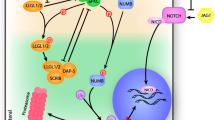
Abstract
MicroRNAs (miRNAs), approximately 19–25 nucleotides in length, are posttranscriptional regulators of protein expression that target and inhibit translation of messenger (m) RNAs. Recent research on miRNAs has produced a plethora of new material on the role of miRNAs in disease. Deregulation or ablation of miRNA expression has led to major pathologies including heart disease and cancer. Signatures of differential miRNA expression have been uncovered for nearly every disease. Recent research has focused on exploitation of the selectivity of these signatures as markers of disease and for therapeutic applications. The significance of additional mechanisms of abnormal posttranscriptional regulation, such as ultraconserved genes (UCGs), has recently been recognized. This review focuses on the identification of aberrant posttranscriptional regulators (miRNAs and UCGs) in cancer and cardiovascular disease and addresses the applications of this work towards diagnosis and therapy.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bagga, S., Bracht, J., Hunter, S., Massirer, K., Holtz, J., Eachus, R., et al. (2005). Regulation by let-7 and lin-4 miRNAs results in target mRNA degradation. Cell, 122(4), 553–563.
Wang, Y., Liang, Y., & Lu, Q. (2008). MicroRNA epigenetic alterations: Predicting biomarkers and therapeutic targets in human diseases. Clinical Genetics, 74(4), 307–315.
Borchert, G. M., Lanier, W., & Davidson, B. L. (2006). RNA polymerase III transcribes human microRNAs. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 13(12), 1097–1101.
Gregory, R. I., Yan, K. P., Amuthan, G., Chendrimada, T., Doratotaj, B., Cooch, N., et al. (2004). The Microprocessor complex mediates the genesis of microRNAs. Nature, 432(7014), 235–40.
Hutvágner, G., & Zamore, P. D. (2002). A microRNA in a multiple-turnover RNAi enzyme complex. Science, 297(5589), 2056–2060.
Bejerano, G., Pheasant, M., Makunin, I., Stephen, S., Kent, W. J., Mattick, J. S., et al. (2004). Ultraconserved elements in the human genome. Science, 304(5675), 1321–1325.
Mattick, J. S. (2009). The genetic signatures of noncoding RNAs. PLoS Genet, 5(4), e1000459.
Calin, G. A., Liu, C. G., Ferracin, M., Hyslop, T., Spizzo, R., Sevignani, C., et al. (2007). Ultraconserved regions encoding ncRNAs are altered in human leukemias and carcinomas. Cancer Cell, 12(3), 215–229.
Strong, K., Mathers, C., Leeder, S., & Beaglehole, R. (2005). Preventing chronic diseases: How many lives can we save? Lancet, 366(9496), 1578–1582.
Lloyd-Jones, D., Adams, R. J., Brown, T. M., Carnethon, M., Dai, S., De Simone, G., Ferguson, T. B., Ford, E., Furie, K., Gillespie, C., Go, A., Greenlund, K., Haase, N., Hailpern, S., Ho, P. M., Howard, V., Kissela, B., Kittner, S., Lackland, D., Lisabeth, L., Marelli, A., McDermott, M. M., Meigs, J., Mozaffarian, D., Mussolino, M., Nichol, G., Roger, V., Rosamond, W., Sacco, R, Sorlie, P., Stafford, R., Thom, T., Wasserthiel-Smoller, S., Wong, N. D., Wylie-Rosett, J., on behalf of the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. (2009) Heart disease and stroke statistics—2010 update. A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation.
Jemal, A., Siegel, R., Ward, E., Murray, T., Xu, J., & Thun, M. J. (2007). Cancer statistics, 2007. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 57(1), 43–66.
Chen, J. F., Murchison, E. P., Tang, R., Callis, T. E., Tatsuguchi, M., Deng, Z., et al. (2008). Targeted deletion of Dicer in the heart leads to dilated cardiomyopathy and heart failure. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105(6), 2111–2116.
Zhao, Y., Ransom, J. F., Li, A., Vedantham, V., von Drehle, M., Muth, A. N., et al. (2007). Dysregulation of cardiogenesis, cardiac conduction, and cell cycle in mice lacking miRNA-1-2. Cell, 129(2), 303–317.
Thum, T., Galuppo, P., Wolf, C., Fiedler, J., Kneitz, S., van Laake, L. W., et al. (2007). MicroRNAs in the human heart: A clue to fetal gene reprogramming in heart failure. Circulation, 116(3), 258–267.
van Rooij, E., Sutherland, L. B., Liu, N., Williams, A. H., McAnally, J., Gerard, R. D., et al. (2006). A signature pattern of stress-responsive microRNAs that can evoke cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103(48), 18255–18260.
Hunter, J. J., & Chien, K. R. (1999). Signaling pathways for cardiac hypertrophy and failure. New England Journal of Medicine, 341(17), 1276–1283.
Sayed, D., Hong, C., Chen, I. Y., Lypowy, J., & Abdellatif, M. (2007). MicroRNAs play an essential role in the development of cardiac hypertrophy. Circulation Research, 100(3), 416–424.
Carè, A., Catalucci, D., Felicetti, F., Bonci, D., Addario, A., Gallo, P., et al. (2007). MicroRNA-133 controls cardiac hypertrophy. Nature Medicine, 13(5), 613–618.
Xu, C., Lu, Y., Pan, Z., Chu, W., Luo, X., Lin, H., et al. (2007). The muscle-specific microRNAs miR-1 and miR-133 produce opposing effects on apoptosis by targeting HSP60, HSP70 and caspase-9 in cardiomyocytes. Journal of Cell Science, 120(Pt 17), 3045–3052.
Xiao, J., Luo, X., Lin, H., Zhang, Y., Lu, Y., Wang, N., et al. (2007). MicroRNA miR-133 represses HERG K+channel expression contributing to QT prolongation in diabetic hearts. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 282(17), 12363–12367.
Chan, J. A., Krichevsky, A. M., & Kosik, K. S. (2005). MicroRNA-21 is an antiapoptotic factor in human glioblastoma cells. Cancer Research, 65(14), 6029–6033.
Si, M. L., Zhu, S., Wu, H., Lu, Z., Wu, F., & Mo, Y. Y. (2007). miR-21-mediated tumor growth. Oncogene, 26(19), 2799–2803.
Cheng, Y., Ji, R., Yue, J., Yang, J., Liu, X., Chen, H., et al. (2007). MicroRNAs are aberrantly expressed in hypertrophic heart: Do they play a role in cardiac hypertrophy? American Journal of Pathology, 170(6), 1831–1840.
Tatsuguchi, M., Seok, H. Y., Callis, T. E., Thomson, J. M., Chen, J. F., Newman, M., et al. (2007). Expression of microRNAs is dynamically regulated during cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology, 42(6), 1137–1141.
Thum, T., Gross, C., Fiedler, J., Fischer, T., Kissler, S., Bussen, M., et al. (2008). MicroRNA-21 contributes to myocardial disease by stimulating MAP kinase signalling in fibroblasts. Nature, 456(7224), 980–984.
Calin, G. A., & Croce, C. M. (2009). Chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Interplay between noncoding RNAs and protein-coding genes. Blood, 114(23), 4761–4770.
Liu, C. G., Spizzo, R., Calin, G. A., & Croce, C. M. (2008). Expression profiling of microRNA using oligo DNA arrays. Methods, 44(1), 22–30.
Volinia, S., Calin, G. A., Liu, C. G., Ambs, S., Cimmino, A., Petrocca, F., et al. (2006). A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103(7), 2257–2261.
Calin, G. A., & Croce, C. M. (2006). MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nature ReviewsCancer, 6(11), 857–866.
Esquela-Kerscher, A., & Slack, F. J. (2006). Oncomirs-microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nature ReviewsCancer, 6(4), 259–269.
Calin, G. A., Dumitru, C. D., Shimizu, M., Bichi, R., Zupo, S., Noch, E., et al. (2002). Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro-RNA genes miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 99(24), 15524–15529.
Aqeilan, R. I., Calin, G. A., & Croce, C. M. (2010). miR-15a and miR-16-1 in cancer: Discovery, function and future perspectives. Cell Death and Differentiation, 17(2), 215–220.
Nicoloso, M. S., Spizzo, R., Shimizu, M., Rossi, S., & Calin, G. A. (2009). MicroRNAs—The micro steering wheel of tumour metastases. Nature ReviewsCancer, 9(4), 293–302.
Schetter, A. J., Leung, S. Y., Sohn, J. J., Zanetti, K. A., Bowman, E. D., Yanaihara, N., et al. (2008). MicroRNA expression profiles associated with prognosis and therapeutic outcome in colon adenocarcinoma. JAMA, 299(4), 425–436.
Reinhart, B. J., Slack, F. J., Basson, M., Pasquinelli, A. E., Bettinger, J. C., Rougvie, A. E., et al. (2000). The 21-nucleotide let-7 RNA regulates developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature, 403(6772), 901–906.
Takamizawa, J., Konishi, H., Yanagisawa, K., Tomida, S., Osada, H., Endoh, H., et al. (2004). Reduced expression of the let-7 microRNAs in human lung cancers in association with shortened postoperative survival. Cancer Research, 64(11), 3753–3756.
Johnson, S. M., Grosshans, H., Shingara, J., Byrom, M., Jarvis, R., Cheng, A., et al. (2005). RAS is regulated by the let-7 microRNA family. Cell, 120(5), 635–647.
Eccles, S. A., & Welch, D. R. (2007). Metastasis: Recent discoveries and novel treatment strategies. Lancet, 369(9574), 1742–1757.
Tavazoie, S. F., Alarcón, C., Oskarsson, T., Padua, D., Wang, Q., Bos, P. D., et al. (2008). Endogenous human microRNAs that suppress breast cancer metastasis. Nature, 451(7175), 147–152.
Wang, S., Aurora, A. B., Johnson, B. A., Qi, X., McAnally, J., Hill, J. A., et al. (2008). The endothelial-specific microRNA miR-126 governs vascular integrity and angiogenesis. Developments Cell, 15(2), 261–271.
Wang, S., & Olson, E. N. (2009). AngiomiRs—Key regulators of angiogenesis. Current Opinion in Genetics and Development, 19(3), 205–211.
Fish, J. E., Santoro, M. M., Morton, S. U., Yu, S., Yeh, R. F., Wythe, J. D., et al. (2008). miR-126 regulates angiogenic signaling and vascular integrity. Developments Cell, 15(2), 272–284.
Ullah, M. F., & Aatif, M. (2009). The footprints of cancer development: Cancer biomarkers. Cancer Treatment Reviews, 35(3), 193–200.
Lu, J., Getz, G., Miska, E. A., Alvarez-Saavedra, E., Lamb, J., Peck, D., et al. (2005). MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature, 435(7043), 834–838.
Rosenfeld, N., Aharonov, R., Meiri, E., Rosenwald, S., Spector, Y., Zepeniuk, M., et al. (2008). MicroRNAs accurately identify cancer tissue origin. Nature Biotechnology, 26(4), 462–469.
Mercer, T. R., Dinger, M. E., & Mattick, J. S. (2009). Long non-coding RNAs: Insights into functions. Nature Reviews Genetics, 10(3), 155–159.
Reis, E. M., Nakaya, H. I., Louro, R., Canavez, F. C., Flatschart, A. V., Almeida, G. T., et al. (2004). Antisense intronic non-coding RNA levels correlate to the degree of tumor differentiation in prostate cancer. Oncogene, 23(39), 6684–6692.
Calin, G. A., Ferracin, M., Cimmino, A., Di Leva, G., Shimizu, M., Wojcik, S. E., et al. (2005). A MicroRNA signature associated with prognosis and progression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. New England Journal of Medicine, 353(17), 1793–1801. Erratum in: N Engl J Med355(5):533.
Girard, A., Sachidanandam, R., Hannon, G. J., & Carmell, M. A. (2006). A germline-specific class of small RNAs binds mammalian Piwi proteins. Nature, 442(7099), 199–202.
Aravin, A., Gaidatzis, D., Pfeffer, S., Lagos-Quintana, M., Landgraf, P., Iovino, N., et al. (2006). A novel class of small RNAs bind to MILI protein in mouse testes. Nature, 442(7099), 203–207.
Saito, K., Nishida, K. M., Mori, T., Kawamura, Y., Miyoshi, K., Nagami, T., et al. (2006). Specific association of Piwi with rasiRNAs derived from retrotransposon and heterochromatic regions in the Drosophila genome. Genes and Development, 20(16), 2214–2222.
O’Donnell, K. A., & Boeke, J. D. (2007). Mighty Piwis defend the germline against genome intruders. Cell, 129(1), 37–44.
Klattenhoff, C., & Theurkauf, W. (2008). Biogenesis and germline functions of piRNAs. Development, 135(1), 3–9.
Lau, N. C., Seto, A. G., Kim, J., Kuramochi-Miyagawa, S., Nakano, T., Bartel, D. P., et al. (2006). Characterization of the piRNA complex from rat testes. Science, 313(5785), 363–367.
Gunawardane, L. S., Saito, K., Nishida, K. M., Miyoshi, K., Kawamura, Y., Nagami, T., et al. (2007). A slicer-mediated mechanism for repeat-associated siRNA 5′ end formation in Drosophila. Science, 315(5818), 1587–1590.
Wurdinger, T., & Costa, F. F. (2007). Molecular therapy in the microRNA era. Pharmacogenomics Journal, 7(5), 297–304.
Aravin, A., & Tuschl, T. (2005). Identification and characterization of small RNAs involved in RNA silencing. FEBS Letters, 579(26), 5830–5840.
Rossi, S., Sevignani, C., Nnadi, S. C., Siracusa, L. D., & Calin, G. A. (2008). Cancer-associated genomic regions (CAGRs) and noncoding RNAs: Bioinformatics and therapeutic implications. Mammalian Genome, 19(7–8), 526–540.
Weiler, J., Hunziker, J., & Hall, J. (2006). Anti-miRNA oligonucleotides (AMOs): Ammunition to target miRNAs implicated in human disease? Gene Therapy, 13(6), 496–502.
Krützfeldt, J., Rajewsky, N., Braich, R., Rajeev, K. G., Tuschl, T., Manoharan, M., et al. (2005). Silencing of microRNAs in vivo with ‘antagomirs’. Nature, 438(7068), 685–689.
Martinez, J., Patkaniowska, A., Urlaub, H., Lührmann, R., & Tuschl, T. (2002). Single-stranded antisense siRNAs guide target RNA cleavage in RNAi. Cell, 110(5), 563–574.
Cimmino, A., Calin, G. A., Fabbri, M., Iorio, M. V., Ferracin, M., Shimizu, M., et al. (2005). miR-15 and miR-16 induce apoptosis by targeting BCL2. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 102(39), 13944–13949.
Calin, G. A., Cimmino, A., Fabbri, M., Ferracin, M., Wojcik, S. E., Shimizu, M., et al. (2008). miR-15a and miR-16-1 cluster functions in human leukemia. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105(13), 5166–5171.
Weidhaas, J. B., Babar, I., Nallur, S. M., Trang, P., Roush, S., Boehm, M., et al. (2007). MicroRNAs as potential agents to alter resistance to cytotoxic anticancer therapy. Cancer Research, 67(23), 11111–11116.
Duisters, R. F., Tijsen, A. J., Schroen, B., Leenders, J. J., Lentink, V., van der Made, I., et al. (2009). miR-133 and miR-30 regulate connective tissue growth factor: Implications for a role of microRNAs in myocardial matrix remodeling. Circulation Research, 104(2), 170–178. 6p following 178.
van Rooij, E., Sutherland, L. B., Qi, X., Richardson, J. A., Hill, J., & Olson, E. N. (2007). Control of stress-dependent cardiac growth and gene expression by a microRNA. Science, 316(5824), 575–579.
Meng, F., Henson, R., Wehbe-Janek, H., Ghoshal, K., Jacob, S. T., & Patel, T. (2007). MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer. Gastroenterology, 133(2), 647–658.
Asangani, I. A., Rasheed, S. A., Nikolova, D. A., Leupold, J. H., Colburn, N. H., Post, S., et al. (2008). MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene, 27(15), 2128–2136.
Zhu, S., Si, M. L., Wu, H., & Mo, Y. Y. (2007). MicroRNA-21 targets the tumor suppressor gene tropomyosin 1 (TPM1). Journal of Biological Chemistry, 282(19), 14328–14336.
Iorio, M. V., Ferracin, M., Liu, C. G., Veronese, A., Spizzo, R., Sabbioni, S., et al. (2005). MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast cancer. Cancer Research, 65(16), 7065–7070.
Gironella, M., Seux, M., Xie, M. J., Cano, C., Tomasini, R., Gommeaux, J., et al. (2007). Tumor protein 53-induced nuclear protein 1 expression is repressed by miR-155, and its restoration inhibits pancreatic tumor development. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104(41), 16170–16175.
Harris, T. A., Yamakuchi, M., Ferlito, M., Mendell, J. T., & Lowenstein, C. J. (2008). MicroRNA-126 regulates endothelial expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule 1. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105(5), 1516–1521.
Ma, L., Teruya-Feldstein, J., & Weinberg, R. A. (2007). Tumour invasion and metastasis initiated by microRNA-10b in breast cancer. Nature, 449(7163), 682–688.
He, L., Thomson, J. M., Hemann, M. T., Hernando-Monge, E., Mu, D., Goodson, S., et al. (2005). A microRNA polycistron as a potential human oncogene. Nature, 435(7043), 828–833.
Dews, M., Homayouni, A., Yu, D., Murphy, D., Sevignani, C., Wentzel, E., et al. (2006). Augmentation of tumor angiogenesis by a Myc-activated microRNA cluster. Nature Genetics, 38(9), 1060–1065.
Bonauer, A., Carmona, G., Iwasaki, M., Mione, M., Koyanagi, M., Fischer, A., et al. (2009). MicroRNA-92a controls angiogenesis and functional recovery of ischemic tissues in mice. Science, 324(5935), 1710–1713.
Acknowledgements
G.A.C. is supported as a Fellow at The University of Texas M. D. Anderson Research Trust, as a Fellow of The University of Texas System Regents Research Scholar, and by the Ladjevardian Regents Research Scholar Fund. Work in Dr. Calin’s laboratory is supported in part by an NIH, DOD, a Breast Cancer SPORE Developmental Research Award, an Ovarian Cancer SPORE Developmental Research Award, a CTT/3I-TD grant and by 2009 Seena Magowitz-Pancreatic Cancer Action Network-AACR Pilot Grant. W.A. and R.P. receive support from the Gillson-Longenbaugh Foundation, the Marcus Foundation, DOD, NIH, and NCI.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Edwards, J.K., Pasqualini, R., Arap, W. et al. MicroRNAs and Ultraconserved Genes as Diagnostic Markers and Therapeutic Targets in Cancer and Cardiovascular Diseases. J. of Cardiovasc. Trans. Res. 3, 271–279 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12265-010-9179-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12265-010-9179-5