling of drug delivery to malignant brain tumour. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 8:257
Levy G, Anello JA (1968) Effect of complex formation on drug absorption V. Studies on the mechanism on the secobarbital absorption enhancing of polysorbate 80 in goldfish. J Pharm Sci 57:101
Matsuzawa T, Fujisawa H, Aoki H, Mima H (1969) Effect of some non-ionic surfactants on the absorption of enduricidin from the muscles. Chem Pharm Bull 17:999
Neuwelt EA, Diehl JT, Vu LH, Hill SA, Michael AJ, Frenkel EP (1981a) Monitoring of methotrexate delivery in patients with malignant brain tumours after osmotic blood-brain barrier disruption. Ann Intern Med 94:449
Neuwelt EA, Pagel M, Barnett P, Glassberg M, Frenkel EP (1981b) Pharmacology of toxicity of intracarotid adriamycin administration following osmotic blood-brain barrier modification. Cancer Res 41:4466
Nissim JA (1960) Action of some surface-active compounds on the gastro-intestinal mucosa. Nature 137–805
Rosen GA, Ghavimi F, Nirenberg A, et al. (1977) High-dose methotrexate with citrovorum-factor rescue for treatment of central nervous system tumours in children. Cancer Treat Rep 61:681
Shapiro WR, Young DF, Mehta BM (1975) Methotrexate distribution in cerebrospinal fluid after intravenous, ventricular and lumbar injections. N Engl J Med 293:161
Treon JF, Gongwer LE, Nelson MF, Kirschman JC (1967) Physiology and metabolic patterns of non-ionic surfactants. In: Paquot P (ed) Chemistry, physics and application of surface-active substances vol 3. Gordon and Breach, London, p 381
Walters KA, Dugard PH, Florence AT (1981) Nonionic surfactants and gastric-mucosa transport of paraquat. J Pharm Pharmacol 33:207
Whitemore DA, Brookes LG, Wheeler KP (1979) Relative effects of different surfactants on intestinal absorption and release of proteins and phospholipids from tissue. J Pharm Pharmacol 31:277
Yamada H, Yamamoto R (1965) Biopharmaceutical studies on factors affecting rate of absorption of drug: I. Absorption of salicylamide in micellar solution. Chem Pharm Bull 13:1279
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azmin, M.N., Stuart, J.F.B. & Florence, A.T. The distribution and elimination of methotrexate in mouse blood and brain after concurrent administration of polysorbate 80. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 14, 238–242 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00258124
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00258124