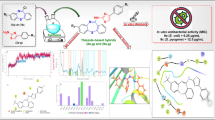
Abstract
The present work deals with the synthesis of various enoxacin analogues via nucleophilic substitution of 3-carboxylic acid moiety of the drug by aromatic amines. The free carboxylic group was utilized in the formation of amides and the effect of functional group exchange on different biological activities of the parent was evaluated. The structure of these derivatives was established by various spectroscopic techniques and mass spectrometry. The derivatives were evaluated as antibacterial agents against a series of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria whereby some of them displayed considerably improved antimicrobial profile against Gram-negative test strains. Additionally unlike enoxacin, the derivatives were also found to modulate oxidative burst response of phagocytes exhibiting moderate to significant inhibitory activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anacona, J. R. and Toledo, C., Synthesis and antibacterial activity of metal complexes of ciprofloxacin. Transi. Metal Chem., 26, 228–231 (2001).
Anderson, V. E. and Osheroff, N., Type II topoisomerases as targets for quinolone antibacterials: Turning Dr. Jekyll into Mr. Hyde. Curr. Pharmaceut. Design., 7, 339–355 (2001).
Ball, P., Fernald, A., and Tillotson, G., Therapeutic advances of new fluoroquinolones., Expert. Opin. Invest. Drugs., 7, 761–783 (1998).
Ball, P., Quinolone-induced QT interval prolongation: a notso-unexpected class effect. J. Antimicrob. Chemother., 45, 557–559 (2000).
Bauer, A. W., Kirby, W. M. M., Sherris, J. C., and Turck, M., Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standard single disk method. Am. J. Clin. Pathol., 45, 493–496 (1966).
Blandeau, J. M., Expanded activity and utility of the new fluoroquinolones: A review. Clini. Therap., 21, 3–40 (1999).
Chapman, J. S. and Georgopapadakou, N. H., Routes of quinolone permeation in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Chemother., 32, 438–442 (1988).
Chin, N. X. and Neu, H. C., In vitro activity of enoxacin, a quinolone carboxylic acid, compared with those of norfloxacin, new beta-lactams, aminoglycosides, and trimethoprim. Antimicrob. Chemother., 24, 754–763 (1983).
Chu, D. T. W., Fernandes, P. B., Claiborne, A. K., Pihuleac, E., Nordeen., and Pernet, A. G., Synthesis and structureactivity relationships of novel arylfluoroquinolone antibacterial agents. J. Med. Chem., 28, 1558–1564 (1985).
Crumplin, G. C., Aspects of chemistry in the development of the 4-quinolone antibacterial agents. Clin. Infect. Dis. [Rev Infect Dis], 10, 1–9 (1988).
Daniel, T. W. C. and Prabhavathi, B. F., Structure-activity relationships of the fluoroquinolones. Antimicrob. Chemother., 33, 131–135 (1989).
Domagala, J. M., Heifetz, C. L., Hutt, M. P., Mich, T. F., Nichols, J. B., Solomon, M., and Worth, D. F., 1-Substituted 7-[3-[(ethylamino) methyl]-1-pyrrolidinyl]-6, 8-difluoro-1, 4-dihydro-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acids. New quantitative structure activity relationships at N1 for the quinolone antibacterials. J. Med. Chem., 31, 991–1001 (1988).
Foroumadi, A., Emami, S., Hassanzadeh, A., Rajaee, M., Sokhanvar, K., Moshafi, M. H., and Shafiee, A., Synthesis and antibacterial activity of N-(5-benzylthio-1, 3, 4-thiadiazol-2-yl) and N-(5-benzylsulfonyl-1, 3, 4-thiadiazol-2-yl) piperazinyl quinolone derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 15, 4488–4492 (2005).
Foroumadi, A., Emami, S., Mansouri, S., Javidnia, A., Saeid-Adeli, N., Shirazi, F. H., and Shafiee, A., Synthesis and antibacterial activity of levofloxacin derivatives with certain bulky residues on piperazine ring. Eur. J. Med. Chem., 42, 985–992 (2007).
Foroumadi, A., Emami, S., Mehni, M., Moshafi, M. H., and Shafiee, A., Synthesis and antibacterial activity of N-[2-(5-bromothiophen-2-yl)-2-oxoethyl] and N-[(2-5-bromothiophen-2-yl)-2-oximinoethyl] derivatives of piperazinyl quinolones. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 15, 4536–4539 (2005).
Foroumadi, A., Mansouri, S., Kiani, Z., and Rahmani, A., Synthesis and in vitro antibacterial evaluation of N-[5-(5-quinolones. Eur. J. Med. Chem., 38, 851–854 (2003).
Franklin, V., Tamara, Z., Carlos, R., Alvaro, R., Tulynan. C., Yrene, D., Carla, I., Ylec, M. C., Verónica, L., Lubimar, G., Jessenia, O., and Alberto, F., Synthesis, primary photo-physical and antibacterial properties of naphthyl ester cinoxacin and nalidixic acid derivatives. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B: Biol., 92, 83–90 (2008).
Helfand, S. L., Werkmeister, J., and Roder, J. C., Chemiluminescence response of human natural killer cells. I. The relationship between target cell binding, chemiluminescence, and cytolysis. J. Exp. Med., 156, 492–505 (1982).
Hirosato, K., Fumio, S., Kiyotaka, K., and Goro, T., Studies on prodrugs. 7. Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of 3-formylquinolone derivatives. J. Med. Chem., 31, 221–225 (1988).
Janknegt, R., Fluorinated quinolones. A review of their mode of action, antimicrobial activity, pharmacokinetics and clinical efficacy. Pharm Weekbl [Sci]., 8, 1–21 (1986).
Klopman, G., Macina, O. T., Levinson, M. E., and Rosenkranz, H. S., Computer automated structure evaluation of quinolone antibacterial agents. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 31, 1831–1840 (1987).
Koga, H., Itoh, A., Murayama, S., Suzue, S., and Irikura, T., Structure-activity relationships of antibacterial 6, 7-and 7, 8-disubstituted 1-alkyl-1, 4-dihydro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acids. J. Med. Chem., 23, 1358–1363 (1980).
Lesher, G. Y., Froelich, E. J., Gruett, M. D., Bailey, J. H., and Brundage, R. P., 1,8-Naphthyridine Derivatives. A New Class of Chemotherapeutic Agents. J. Med. Pharm. Chem., 5, 1063–1065 (1962).
Lester, A. M., Bacterial topoisomerase inhibitors: Quinolone and pyridone antibacterial agents. Chem. Rev., 105, 559–592 (2005).
Li, Z. R., Guo, H. Y., and Zhang, Z. P., Studies on pyridone carboxylic acids as anti-bacterial agents. IX. Study on prodrugs of some pyridone carboxylic acids. Yao Xue Xue Bao., 26, 111–6 (1991).
Mascellino, M. T., Farinelli, S., Iegri, F., Iona, E., and De Simone, C., Antimicrobial activity of fluoroquinolones and other antibiotics on 1, 116 clinical Gram-positive and Gramnegative isolates. Drugs Expert. Clin. Res., 24, 139–151 (1998)
Paton, J. H. and Reeves, D. S., Fluoroquinolone antibiotics. Microbiology, pharmacokinetics and clinical use. Drugs., 36, 193–228 (1988).
Pfeiffer, S., Lass, A., Schmidt, K., Mayer, B., Protein tyrosine nitration in mouse peritoneal macrophages activated in vitro and in vivo: evidence against an essential role of peroxynitrite. FASEB J., 15, 2355–64 (2001).
Sanders, C. C., Ciprofloxacin: in vitro activity, mechanism of action, and resistance. Rev Infect Dis., 10, 516–527 (1988).
Shen, L. L., Mitscher, L. A., Sharma, P. N., O’Donnell, T. J., Chu, D. W. T., Cooper, C. S., Rosen, T., and Pernet, A. G., Mechanism of inhibition of DNA gyrase by quinolone antibacterials: A cooperative drug-DNA binding model. Biochemistry., 28, 3886–3894 (1989).
Sissi, C. and Palumbo, M., The quinolone family: From antibacterial to anticancer agents. Curr. Med. Chem.-Anti-Cancer Agents., 3, 439–450 (2003).
Tauber, S. C. and Nau, R., Immunomodulatory properties of antibiotics. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol., 1, 68–79 (2008).
Tomišic, Z. B., Kujundžic, N., Krajacic, M. B., Višnjevac, A., and Kojic-Prodic, B., Molecular structures of new ciprofloxacin derivatives. J. Mol. Struct., 611, 73–81 (2002).
Turnidge, J., Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of fluoroquinolones. Drugs., 58, 29–36 (1999).
Wiik, P., Opstad, P. K., Boyum, A., Granulocyte chemiluminescence response to serum opsonized zymosan particlesex vivo during long-term strenuous exercise, energy and sleep deprivation in humans. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol., 73, 251–258 (1996).
Wood, M. J., Tissue penetration and clinical efficacy of enoxacin in respiratory tract infections. Clin. Pharmacokinet., 16, 38–45 (1989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saeed Arayne, M., Sultana, N., Haroon, U. et al. Synthesis and biological evaluations of enoxacin carboxamide derivatives. Arch. Pharm. Res. 32, 967–974 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-009-1700-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-009-1700-5