Abstract
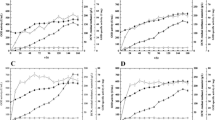
L-glutamate oxidase (GLOD) and L-amino acid oxidase (AAO) were reported to be capable of convert L-glutamic acid to α-aketoglutaric acid (α-KG). These two enzymes gene have been successfully expressed by using pHBM905BDM in Pichia pastoris to produce α-aketoglutaric acid from L-glutamic acid in our previous studies. Here these two enzymes were displayed on P. pastoris to achieve the conversion. We constructed multi-copy expression plasmids using plasmid pHBM905BDM. By using this plasmid, multi-copy strains were constructed and named as PGLOD(1–3)-AGα1 and PAAO(1–3)-AGα1, respectively. The following results showed that expression of GLOD(1–3)-AGα1 and AAO(1–3)-AGα1 in multi-copy strains increased as designed and strain PGLOD3-AGα1 and PAAO3-AGα1 was chosen for high-density fermentation and enzyme activity experiments. By using a multi-copy expression approach and high-density fermentation, we achieved a GLOD expression yield of 688.5 U/g dry cell weight and AAO expression yield of 626.7 U/g dry cell weight. By using displayed GLOD, the average production rate of L-glutamic acid to α-KG was 6.22 g/L/h and the highest α-KG titer (124.5 g/L) was converted from 135 g/L L-glutamic acid. By using displayed AAO, the average production rate of L-glutamic acid to α-KG was 5.78 g/L/h and the highest α-KG titer (115.6 g/L) was converted from 135 g/L L-glutamic acid. It showed that displaying enzymes on P. pastoris are suitable for use in industrial applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Doucette, C. D., D. J. Schwab, N. S. Wingreen, and J. D. Rabinowitz (2011) α-ketoglutarate coordinates carbon and nitrogen utilization via enzyme I inhibition. Nat. Chem. Biol. 7: 894–901.
Morgunov, I. G., S. V. Kamzolova, and V. A. Samoilenko (2013) Enhanced α-ketoglutaric acid production and recovery in Yarrowia lipolytica yeast by effective pH controlling. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 97: 8711–8718.
Finogenova, T. V., I. G. Morgunov, S. V. Kamzolova, and O. G Chernyavskaya (2005) Organic acid production by the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica: a review of prospects. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 41: 418–425.
Stottmeister, U., A. Aurich, H. Wilde, J. Andersch, S. Schmidt, and D. Sicker (2005) White biotechnology for green chemistry: fermentative 2-oxocarboxylic acids as novel building blocks for subsequent chemical syntheses. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 32: 651–664.
Otto, C., V. Yovkova, and G. Barth (2011) Overproduction and secretion of α-ketoglutaric acid by microorganisms. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 92: 689–695.
Yovkova, V., C. Otto, A. Aurich, S. Mauersberger, and G. Barth (2014) Engineering the α-ketoglutarate overproduction from raw glycerol by overexpression of the genes encoding NADP-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenase and pyruvate carboxylase in Yarrowia lipolytica. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 98: 2003–2013.
Liu, L., Y. Li, Y. Zhu, G. Du, and J. Chen (2007) Redistribution of carbon flux in Torulopsis glabrata by altering vitamin and calcium level. Metab. Eng. 9: 21–29.
Yu, Z., G. Du, J. Zhou, and J. Chen (2012) Enhanced α-ketoglutaric acid production in Yarrowia lipolytica WSH-Z06 by an improved integrated fed-batch strategy. Bioresour. Technol. 114: 597–602.
Liu, L., G. S. Hossain, H. Shin, J. Li, G. Du, and J. Chen (2013) One-step production of α-ketoglutaric acid from glutamic acid with an engineered L-amino acid deaminase from Proteus mirabilis. J. Biotechnol. 164: 97–104.
Wang, Y. P., B. Rao, H. Yan, R. Han, L. Li, P. A. Liao, and L. X. Ma (2017) High-level expression of L-glutamate oxidase in Pichia pastoris using multi-copy expression strains and high cell density cultivation. Protein Exp. Purif. 129: 108–114.
Fan, X., R. Chen, L. Chen, and L. Liu (2016) Enhancement of alpha-ketoglutaric acid production from l-glutamic acid by high-cell-density cultivation. J. Mol. Catal. B. Enzym. 126: 10–17.
Niu, P., X. Dong, Y. Wang, and L. Liu (2014) Enzymatic production of α-ketoglutaric acid from l-glutamic acid via l-glutamate oxidase. J. Biotechnol. 179: 56–62.
Allain, C. C., L. S. Poon, C. S. Chan, W. Richmond, and P. C. Fu (1974) Enzymatic determination of total serum cholesterol. Clin. Chem. 20: 470–475.
Zhang, D., N. Liang, Z. Shi, L. Liu, J. Chen, and G. Du (2009) Enhancement of α-ketoglutarate production in Torulopsis glabrata: redistribution of carbon flux from pyruvate to α-ketoglutarate. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 14: 134–139.
Kommoju, P. R., P. Macheroux, and S. Ghisla (2007) Molecular cloning, expression and purification of l-amino acid oxidase from the Malayan pit viper Calloselasma rhodostoma. Protein Exp. Purif. 52: 89–95.
Jo, J. H., E. M. Im, S. H. Kim, and H. H. Lee (2011) Surface display of human lactoferrin using a glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored protein of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in Pichia pastoris. Biotechnol. Lett. 33: 1113–1120.
Su, G. D., X. Zhang, and Y. Lin (2010) Surface display of active lipase in Pichia pastoris using Sed1 as an anchor protein. Biotechnol. Lett. 32: 1131–1136.
Su, G. D., D. F. Huang, S. Y. Han, S. P. Zheng, and Y. Lin (2010) Display of Candida antarctica lipase B on Pichia pastoris and its application to flavor ester synthesis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 86: 1493–1501.
Matsumoto, T., H. Fukuda, M. Ueda, A. Tanaka, and A. Kondo (2002) Construction of yeast strains with high cell surface lipase activity by using novel display systems based on the FLO1p flocculation functional domain. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 68: 4517–4522.
Tanino, T., H. Fukuda, and A. Kondo (2006) Construction of a Pichia pastoris cell-surface display system using Flop anchor system. Biotechnol. Prog. 22: 989–993.
Ren, R., Z. Jiang, M. Liu, X. Tao, Y. Ma, and D. Wei (2007) Display of adenoregulin with a novel Pichia pastoris cell surface display system. Mol. Biotechnol. 35: 103–108.
Yang, H., C. Zhai, X. Yu, Z. Li, W. Tang, Y. Liu, X. Ma, X. Zhong, G. Li, D. Wu, and L. Ma (2016) High-level expression of Proteinase K from Tritirachium album Limber in Pichia pastoris using multi-copy expression strains. Protein Exp. Purif. 122: 38–44.
Rao, B., X. Zhong, Y. P. Wang, Q. Wu, Z. B. Jiang, and L. Ma (2010) Efficient vectors for expression cloning of large numbers of PCR fragments in P. pastoris. Yeast. 27: 285–292.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge financial support of National Key R D Program of China (2017YFD0200900) Subject 2 (2017 YFD0200902), Joint Open Fund of National Biopesticide Engineering Research Centre and Scientific Observation and Experimental Station of Utilization of microbial resources (Central China), Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs (Grant No. JF-NBCOES-1807), Natural Science Foundation of China (31300074, 21606076), Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (2014CFB541), Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (20124208120004), Key project of educational commission of Hubei province of China(D20171002).
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Neither ethical approval nor informed consent was required for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information S1
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rao, B., Zhou, R., Dong, Q. et al. Efficient Surface Display of L-glutamate Oxidase and L-amino Acid Oxidase on Pichia pastoris Using Multi-copy Expression Strains. Biotechnol Bioproc E 25, 571–579 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-019-0370-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-019-0370-5